Report on the Crisis in the Central Sahel and its Impact on Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Summary
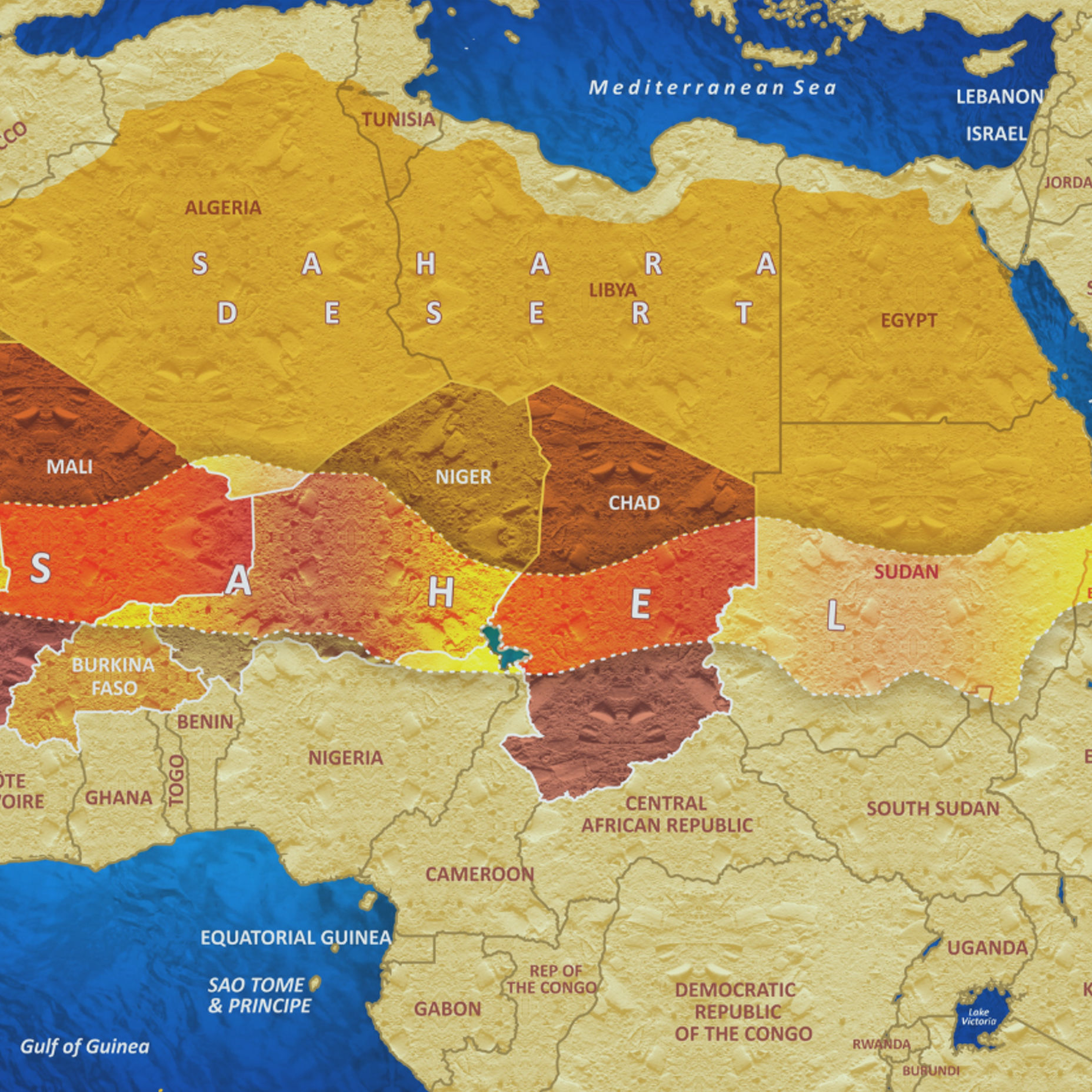
The Central Sahel region, encompassing Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger, is experiencing a severe crisis characterized by armed conflict, inter-communal violence, and entrenched insurgency. Actions by armed Islamist groups and state security forces have resulted in widespread human rights violations, likely amounting to war crimes and crimes against humanity. This escalating violence and political instability present a direct and profound threat to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), systematically undermining progress on peace, justice, gender equality, education, and basic human welfare.
