Global Progress on Sustainable Development Goals: A Mid-Term Assessment
This report provides a comprehensive overview of the current status of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Analysis of global data indicates that while progress has been made in several areas, significant challenges remain, threatening the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by the target year.
Key Achievements and Positive Trends
- SDG 1 (No Poverty): The rate of extreme poverty has continued its long-term decline, although the pace has slowed considerably in recent years.
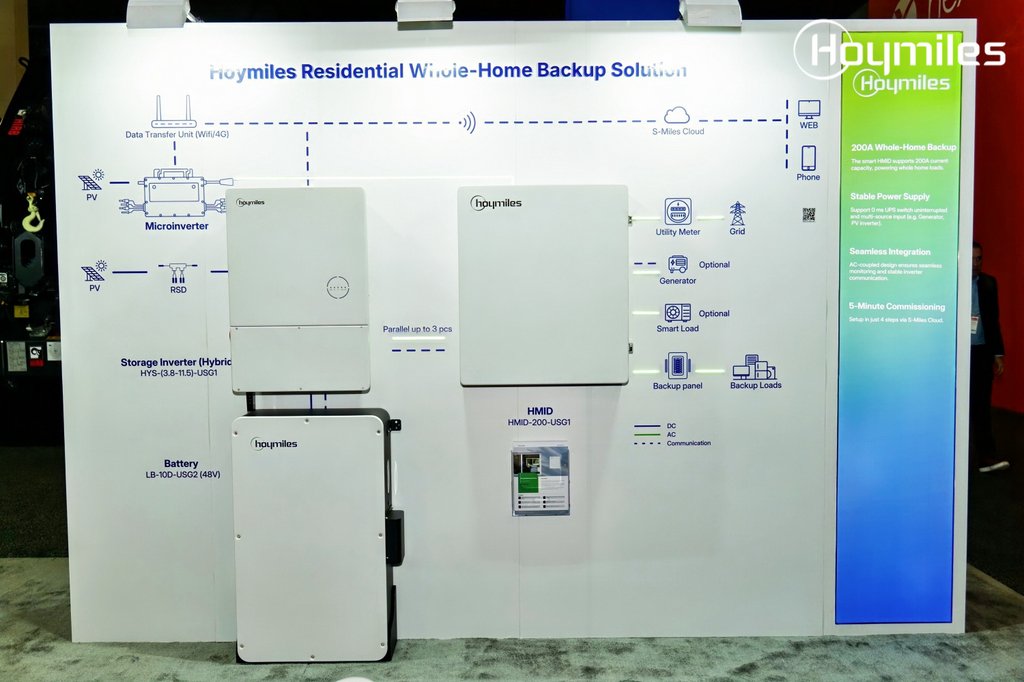
- SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy): Access to electricity has expanded globally, with significant gains in renewable energy capacity installation.
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Global child mortality rates have decreased, and access to essential health services has improved in many regions.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure): Mobile-cellular network coverage is now nearly universal, connecting the vast majority of the global population.
Significant Challenges and Areas of Concern
- SDG 13 (Climate Action): Greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, and the world is not on track to meet the targets set by the Paris Agreement, exacerbating climate-related disasters.
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger): After decades of decline, the number of undernourished people has been increasing, driven by conflict, climate shocks, and economic downturns.
- SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities): Income inequality persists and, in some nations, is worsening. Disparities in access to services and opportunities remain stark between and within countries.
- SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions): Global levels of conflict and violence are on the rise, undermining development efforts and displacing millions.
In-Depth Analysis of Selected Goals
SDG 4: Quality Education
Progress towards inclusive and equitable quality education has been severely hampered. The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruption to education systems worldwide, leading to significant learning losses. Foundational learning proficiency remains critically low in many developing countries.
- An estimated 244 million children and youth were out of school in 2021.
- A large percentage of students in low- and middle-income countries cannot read and understand a simple text by age 10.
- There is a persistent shortage of qualified teachers, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia.
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
While access to safely managed drinking water has improved, billions of people still lack basic sanitation services. The consequences for public health, environmental integrity, and economic productivity are profound.
- Approximately 2.2 billion people lack access to safely managed drinking water.
- Over 3.5 billion people lack access to safely managed sanitation services.
- Water stress is affecting countries on every continent, jeopardizing food security and peace.
Strategic Recommendations for Accelerating Progress
Policy and Financial Commitments
A significant scaling-up of investment and political will is required to rescue the SDGs. Governments and international partners must redouble their efforts to mobilize financial resources and implement evidence-based policies.
- Increase Official Development Assistance (ODA): Donor countries should meet their commitment to provide 0.7% of Gross National Income to ODA.
- Strengthen Data Systems: Investment in robust national statistical systems is crucial for monitoring progress, guiding policy, and ensuring accountability.
- Mobilize Private Finance: Create incentive structures and regulatory frameworks that align private sector investment with the SDGs.
Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration
Achieving the 2030 Agenda is a shared responsibility that requires unprecedented cooperation among all segments of society.
- Enhance public-private partnerships to drive innovation and investment in sustainable infrastructure.
- Empower civil society organizations and local communities to participate in planning and implementation processes.
- Foster collaboration with academic and scientific institutions to leverage expertise and data for sustainable solutions.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Addressed Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- The provided article contains no textual content or data discussing any issues.
- Therefore, no specific SDGs can be identified as being addressed or connected to the article’s content.
2. Identifiable SDG Targets
- As no SDGs could be linked to the article, no corresponding targets can be identified.
- The article lacks the necessary information to pinpoint any specific SDG targets.
3. Mentioned or Implied Indicators
- The article does not mention or imply any indicators.
- Without identifiable targets, and due to the absence of data in the article, no indicators for measuring progress can be determined.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Summary
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| No SDGs could be identified from the article. | No targets could be identified from the article. | No indicators could be identified from the article. |
Source: statista.com