A Threat to Ecosystems is a Threat to Portfolios
A threat to our ecosystem is a threat to your portfolio. That’s what the latest research from Sustainalytics on investing risks related to land use and biodiversity tells us.
Biodiversity Risks for Investors on the Rise
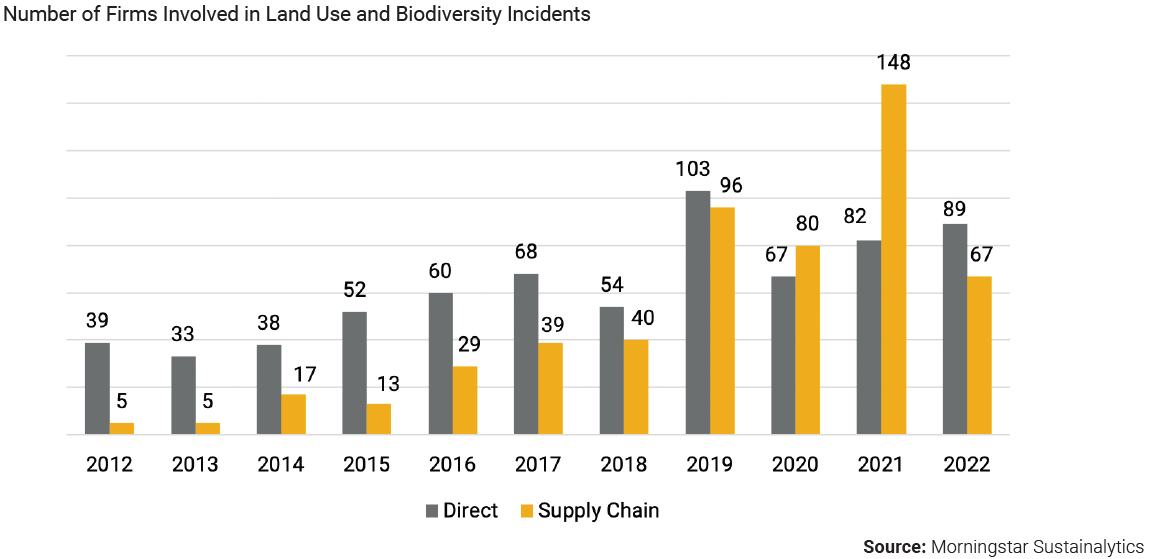
Biodiversity loss and potential portfolio risks are increasingly of interest to investors, according to the authors of the latest ESG Spotlight Report from Sustainalytics, Martin Vezér and Qi Sang. “In a recent edition of our ESG Spotlight Report Series, we found that the most common type of incidents related to supply chain management relates to land use and biodiversity, with 1,659 cases having occurred between 2012 and Q1 2023,” says the authors, “Increased NGO reporting and improvements in our incidents tracking abilities have contributed to a growing number of firms being linked to land use and biodiversity controversies over the past decade (2012-2023). During this period, 1,659 land use and biodiversity incidents were associated with supply chain management and 776 pertained to direct operational involvement. The Food Products industry accounts for most of cases.” And the risks have been rising in recent years.
Biodiversity Risks Can Affect Returns
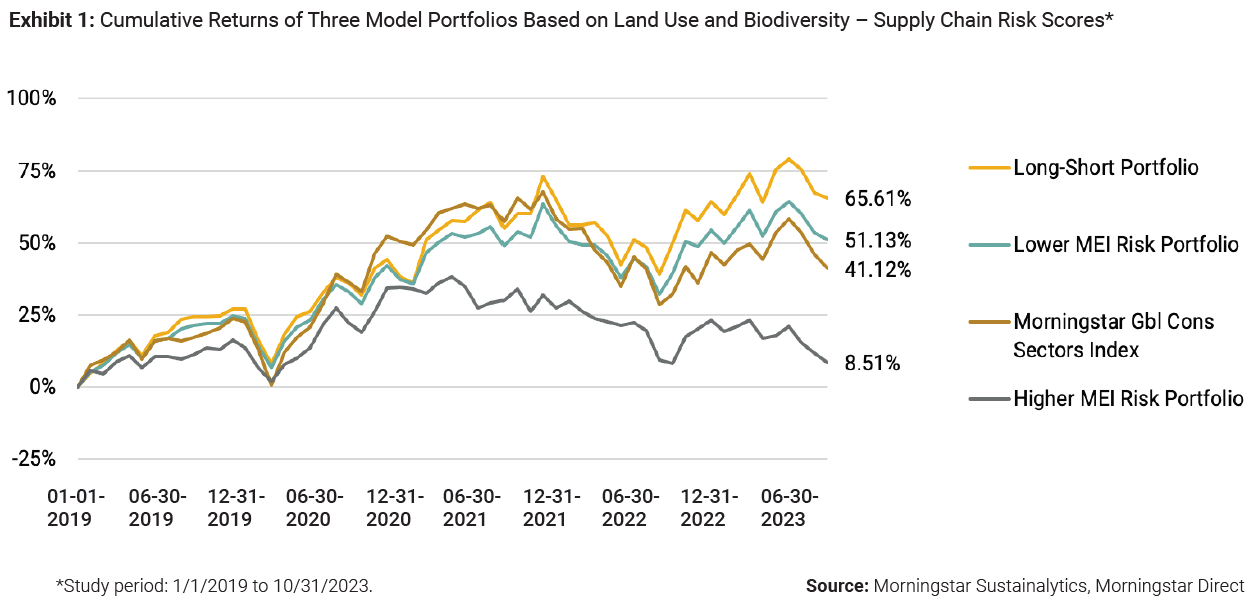
What do these biodiversity risks look like in a portfolio? Those holding consumer sector stocks could be subject to significant underperformance based on their exposure to related material ESG issues (MEI), the study found, using proxy portfolios of the Morningstar Global Consumer Sectors Index.
