Report on the Air India Flight 171 Accident and its Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
Incident Summary
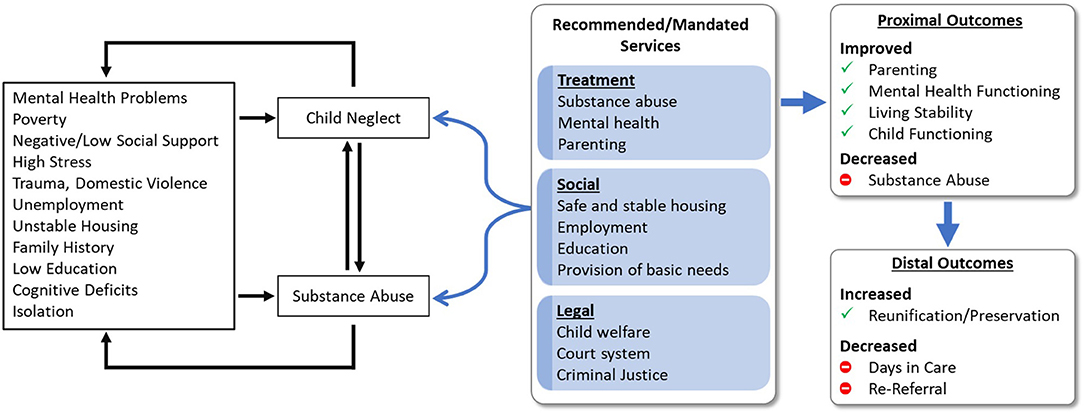
A preliminary investigation into the crash of Air India Flight 171 on June 12, 2025, has focused on the deactivation of two critical fuel switches shortly after takeoff. The incident, which resulted in the loss of 241 lives on board and 19 on the ground, raises significant questions regarding aviation safety protocols, regulatory oversight, and human factors. This report analyzes the accident through the lens of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), highlighting critical intersections with public health, infrastructure resilience, and institutional accountability.
Analysis of Human Factors and Occupational Health (SDG 3 & SDG 8)
Pilot Well-being and SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
The investigation is examining the medical history of the pilot-in-command, Captain Sumeet Sabharwal, amid allegations of past mental health challenges. This focus directly aligns with SDG 3, Target 3.4, which seeks to promote mental health and well-being.
- Reports suggest the captain had previously taken medical leave, allegedly for mental health reasons, although these claims are contested by the airline’s parent company.
- Both pilots had reportedly passed a Class I medical examination, which evaluates psycho-physical capabilities. However, the incident underscores the potential gap between periodic certification and the continuous monitoring of mental fitness for safety-critical roles.
- The tragedy highlights the urgent need for a supportive and non-punitive environment for aviation professionals to report mental health issues, thereby ensuring the well-being of crew and the safety of the public.
Occupational Safety and SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The circumstances of the crash are intrinsically linked to SDG 8, Target 8.8, which calls for the protection of labour rights and the promotion of safe and secure working environments. A failure to ensure the mental and physical fitness of flight crews represents a significant lapse in occupational safety, with catastrophic consequences for both workers and the public.
Infrastructure, Regulation, and Institutional Integrity (SDG 9, 11, & 16)
Aircraft Systems and Resilient Infrastructure (SDG 9)
The preliminary report indicates a manual deactivation of the fuel switches, which are designed with a locking feature to prevent inadvertent operation. This technical aspect of the investigation relates to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), which advocates for the development of quality, reliable, and resilient infrastructure.
- The design of the fuel control levers on the Boeing 787 Dreamliner is intended to be robust against accidental operation.
- A 2018 Special Airworthiness Information Bulletin from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) had previously warned that similar switches on other Boeing models could have disengaged locking features.
- The non-mandatory nature of this bulletin raises questions about the efficacy of advisory safety communications and the responsibility of operators to proactively enhance equipment resilience beyond minimum requirements.
Urban Impact and Community Safety (SDG 11)
The aircraft crashed into the residential area of Meghani Nagar, resulting in ground fatalities. This outcome directly engages SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), particularly Target 11.5, which aims to significantly reduce the number of deaths and people affected by disasters. The event serves as a stark reminder of the risks that transportation infrastructure can pose to urban communities and the importance of flight path planning and emergency protocols that minimize ground-level impact.
Institutional Accountability and Justice (SDG 16)
The response to the crash and the subsequent investigation are a test of SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions). The goal’s emphasis on effective, accountable, and transparent institutions is paramount in this context.
- The Indian Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) is leading the formal inquiry.
- Accusations from victims’ relatives of a cover-up to protect the airline and government challenge the transparency of the process.