Analysis of the Conflict and Human Rights Violations
Actions by Armed Insurgent Groups
Armed Islamist groups, including those affiliated with al-Qaeda (JNIM) and the Islamic State Sahel Province (IS-Sahel), are perpetrating recurrent abuses against civilian populations. Their tactics directly impede development and security, with significant consequences for multiple SDGs.
- Systematic Violence and Control: Groups employ sieges, threats, kidnappings, and improvised explosive devices (IEDs) to control territory and supply routes.
- Impediment to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and SDG 6 (Clean Water): They deliberately block humanitarian aid, causing starvation, and strategically destroy essential civilian infrastructure, including food reserves and water services.
- Violation of SDG 5 (Gender Equality): In areas under their control, they enforce a severe and discriminatory interpretation of Sharia law, targeting women and girls.
- Attack on SDG 4 (Quality Education): Insurgents systematically target secular education by burning schools and threatening, abducting, or killing teachers, denying children their right to a safe learning environment.
Actions by State Security Forces and Allied Militias
Counterterrorism operations conducted by state security forces and their allies have frequently resulted in grave human rights violations, further destabilizing the region and violating foundational principles of SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions).
- Crimes Against Humanity and War Crimes: The Malian Armed Forces (FAMa), alongside the Russian state-controlled Africa Corps (formerly Wagner Group), are implicated in summary executions, indiscriminate airstrikes, rape, sexual violence, and torture against civilians.
- Exacerbation of Inter-Communal Conflict (SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities): State-sponsored militias in Burkina Faso, such as the Volunteers for the Defense of the Homeland (VDP), have been implicated in grave crimes along ethnic lines, particularly targeting Fulani civilians in retaliatory attacks.
Political Instability and Institutional Collapse
The region has experienced significant political upheaval, including military takeovers in all three countries. These developments have weakened governance and undermined regional cooperation, directly impacting SDG 16 and SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals).
- Erosion of the Rule of Law (SDG 16): Military regimes have repressed civic and political space through measures like forcible conscription and the arbitrary arrest of critics, human rights defenders, and political opponents.
- Regional Fragmentation (SDG 17): The decision by the three military regimes to form the Alliance of Sahel States and withdraw from the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) undermines regional partnerships crucial for peace and development.
- Culture of Impunity: Accountability for atrocity crimes remains severely limited, with few alleged perpetrators being prosecuted, which contravenes the principles of justice central to SDG 16.
Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
The conflict represents a catastrophic failure to achieve SDG 16. The foundations of peaceful, just, and inclusive societies are being systematically dismantled.
- Target 16.1 (Reduce Violence): The escalating violence from all armed actors, including indiscriminate attacks and massacres, directly contravenes the goal of reducing all forms of violence and related death rates.
- Target 16.2 (Protect Children): Grave violations against children, including killings, abductions, and attacks on schools, demonstrate a complete disregard for their protection.
- Target 16.3 (Rule of Law & Access to Justice): Pervasive impunity for atrocities and the weakening of judicial systems prevent equal access to justice and undermine the rule of law.
- Target 16.10 (Protect Fundamental Freedoms): The crackdown on civil society, journalists, and political opposition inhibits public access to information and violates fundamental freedoms.
Setbacks to Foundational Human Development Goals
The conflict has reversed progress on essential development goals, creating a severe humanitarian crisis.
- SDG 2 (Zero Hunger): The use of sieges and the destruction of food reserves as a tactic of war are creating conditions of starvation.
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): The looting and destruction of health centers deprive communities of essential healthcare services.
- SDG 4 (Quality Education): The deliberate targeting of the education sector has destroyed learning environments and denied a generation of children access to quality education.
- SDG 5 (Gender Equality): The imposition of discriminatory rules and the use of sexual violence as a weapon of war constitute severe violations of the rights of women and girls.
- SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities): The targeting of populations based on ethnic identity, particularly the Fulani, fuels inter-communal tensions and deepens inequality.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): The destruction of cultural heritage, including places of worship, erodes the social fabric of communities.
