Students at Cal State Fullerton Engage in Sustainable Manufacturing Projects
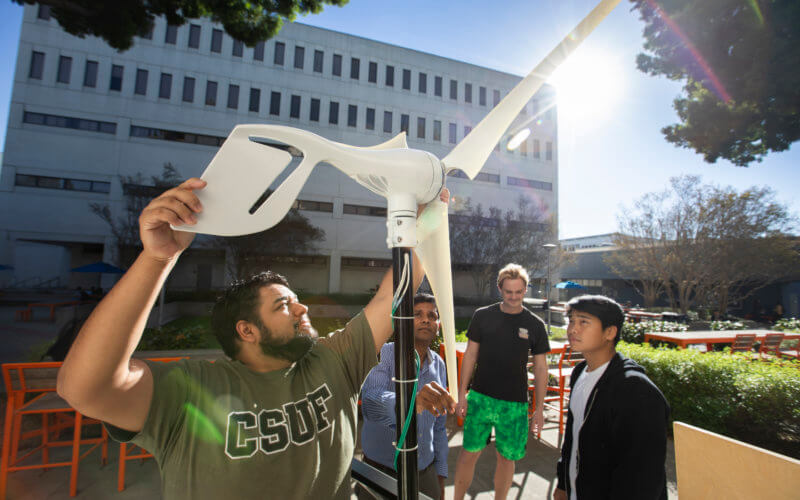

Cal State Fullerton mechanical engineering major Matthew Lindwall is currently involved in a manufacturing project aimed at reducing carbon emissions in transportation by utilizing “green” hydrogen as a clean energy source. Lindwall’s project is aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy and SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
Another student, Rahul Pashpuleti, is working on developing a 3D-printed artificial meniscus made of biodegradable and environmentally friendly materials to replace damaged knee cartilage. This project contributes to SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
As the manufacturing industry recognizes the financial and environmental benefits of eco-friendly practices, students at Cal State Fullerton are learning about green technology, also known as “greentech,” and sustainable manufacturing to shape the future of the industry. These initiatives align with SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production and SDG 13: Climate Action.
Importance of Greentech Manufacturing
Sagil James, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, emphasizes the significance of greentech manufacturing in promoting environmental responsibility, resource efficiency, and the shift towards renewable energy sources and eco-friendly materials. This approach is crucial for achieving SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy, SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Greentech manufacturing not only drives innovation but also supports a sustainable future for the industry and the planet. It contributes to SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth and SDG 13: Climate Action.
Real-World Projects
Lindwall and Pashpuleti are among the students working on real-world projects that focus on cutting-edge technologies and practices in eco-manufacturing, clean energy manufacturing, and cyber-manufacturing. These projects align with various SDGs, including SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy, SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production, and SDG 13: Climate Action.
Students at Cal State Fullerton also receive a strong foundation in sustainable manufacturing principles through coursework in the College of Engineering and Computer Science. This equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge to contribute to SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Green Projects Explored by Students
Lindwall and his team of mechanical engineering majors are developing a hydrogen-powered, remote-controlled speed boat. This project aims to showcase the potential of green hydrogen as a sustainable fuel source for transportation. It contributes to SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy and SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
Pashpuleti is using bioprinting technology to develop a 3D-printed artificial meniscus made of biodegradable and environmentally friendly materials. This project aligns with SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Amarjeet Singh, a mechanical engineering graduate student, is working on an augmented reality research project that combines innovative technology with sustainable manufacturing processes. This project contributes to SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Preparing Students for the Green Workforce
The demand for professionals knowledgeable in sustainability, renewable energy, and environmental management is increasing. Lindwall and Pashpuleti believe that their research experiences and coursework have prepared them for careers in sustainable manufacturing. These initiatives contribute to SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
By incorporating sustainable practices into their future careers, these students aim to make a positive impact on the environment and society. Their efforts align with SDG 13: Climate Action and SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals.