- Maintaining public trust requires an impartial investigation that addresses all potential causes, including human factors, technical malfunction, and regulatory shortcomings, thereby upholding the principles of accountability central to SDG 16.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being: The article extensively discusses the pilot’s mental health, including claims of depression and medical leave, which is a central part of the crash investigation. It also covers the significant loss of life resulting from the crash.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article touches upon the safety and reliability of aviation infrastructure, specifically the Boeing 787 Dreamliner aircraft. It details a potential design flaw concerning the fuel switches and references a safety bulletin issued by the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The plane crash occurred in a residential area named Meghani Nagar, causing deaths on the ground and significant damage. This highlights the vulnerability of urban communities to such disasters.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
-
Target 3.4: “By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.”
- Explanation: The investigation’s focus on the pilot’s alleged depression and history of taking medical leave for mental health issues directly relates to this target. The article states, “investigations into the Air India plane crash are looking into the pilots’ medical records as it’s claimed one of them had depression and mental health issues.” This highlights the critical importance of mental health promotion and treatment, especially in high-stakes professions.
-
Target 3.6: “By 2020, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents.”
- Explanation: Although this target specifically mentions “road traffic,” its principle extends to all forms of transportation accidents. The plane crash resulted in a massive loss of life, with the article stating it was “killing 241 people on board and claiming 19 more lives of those on the ground.” This event represents a failure to prevent deaths from a transportation disaster.
-
Target 3.4: “By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being.”
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
-
Target 9.1: “Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being.”
- Explanation: The article questions the reliability of the aircraft’s infrastructure. It discusses the fuel switches on the Boeing 787 Dreamliner and a previous FAA warning about them. The FAA bulletin warned that “the switch can be moved between the two positions without lifting the switch during transition, and the switch would be exposed to the potential of inadvertent operation,” which directly concerns the reliability and safety of the infrastructure.
-
Target 9.1: “Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure…to support economic development and human well-being.”
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
-
Target 11.5: “By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected…caused by disasters…with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations.”
- Explanation: The plane crash is treated as a man-made disaster that directly impacted an urban community. The article specifies that the aircraft “plummeted into a residential area, called Meghani Nagar,” which resulted in “19 more lives of those on the ground.” This directly aligns with the target’s goal of reducing deaths caused by disasters in human settlements.
-
Target 11.5: “By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected…caused by disasters…with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations.”
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For Target 3.4 (Promote mental health and well-being):
- Indicator (Implied): The article implies the need for robust mental health screening and support systems. It mentions that the pilot had been “‘medically cleared’ by Air India” and that both pilots had “passed the Class I medical exam, which makes an evaluation of their psycho-physical capabilities.” The effectiveness of these screenings is implicitly questioned, suggesting that “prevalence and effectiveness of mental health assessments for professionals in critical safety roles” could be a measurable indicator.
- Indicator 3.4.2 (Suicide mortality rate): The investigation is exploring whether the crash was a “deliberate manual selection” and a “pilot-induced crash.” This line of inquiry directly relates to measuring mortality due to potential suicide, a key component of mental health outcomes.
-
For Target 3.6 (Reduce deaths from transport accidents):
- Indicator 3.6.1 (Death rate due to road traffic injuries): Adapted for aviation, this would be the death rate from air transport accidents. The article provides precise data for this indicator: “killing 241 people on board and claiming 19 more lives of those on the ground,” for a total of 260 fatalities.
-
For Target 9.1 (Develop reliable and resilient infrastructure):
- Indicator (Implied): The article points to a failure in regulatory compliance or action. It notes that the FAA bulletin was “‘advisory and not mandatory'” and that “Air India has suggested such inspections were not carried out.” This suggests an indicator such as the “rate of implementation of advisory safety bulletins by airlines” to measure how proactively the industry addresses potential infrastructure vulnerabilities.
-
For Target 11.5 (Reduce deaths from disasters):
- Indicator 11.5.1 (Number of deaths…attributed to disasters): The article provides the exact numbers needed for this indicator. It states there were 241 deaths among passengers and crew and 19 deaths on the ground, which can be used to calculate the number of deaths attributed to this specific disaster.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
3.4: Promote mental health and well-being.
3.6: Halve the number of global deaths and injuries from transport accidents. |
Implied: Effectiveness of mental health screenings for pilots (e.g., Class I medical exam). 3.4.2: Suicide mortality rate (implied by the investigation into a “pilot-induced crash”). 3.6.1 (Adapted): Death rate due to air transport accidents (260 fatalities mentioned). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure. | Implied: Rate of airline compliance with advisory safety bulletins (related to the FAA warning about fuel switches). |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.5: Significantly reduce the number of deaths and people affected by disasters. | 11.5.1: Number of deaths attributed to disasters (241 on board, 19 on the ground). |
Source: dailymail.co.uk