“On a cumulative returns basis, the Lower MEI Risk portfolio outperformed the Higher MEI Risk portfolio by more than 42 percentage points over a five-year period,” the authors found, with myriad potential causes at the business level.
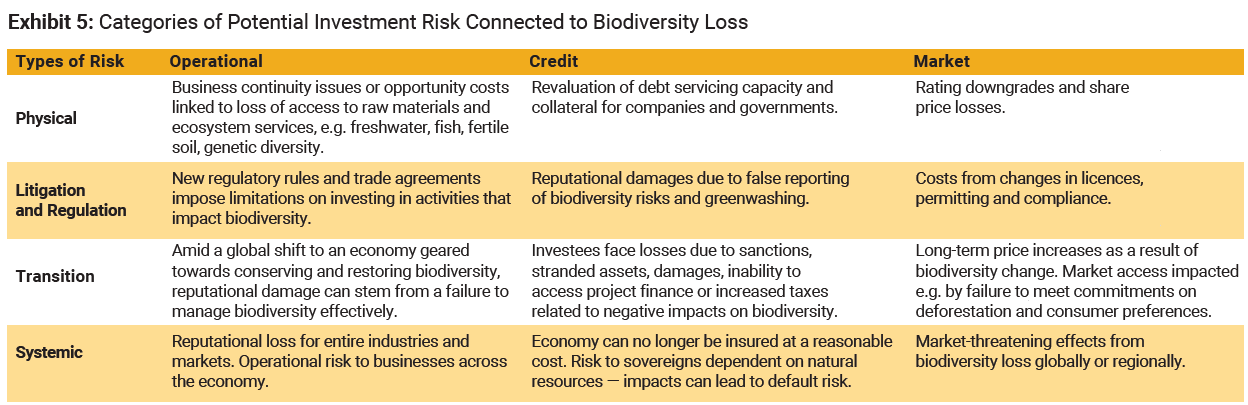
How Does Biodiversity Loss Hurt Business?
Which Industries are Driving Biodiversity Loss?
Some risks to business from biodiversity losses affect some industries more than others, which makes for some key intersections for investors to consider. “Industrial activities have led to biodiversity loss on a global scale,” say the authors, “Primary drivers include land and sea use change for large scale food production, overexploitation linked to overfishing, overhunting and overharvesting, climate change, pollution and invasive alien species.”
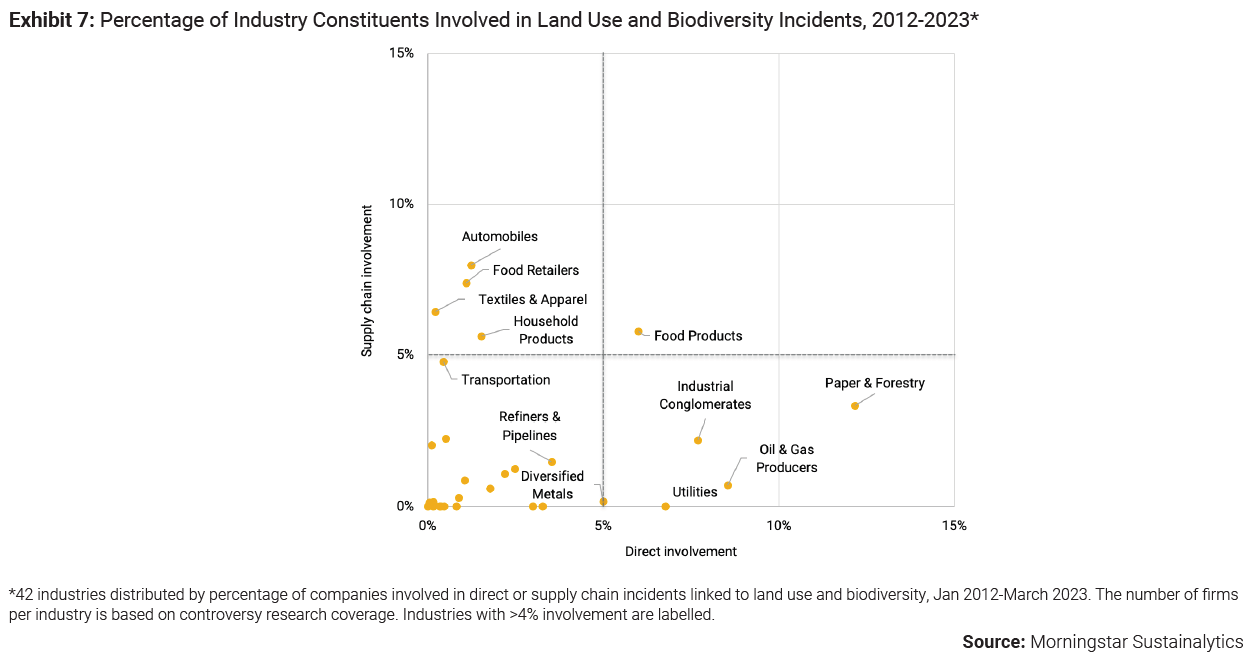
“Data from Global Forest Watch, an online platform that provides data and tools for monitoring forests, indicate that the main drivers of deforestation over the past two decades were forestry, activities related to commodities, wildfire and shifting agriculture,” say the authors, “Commodity-driven deforestation is fueled by a growing demand for consumer goods, the manufacturing of which requires commodities like palm oil, soya, cattle, timber, cocoa, coffee, rubber and precious metals.” The industries with the largest portion of direct involvement in land use and biodiversity incidents are Paper & Forestry (12%), Oil & Gas Producers (9%), Industrial Conglomerates (8%) and Utilities (7%), according to the report.
The report includes individual cases of biodiversity loss incidents at a business level and by industry. From illegal palm oil plantations in Indonesia to mines that threaten orangutans in Africa, to car seat leather being linked to deforestation in Brazil, the problems continue and are increasingly tangible. For example, Procter & Gamble PG’s exposure to deforestation and peatland clearing in its supply chain is estimated to be valued at US$ 41 billion, according to the report. And investors have reacted. “A 2020 shareholder proposal [at P&G] to address forest-related supply chain issues won majority support,” the authors noted. While the company manages the risk, in recent years it has been a major contributor in terms of returns in a lower MEI risk portfolio, according to the report.
Businesses Driving Change for the Better
Other companies have emerged as both champions of change and annualized return leaders among stocks in a lower MEI risks portfolio, especially in the home improvement space. “Both Home Depot HD and Lowe’s LOW disclose strong supplier environmental programmes,” the authors found, with Lowe’s standing out, “Lowe’s leads the subindustry with a best-in-class green procurement policy that includes initiatives to engage with suppliers to improve environmental performance and policies to address related product and process requirements.”