Risk Factors and Recommendations
Key Risk Factors for Atrocity Crimes
- A militarized approach to counterinsurgency that stigmatizes entire communities.
- The use of ethnic militias and self-defense groups, which perpetuates cycles of reprisal attacks.
- Systemic impunity for past and ongoing atrocities committed by all armed actors.
- The widespread availability of arms and ammunition.
- A systematic crackdown on civic space, the rule of law, and dissenting voices.
Recommendations for Advancing the SDGs
- Ensure Compliance with International Law: All armed actors must conduct operations in compliance with International Humanitarian Law (IHL) to protect civilians, a prerequisite for achieving any development goals.
- Strengthen Accountability (SDG 16): The military authorities in the Sahel must investigate all violations of IHL and International Human Rights Law. International partners should support accountability mechanisms to end the cycle of impunity.
- Protect Civic Space (SDG 16): Authorities must cease all threats and reprisals against civil society, ensuring they can operate without fear to monitor human rights and support vulnerable populations.
- Promote Regional Cooperation (SDG 17): The African Union (AU) and other regional bodies must intensify efforts to address the crisis, denounce abuses, and foster political settlements.
- Address Root Causes: To build a foundation for lasting peace and sustainable development, measures must be implemented to end arms proliferation, improve land management, and resolve long-standing inter-communal grievances.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- The article extensively details the breakdown of peace and security in the Central Sahel (Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger). It describes “recurrent and expanding violence,” “armed conflict,” “war crimes,” and “crimes against humanity.” It also highlights the failure of justice systems, evidenced by “limited accountability” and “impunity for past and ongoing atrocities.” The weakening of institutions is shown through “military takeovers,” “weak governance,” the repression of “civic and political space,” and the withdrawal from regional bodies like ECOWAS.
SDG 5: Gender Equality
- The article explicitly mentions violations of gender equality. Armed Islamist groups are reported to have “enforced their own interpretation of Sharia law… imposing severe gender discriminatory rules.” Furthermore, sexual violence is used as a weapon of war, with security forces and allied groups implicated in “rape and sexual violence.”
SDG 4: Quality Education
- The right to education is directly under attack. The article states that insurgents “routinely perpetrate grave violations against children and target secular state education, burning schools and threatening, abducting or killing teachers.” This directly undermines the goal of providing safe and inclusive learning environments.
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- The article points to actions that directly cause hunger and food insecurity. It notes that armed groups are “blocking humanitarian aid to civilians and causing starvation” and strategically destroying “food reserves.” These tactics use hunger as a weapon of war.
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Access to healthcare is severely compromised. The article mentions the strategic destruction and looting of civilian objects, including “health centers,” which deprives the population of essential medical services amidst a violent conflict.
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The conflict impacts access to basic services like water. The article reports that armed groups are “strategically destroying and looting civilian objects, including… water services,” which is a violation of International Humanitarian Law and a direct threat to public health.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- The safety of communities and the protection of cultural heritage are threatened. The article describes the destruction of “places of worship” and references the conviction of an individual by the ICC for the “intentional destruction of cultural sites” in Timbuktu, Mali.
Specific SDG Targets Identified
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Target 16.1: Significantly reduce all forms of violence and related death rates everywhere. The article is replete with examples of failure to meet this target, describing “summary executions,” “indiscriminate airstrikes,” “massacres of ethnic Fulani civilians,” and attacks on worshippers, all contributing to high death rates from violence.
- Target 16.2: End abuse, exploitation, trafficking and all forms of violence against and torture of children. This target is relevant due to the mention of insurgents who “routinely perpetrate grave violations against children” and the targeting of schools, which includes abducting or killing teachers.
- Target 16.3: Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all. The article highlights a complete failure in this area, citing “impunity for past and ongoing atrocities,” “limited accountability with few alleged perpetrators having been arrested, prosecuted or tried,” and the undermining of the rule of law through military takeovers.
- Target 16.10: Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements. This target is directly contradicted by the actions described in the article, such as the “crackdown against human rights defenders and civic space,” the “forcible conscription, arbitrary arrests or kidnapping of dozens of perceived critics,” and the outlawing of political parties in Mali.
SDG 5: Gender Equality
- Target 5.1: End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere. The imposition of “severe gender discriminatory rules” by armed groups in areas under their control is a direct violation of this target.