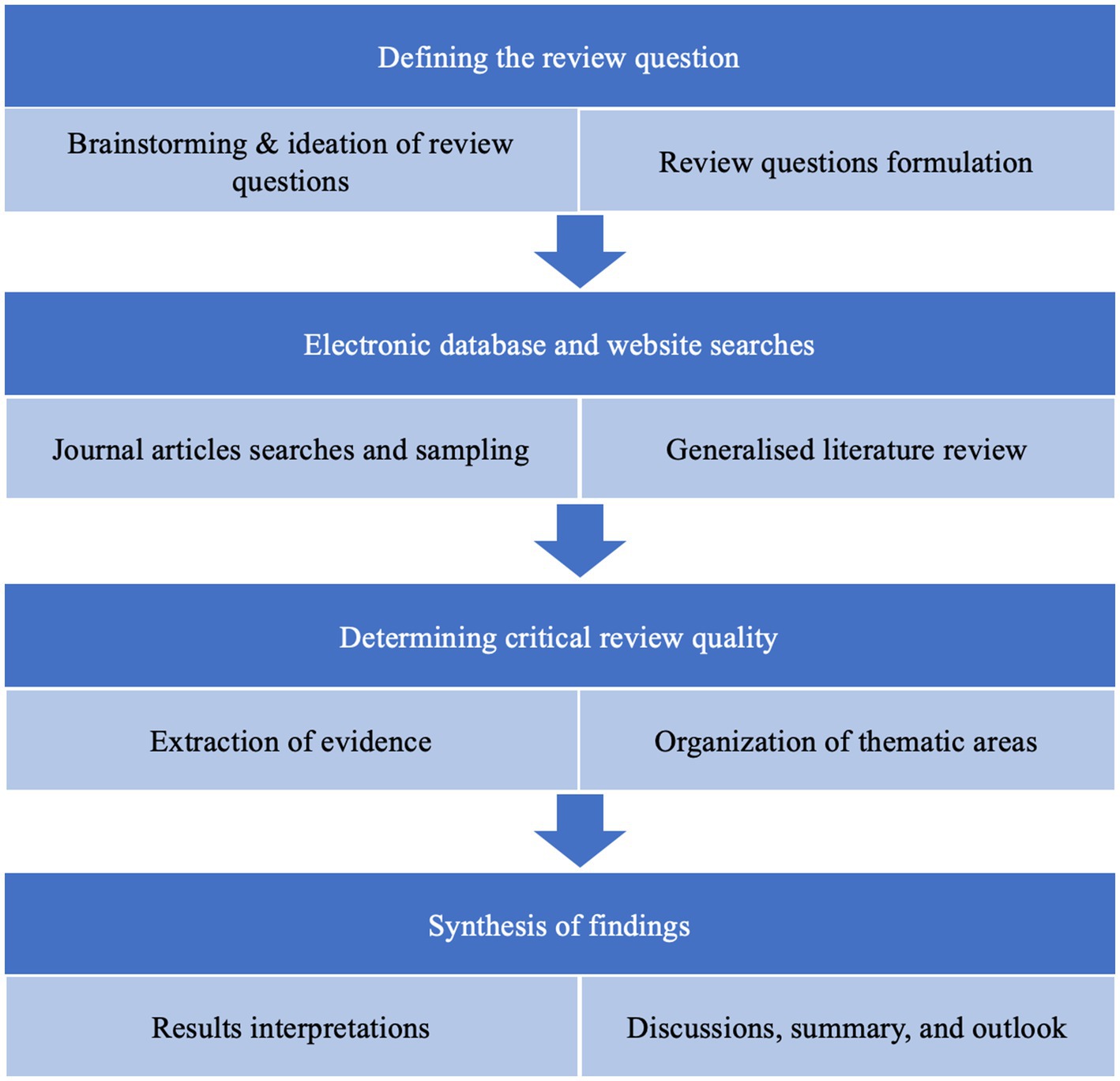
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
- Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
- Indicator 13.2.1: Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic, and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer.
Analysis
The article discusses the efforts of mechanical engineering students and faculty at Cal State Fullerton to promote green technology and sustainable manufacturing. Based on the content of the article, the following SDGs, targets, and indicators can be identified:
1. SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The article highlights the use of “green” hydrogen as a clean energy source in transportation. This aligns with SDG 7, which aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.
2. SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The article emphasizes the importance of sustainable manufacturing methods and eco-friendly materials. This relates to SDG 9, which focuses on promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation.
3. SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The article mentions the need for minimizing carbon emissions, reducing waste, and efficiently managing resources. These actions are in line with SDG 12, which aims to ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
4. SDG 13: Climate Action
The article discusses the integration of renewable energy sources and the reduction of carbon emissions. This aligns with SDG 13, which focuses on taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Based on the identified SDGs, the following targets and indicators can be associated with the article’s content:
Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
The article mentions the use of “green” hydrogen as a clean energy source, which contributes to increasing the share of renewable energy.
Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption.
This indicator can be used to measure progress towards achieving Target 7.2 by tracking the percentage of renewable energy used in the total energy consumption.
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes.
The article emphasizes the importance of sustainable manufacturing methods and eco-friendly materials, which aligns with Target 9.4.
Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added.
This indicator can be used to measure progress towards achieving Target 9.4 by tracking the amount of CO2 emissions produced per unit of value added in industries.
Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
The article mentions the need for minimizing waste and efficiently managing resources, which relates to Target 12.2.
Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP.
This indicator can be used to measure progress towards achieving Target 12.2 by tracking the material footprint, material footprint per capita, and material footprint per GDP.
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
The article discusses the integration of renewable energy sources and the reduction of carbon emissions, which aligns with Target 13.2.
Indicator 13.2.1: Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic, and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer.
This indicator can be used to measure progress towards achieving Target 13.2 by tracking the number of countries that have communicated efforts to strengthen capacity-building for climate change adaptation, mitigation, and technology transfer.
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | Indicator 7.2.1: Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes. | Indicator 9.4.1: CO2 emission per unit of value added. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Indicator 12.2.1: Material footprint, material footprint per capita,
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together. Source: news.fullerton.edu
Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.
|