Federal Reserve Chair Powell’s Economic Outlook and Policy Stance: A Report Emphasizing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

Introduction
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell maintains a cautious, more bearish bias following last week’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting and press conference. This report summarizes key points from Powell’s recent testimony, highlighting implications for Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to economic growth, decent work, and reduced inequalities.
Economic Outlook
- General Economic Assessment: The Federal Reserve continues to monitor economic indicators closely to ensure sustainable growth aligned with SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- GDP and Tariffs: Tariff impacts remain a source of uncertainty affecting domestic and global trade, influencing economic stability and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- Domestic Demand: Consumer spending and business investments are key drivers of economic activity, essential for achieving sustained economic growth under SDG 8.
- Consumer and Business Sentiment: Confidence levels influence economic momentum and investment, impacting job creation and SDG 8.
Labor Market
- Employment and Job Growth: Employment trends are critical for reducing unemployment and promoting inclusive economic growth, supporting SDG 8 and SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
- Unemployment Rate: Maintaining low unemployment is vital for social stability and poverty reduction, directly contributing to SDG 1 (No Poverty).
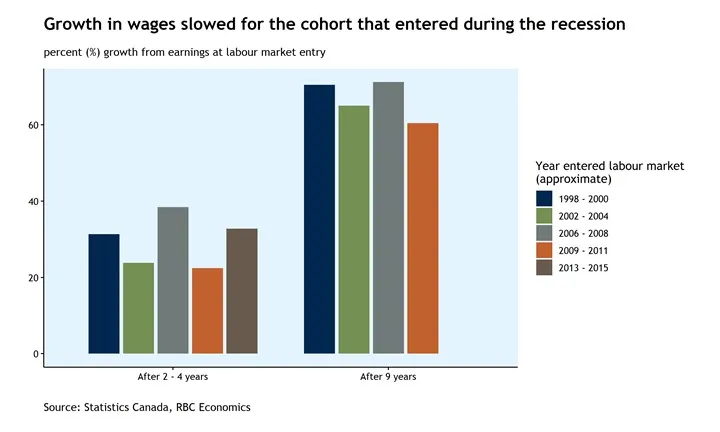
- Wages and Inflation: Wage growth balanced against inflation is important for ensuring decent living standards, aligning with SDG 1 and SDG 8.
- Overall Labor Market Conditions: The Fed monitors labor market health to foster equitable opportunities, supporting SDG 5 (Gender Equality) and SDG 10.
- Demographic Disparities: Addressing disparities in employment among different demographic groups is essential for inclusive growth and SDG 10.
Inflation
- Current Inflation Data: Inflation trends are evaluated to maintain price stability, which is crucial for sustainable economic development and SDG 8.
- Inflation Expectations: Managing expectations helps prevent economic volatility, supporting long-term growth and SDG 8.
- Longer-Term Expectations: Ensuring stable inflation supports investment and job creation, advancing SDG 8.
Monetary Policy
- Current Policy Stance: The Fed maintains a cautious approach, balancing growth and inflation control to support sustainable development goals.
- Balance Sheet Policy: Adjustments to the Fed’s balance sheet aim to stabilize financial markets and promote economic resilience, contributing to SDG 9.
- Policy Outlook: Future policy decisions will depend on inflation data and economic conditions, with a focus on sustaining inclusive growth.
- Tariff Impact and Uncertainty: Tariffs create economic uncertainty, which the Fed considers in policy formulation to protect economic stability and SDG 8.
- On Possible Inflation Persistence: The Fed remains vigilant about inflation risks to avoid undermining economic progress.
- Fed’s Responsibility on Expectations: Managing public and market expectations is key to maintaining confidence and supporting SDG 8.
Conclusion
Federal Reserve Chair Powell’s testimony underscores a balanced approach to monetary policy, emphasizing caution amid economic uncertainties. The Fed’s stance aligns with advancing multiple Sustainable Development Goals, particularly those focused on economic growth, decent work, reduced inequalities, and sustainable industry development. Continued monitoring of inflation and labor market conditions will guide policy to foster a resilient and inclusive economy.
Report compiled by Greg Michalowski at www.forexlive.com.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- The article discusses labor market conditions, employment, job growth, wages, and unemployment rates, which are directly related to promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Demographic disparities in the labor market mentioned in the article relate to reducing inequalities within and among countries.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Inflation and tariff impacts discussed affect economic stability and consumption patterns, linking to sustainable consumption and production.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Monetary policy coordination and economic outlook assessments imply the importance of partnerships and policy coherence for sustainable development.
2. Specific Targets Under Those SDGs Identified
- SDG 8 Targets
- 8.5: Achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value.
- 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation.
- SDG 10 Targets
- 10.2: Empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status.
- SDG 12 Targets
- 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
- 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
- SDG 17 Targets
- 17.14: Enhance policy coherence for sustainable development.
- 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Employment and Unemployment Rates
- Indicators such as the unemployment rate and job growth statistics are implied as measures of labor market health and progress towards SDG 8 targets.
- Wage Growth and Inflation Rates
- Wage levels and inflation data serve as indicators of economic stability and purchasing power, relevant to SDG 8 and SDG 12.
- Demographic Disparities in Employment
- Indicators measuring employment rates across different demographic groups relate to SDG 10 progress.
- Monetary Policy Stance and Tariff Impact
- While not direct SDG indicators, these economic policy variables influence the broader economic environment and can be linked to SDG 17 targets on policy coherence and partnerships.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities |
|
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production |
|
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals |
|
|
Source: tradingview.com