Report on Ecstasy and Its Impact on Health in Relation to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Introduction
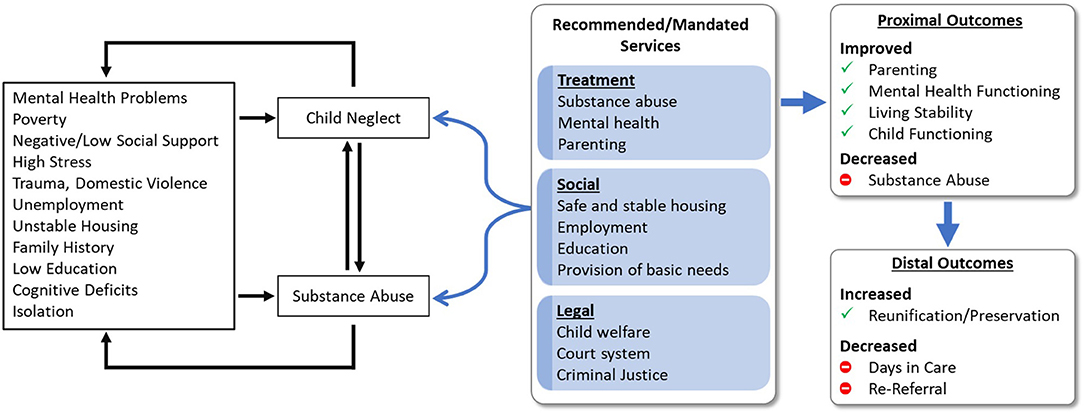
This report examines the health implications of Ecstasy (MDMA) use, emphasizing its relevance to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The analysis includes an electrocardiogram (EKG) image associated with Ecstasy consumption and explores how addressing substance abuse aligns with global development objectives.
Ecstasy and Health Risks
Ecstasy, commonly known as MDMA, is a psychoactive drug that poses significant health risks, including cardiovascular complications. The included EKG image illustrates potential cardiac effects observed in Ecstasy users.
Relevance to Sustainable Development Goals
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Reducing substance abuse is critical to improving overall health outcomes.
- Addressing Ecstasy-related health issues contributes to lowering premature mortality from non-communicable diseases.
- Promoting mental health and well-being by preventing drug misuse.
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- Implementing educational programs to raise awareness about the dangers of Ecstasy.
- Empowering youth with knowledge to make informed decisions regarding drug use.
- SDG 16: Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
- Strengthening policies and institutions to combat illicit drug trafficking and abuse.
- Enhancing law enforcement and healthcare collaboration to manage substance abuse effectively.
Recommendations
- Increase public health campaigns targeting Ecstasy and other substance abuse.
- Integrate substance abuse education into school curricula to support SDG 4.
- Enhance healthcare services to provide timely diagnosis and treatment of Ecstasy-related health conditions.
- Strengthen international cooperation to address drug trafficking and promote safe communities.
Conclusion
Addressing the health risks associated with Ecstasy use is essential for achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals, particularly those related to health, education, and institutional strength. Coordinated efforts across sectors are necessary to mitigate the adverse effects of substance abuse and promote sustainable development.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The article discusses health-related issues, particularly concerning the effects of Ecstasy on the heart, as evidenced by the EKG image.
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- The inclusion of specialty labeling and control suggests an emphasis on educating healthcare professionals or the public about drug effects and health monitoring.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 3 Targets
- Target 3.4: By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.
- Target 3.5: Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol.
- SDG 4 Targets
- Target 4.7: By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including health education.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied in the Article
- For SDG 3 Targets
- Indicator 3.4.1: Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease.
- Indicator 3.5.1: Coverage of treatment interventions (pharmacological, psychosocial and rehabilitation and aftercare services) for substance use disorders.
- The EKG image implies monitoring cardiovascular health as a measure of the impact of substance use.
- For SDG 4 Targets
- Indicator 4.7.1: Extent to which (i) global citizenship education and (ii) education for sustainable development are mainstreamed at all levels in curricula, teacher education and student assessment.
- The labeling and specialty control imply educational measures related to health and substance abuse awareness.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 4: Quality Education |
|
|
Source: cureus.com