Ford Motor Company and Redwood Materials Collaborate to Build Sustainable Battery Supply Chain for Electric Vehicles
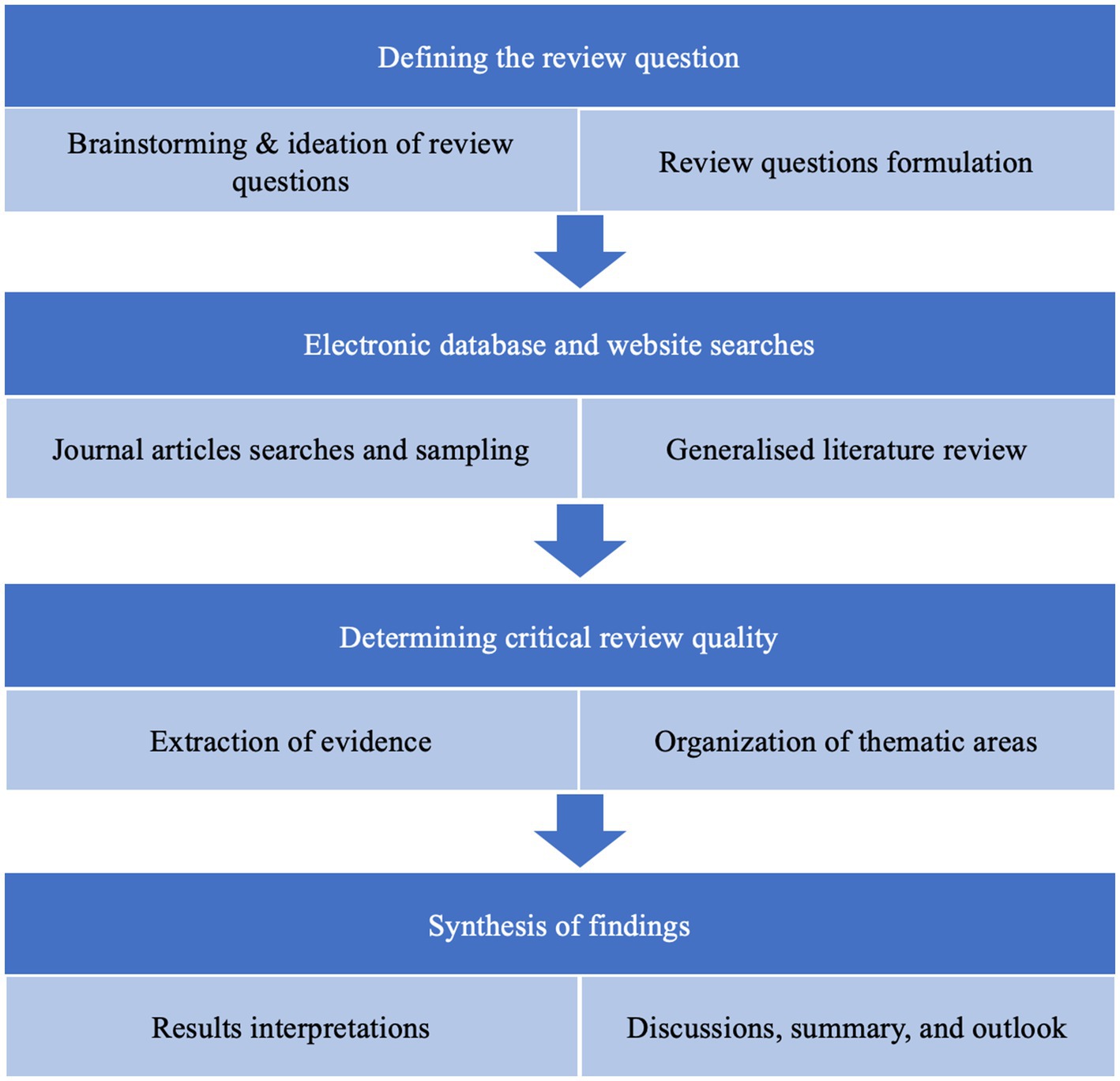
Introduction
Ford Motor Company and Redwood Materials have joined forces to create a sustainable and affordable electric vehicle (EV) market in the United States. By localizing the complex supply chain network, implementing recycling options for end-of-life vehicles, increasing lithium-ion recycling, and boosting U.S. battery production, the partnership aims to make EVs more accessible and environmentally friendly.
Localization of Supply Chain
- Ford and Redwood are working together to establish a circular supply chain for batteries in the U.S.
- The goal is to recycle valuable materials used in battery production, reducing costs and dependence on imports and raw material mining.
- This initiative is a significant step towards making battery electric vehicles sustainable, accessible, and affordable for more Americans.
Investment and Collaboration
- Ford plans to invest over $30 billion in electrification by 2025.
- To further advance their joint business opportunities, Ford has invested $50 million in Redwood Materials.
- This investment will help expand Redwood’s manufacturing footprint.
