Advancements in 24-Hour Solar Electricity Generation and Its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Introduction
Solar electricity has become highly affordable, and recent technological improvements in battery storage have brought the prospect of 24-hour solar power generation within reach. This development is critical for achieving several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy), SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
The Phenomenon of Continuous Solar Power
On June 21st, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the summer solstice, where the “midnight sun” provides 24 hours of daylight, theoretically enabling continuous solar electricity generation. Thanks to advances in battery storage technology, this continuous solar power generation is no longer limited to Arctic regions but is becoming feasible in sunny areas worldwide.
Technological and Economic Advances
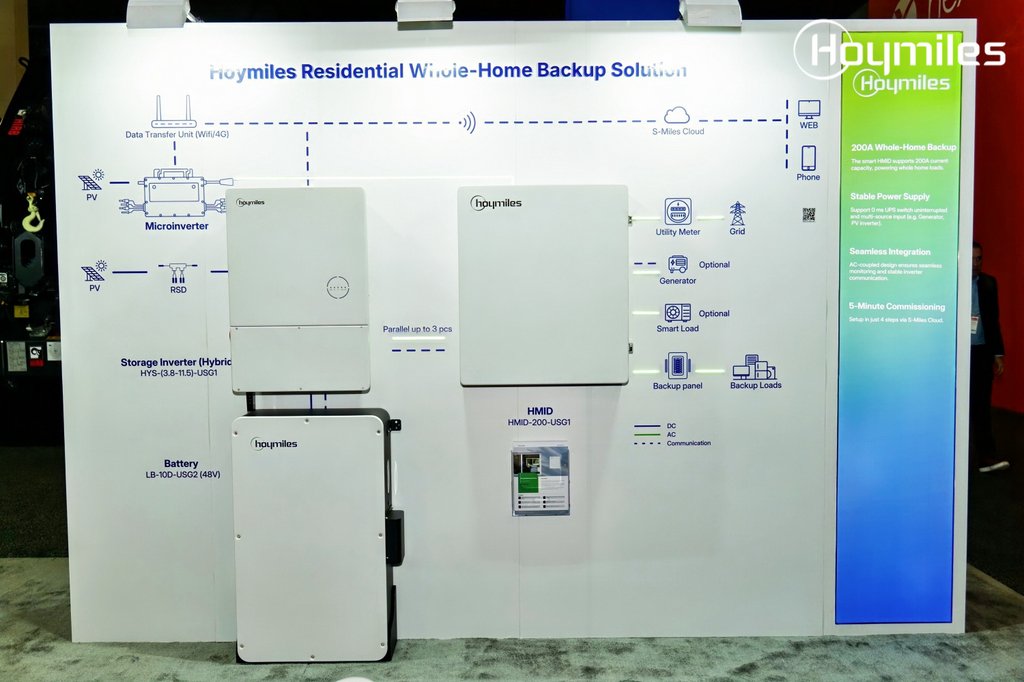
Rapid progress in battery technology, especially cost reductions, has made near-continuous solar power an economic and technological reality in many sunny regions. This progress supports SDG 7 by promoting access to reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.
Applications and Demand for 24-Hour Solar Power
- Industries such as data centers and factories require uninterrupted power to maintain operations, aligning with SDG 9 by fostering resilient infrastructure and innovation.
- The increasing emphasis on hourly-matched carbon-free energy goals, often pursued through corporate Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), is driving demand for clean electricity every hour of the day.
Benefits of 24-Hour Solar Generation
- Combining solar panels with sufficient battery storage enables a stable and clean power supply, even in regions without reliable grid access.
- It helps overcome grid congestion and unreliability, contributing to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) by enhancing energy infrastructure resilience.
- While not a universal solution due to variability in sunlight and demand, it offers a pathway for solar energy to become the backbone of clean power systems in sunny regions and to expand its role in less sunny areas.
Global Outlook and Cost Considerations
This report examines the current status of achieving constant, 24-hour solar electricity generation across 365 days in various cities worldwide and evaluates the associated costs. The findings are essential for policymakers and stakeholders aiming to advance SDG 7 and SDG 13 by scaling up clean energy solutions.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed in the Article
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article focuses on solar electricity affordability and technological advances in battery storage enabling 24-hour clean energy supply.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
- Advancements in battery technology and integration with solar power highlight innovation and infrastructure development.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- The push for carbon-free energy and clean electricity to reduce emissions aligns with climate action goals.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Based on the Article
- SDG 7 Targets:
- Target 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services.
- Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- SDG 9 Targets:
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
- SDG 13 Targets:
- Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies, and planning.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article to Measure Progress
- Indicator for SDG 7:
- Proportion of population with access to electricity (implied through discussion of grid access and reliable power supply).
- Share of renewable energy in total final energy consumption (implied by the focus on solar electricity penetration).
- Energy storage capacity and deployment rates (implied through advances in battery technology enabling 24-hour solar power).
- Indicator for SDG 9:
- Research and development expenditure on clean energy technologies (implied by rapid advances in battery technology).
- Number of industries adopting clean energy solutions (implied by data centres and factories requiring uninterrupted clean power).
- Indicator for SDG 13:
- Carbon intensity of energy consumption (implied by the push for carbon-free energy goals and corporate PPAs).
4. Table: SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action |
|
|
Source: ember-energy.org