- Target 5.2: Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls in the public and private spheres. The article points to the use of “rape and sexual violence” by the Malian Armed Forces and the Wagner Group as a tactic of war, which is an extreme form of violence against women.
SDG 4: Quality Education
- Target 4.a: Build and upgrade education facilities that are child, disability and gender sensitive and provide safe, non-violent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all. The article describes the opposite, with insurgents actively “burning schools and threatening, abducting or killing teachers,” creating an environment of terror that makes education impossible.
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- Target 2.1: By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people… to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round. The article details how armed groups actively work against this target by “blocking humanitarian aid to civilians and causing starvation” and destroying “food reserves.”
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.4: Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage. This target is undermined by the “intentional destruction of cultural sites,” for which an ICC conviction was secured, and the ongoing destruction of “places of worship.”
Implied Indicators for Measuring Progress
Under Target 16.1 (Reduce Violence)
- Indicator 16.1.2: Conflict-related deaths per 100,000 population. The article provides qualitative and some quantitative data on this, such as “at least 20 Fulani civilians were summarily executed,” “at least 130 civilians killed,” and “at least 44 worshippers” killed. Tracking these numbers would be a direct measure of progress.
Under Target 16.3 (Promote Rule of Law)
- Indicator 16.3.3: Proportion of the population who have experienced a dispute in the past two years and who accessed a formal or informal dispute resolution mechanism. The article implies this indicator is near zero for atrocity crimes, stating that “few alleged perpetrators having been arrested, prosecuted or tried for international crimes,” and noting the general state of “impunity.”
Under Target 16.10 (Protect Fundamental Freedoms)
- Indicator 16.10.1: Number of verified cases of killing, kidnapping, enforced disappearance, arbitrary detention and torture of journalists, associated media personnel… and human rights advocates. The article directly implies this indicator by mentioning the “forcible conscription, arbitrary arrests or kidnapping of dozens of perceived critics, human rights defenders,” and that “several pro-democracy activists have gone missing and/or remain detained.”
Under Target 4.a (Safe Education Facilities)
- Number of attacks on schools, students, and teachers. While not an official SDG indicator, it is a key measure used by humanitarian organizations. The article’s mention of “burning schools and threatening, abducting or killing teachers” makes this a critical, implied metric for the region.
Under Target 2.1 (End Hunger)
- Number of people requiring humanitarian food assistance. The article’s reference to “blocking humanitarian aid” and “causing starvation” implies that a key indicator would be the number of people in besieged areas who are cut off from food supplies and require aid.
Summary of Findings
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Mentioned or Implied in the Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions |
16.1: Reduce all forms of violence and related death rates.
16.3: Promote the rule of law and ensure equal access to justice. 16.10: Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms. |
Number of conflict-related deaths (e.g., “at least 130 civilians killed,” “at least 44 worshippers killed”).
Number of perpetrators of international crimes arrested, prosecuted, or tried (implied to be very low due to “impunity”). Number of verified cases of kidnapping, enforced disappearance, and arbitrary detention of human rights defenders and critics (e.g., “dozens of perceived critics” arrested or kidnapped). |
| SDG 5: Gender Equality |
5.1: End all forms of discrimination against women and girls.
5.2: Eliminate all forms of violence against women and girls. |
Existence of discriminatory rules imposed on women (e.g., “severe gender discriminatory rules”).
Incidents of conflict-related sexual violence (e.g., reports of “rape and sexual violence” by armed actors). |
| SDG 4: Quality Education | 4.a: Provide safe, non-violent, and inclusive learning environments. | Number of attacks on educational infrastructure and personnel (e.g., “burning schools,” “abducting or killing teachers”). |
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.1: End hunger and ensure access to food. | Incidents of humanitarian aid obstruction; prevalence of starvation in besieged areas; destruction of food reserves. |
| SDG 3, 6, 11: Good Health, Clean Water, Sustainable Communities |
3.d: Strengthen capacity for health risks. 6.1: Achieve access to safe drinking water. 11.4: Protect cultural heritage. |
Number of civilian objects destroyed, including “health centers,” “water services,” and “places of worship.” |
Source: globalr2p.org