Details of the Collaboration
DEARBORN, Mich. Sept. 22, 2021 – Ford Motor Company and Redwood Materials today announced they are working together to build out battery recycling and a domestic battery supply chain for electric vehicles. Ford and Redwood’s goal is to make electric vehicles more sustainable, drive down the cost for batteries, and ultimately help make electric vehicles accessible and affordable for more Americans.
Ford and Redwood are collaborating to integrate battery recycling into Ford’s domestic battery strategy. Redwood’s recycling technology can recover, on average, more than 95% of the elements like nickel, cobalt, lithium and copper. These materials can be reused in a closed-loop with Redwood moving to produce anode copper foil and cathode active materials for future battery production. By using locally produced, recycled battery materials, Ford can drive down costs, increase battery materials supply and reduce its reliance on imports and mining of raw materials.
“Ford is making electric vehicles more accessible and affordable through products like the all-electric F-150 Lightning, Mustang Mach-E and E-Transit, and much more to come,” said Jim Farley, Ford president and CEO. “Our partnership with Redwood Materials will be critical to our plan to build electric vehicles at scale in America, at the lowest possible cost and with a zero-waste approach.”
Ford is investing more than $30 billion in electrification through 2025, including the collaboration between Ford and Redwood, which will help deliver on Ford’s plans to localize the battery supply chain.
This builds on Ford’s previously announced plans to scale battery production through multiple BlueOvalSK battery plants in North America starting mid-decade. By building out a domestic, sustainable supply chain with recycled materials, Ford can drive down battery costs and help protect the environment. BlueOvalSK is the U.S. joint venture that Ford and SK Innovation intend to form, subject to definitive agreements, regulatory approvals, and other conditions.
Last week, Redwood announced it will produce strategic battery materials, supplying anode copper foil and cathode active materials to U.S. partners. Redwood plans to transform the lithium-ion battery supply chain by offering large-scale sources of these domestic materials to reduce the cost and environmental footprint of electric vehicle production. The local supply of these two materials is a key part of Ford’s commitment to reduce the environmental impact of battery manufacturing and continue to ramp up electric vehicle production in the U.S.
“We are designing our battery supply chain to create a fully closed-loop lifecycle to drive down the cost of electric vehicles via a reliable U.S. materials supply chain,” said Lisa Drake, Ford’s North America chief operating officer. “This approach will help ensure valuable materials in end-of-life products re-enter the supply chain and do not wind up in landfills, reducing our reliance on the existing commodities supply chain that will be quickly overwhelmed by industry demand.”
Redwood Materials, founded by JB Straubel and based in northern Nevada, is creating a circular supply chain for batteries and helping partners across the electric vehicle and clean energy industries by providing pathways, processes, and technologies to recycle and remanufacture lithium-ion batteries.
“Increasing our nation’s production of batteries and their materials through domestic recycling can serve as a key enabler to improve the environmental footprint of U.S. manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries, decrease cost and, in turn, drive up domestic adoption of electric vehicles,” said Straubel, Redwood Materials CEO. “Redwood and Ford share an understanding that to truly make electric vehicles sustainable and affordable, we need to localize the existing complex and expensive supply chain network, create pathways for end-of-life vehicles, ramp lithium-ion recycling and increase battery production, all here in America.”
Longer-term, Ford and Redwood plan to work together on the best approach to collect and disassemble end-of-life batteries from Ford’s electric vehicles for recycling and remanufacturing to help reduce the cost associated with battery repairs and raw materials to manufacture all-new batteries.
“Our work with Redwood will, by design, help ensure the infrastructure is in place to cost-effectively recycle end-of-life Ford batteries to create a robust domestic materials stream and drive down the cost of electric vehicles,” Drake said.
Ford to support Redwood Materials expansion
To further advance these business opportunities between the companies, Ford invested $50 million into Redwood Materials to help the company expand its footprint in the U.S.
MORE: Redwood Materials and Ford Motor Company Announce Strategic Relationship
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse | Indicator: Redwood’s recycling technology can recover, on average, more than 95% of the elements like nickel, cobalt, lithium, and copper |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.2: Promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.6: Enhance North-South, South-South, and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology, and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- SDG 15: Life on Land
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes
- Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning
- Target 15.2: Promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally
- Target 17.6: Enhance North-South, South-South, and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology, and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator: Redwood’s recycling technology can recover, on average, more than 95% of the elements like nickel, cobalt, lithium, and copper (Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse)
4. SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse | Indicator: Redwood’s recycling technology can recover, on average, more than 95% of the elements like nickel, cobalt, lithium, and copper |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 15: Life on Land | 15.2: Promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests, and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.6: Enhance North-South, South-South, and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology, and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms | No specific indicators mentioned in the article |
Copyright: Dive into this article, curated with care by SDG Investors Inc. Our advanced AI technology searches through vast amounts of data to spotlight how we are all moving forward with the Sustainable Development Goals. While we own the rights to this content, we invite you to share it to help spread knowledge and spark action on the SDGs.
Fuente: media.ford.com

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.