Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These goals aim to address various social, economic, and environmental challenges faced by countries around the world. The SDGs provide a framework for sustainable development and serve as a roadmap towards a more inclusive and equitable future.
Goal 1: No Poverty
The first SDG is to end poverty in all its forms everywhere. This goal focuses on eradicating extreme poverty, reducing poverty rates, and ensuring social protection for the most vulnerable populations. It emphasizes the need for inclusive economic growth and access to basic services such as education, healthcare, and clean water.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger
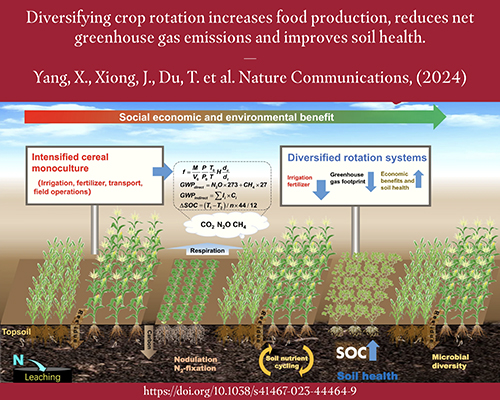
Goal 2 aims to achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. It highlights the importance of ending hunger and malnutrition by increasing agricultural productivity, supporting small-scale farmers, and ensuring access to nutritious food for all.
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
This goal focuses on ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages. It addresses various health issues such as maternal and child mortality, infectious diseases, mental health, and access to essential healthcare services. Goal 3 also emphasizes the importance of universal health coverage and the prevention of non-communicable diseases.
Goal 4: Quality Education
Goal 4 aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education for all. It focuses on providing access to free primary and secondary education, promoting lifelong learning opportunities, and improving the quality of education. This goal also highlights the need to eliminate gender disparities in education and enhance educational infrastructure.
Goal 5: Gender Equality
Goal 5 seeks to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. It addresses various forms of discrimination and violence against women, promotes women’s participation in decision-making processes, and ensures equal access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
Conclusion
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a comprehensive framework for addressing global challenges and promoting sustainable development. Each goal plays a crucial role in creating a more inclusive, equitable, and sustainable future for all. By working towards achieving these goals, countries can contribute to building a better world for present and future generations.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- SDG 13: Climate Action
The article discusses the issues of hunger, malnutrition, lack of access to clean water, and the impact of climate change on agriculture. These issues are directly connected to the SDGs mentioned above.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
- SDG 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular, the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round.
- SDG 2.2: By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women, and older persons.
- SDG 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- SDG 6.1: By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all.
- SDG 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
The article highlights the need to end hunger, malnutrition, and ensure access to safe and nutritious food. It also emphasizes the importance of addressing non-communicable diseases and promoting mental health. Additionally, the article mentions the need for clean water access and building resilience to climate-related hazards.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
- Indicator 2.1.1: Prevalence of undernourishment
- Indicator 2.2.2: Prevalence of stunting among children under 5 years of age
- Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease
- Indicator 6.1.1: Proportion of the population using safely managed drinking water services
- Indicator 13.1.1: Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population
The article mentions the prevalence of undernourishment and stunting as indicators of progress towards ending hunger and malnutrition. It also refers to mortality rates attributed to non-communicable diseases as an indicator for improving health. The need for access to safely managed drinking water is implied as a measure of progress, as well as the number of deaths and affected persons attributed to disasters as an indicator of resilience to climate-related hazards.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular, the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round. | 2.1.1: Prevalence of undernourishment |
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.2: By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women, and older persons. | 2.2.2: Prevalence of stunting among children under 5 years of age |
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one-third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being. | 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease |
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation | 6.1: By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. | 6.1.1: Proportion of the population using safely managed drinking water services |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries. | 13.1.1: Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population |
Behold! This splendid article springs forth from the wellspring of knowledge, shaped by a wondrous proprietary AI technology that delved into a vast ocean of data, illuminating the path towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Remember that all rights are reserved by SDG Investors LLC, empowering us to champion progress together.
Source: grants.ca.gov

Join us, as fellow seekers of change, on a transformative journey at https://sdgtalks.ai/welcome, where you can become a member and actively contribute to shaping a brighter future.