The most undervalued stock in the study’s sample of lower MEI risk stocks, Estée Lauder EL received a sourcing certification for 95% of its fibre cartons in 2022. The company also has a deforestation “due diligence policy” that applies to its operations and supplies, according to the report, noting however that the programme was still too weak. Maybe it needs some due diligence from investors.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
-
SDG 15: Life on Land
- Target 15.1: By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements.
- Indicator 15.1.2: Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
- Indicator 12.6.1: Number of companies publishing sustainability reports.
Analysis
The article highlights the connection between biodiversity loss and potential portfolio risks for investors. It discusses the incidents related to land use and biodiversity that have occurred between 2012 and Q1 2023, with a focus on supply chain management. The risks associated with biodiversity loss are shown to affect consumer sector stocks and can lead to significant underperformance in portfolios.
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The issues highlighted in the article are connected to SDG 15: Life on Land and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production. SDG 15 focuses on the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems, including forests and wetlands. SDG 12 emphasizes responsible consumption and production practices, encouraging companies to adopt sustainable practices and integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, the specific targets under the identified SDGs are:
- Target 15.1: Ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements.
- Target 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, there are indicators mentioned in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
- Indicator 15.1.2: Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type. This indicator can measure progress towards Target 15.1 by assessing the extent to which important biodiversity sites are protected.
- Indicator 12.6.1: Number of companies publishing sustainability reports. This indicator can measure progress towards Target 12.6 by tracking the number of companies that are adopting sustainable practices and reporting on their sustainability performance.
Table: SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 15: Life on Land | Target 15.1: Ensure the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains, and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements. | Indicator 15.1.2: Proportion of important sites for terrestrial and freshwater biodiversity that are covered by protected areas, by ecosystem type. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle. | Indicator 12.6.1: Number of companies publishing sustainability reports. |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: morningstar.ca

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.






