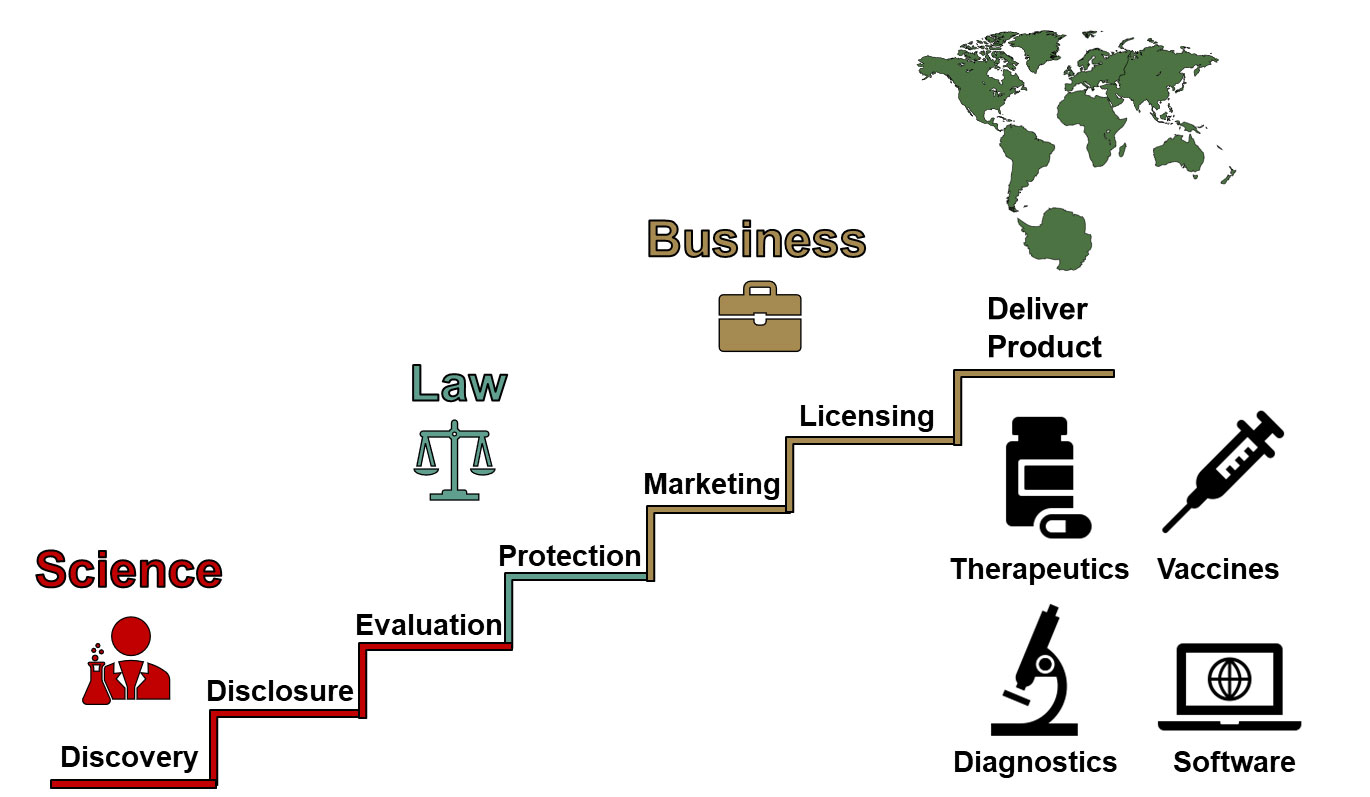
Report on Enterprise AI Infrastructure Preparedness and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
This report analyzes the current landscape of Artificial Intelligence (AI) infrastructure investment, identifies a critical preparedness gap at the enterprise level, and provides strategic recommendations for aligning infrastructure modernization with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
1.0 Global AI Infrastructure Investment and its Link to SDG 9 and SDG 17
A significant acceleration in AI infrastructure investment is underway, driven by major global entities. This trend directly supports the advancement of SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, which calls for building resilient infrastructure, promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation.
- Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships (SDG 17): The formation of a $100 billion AI Infrastructure Fund by entities including xAI, Nvidia, BlackRock, and Microsoft exemplifies a powerful multi-stakeholder partnership, a key principle of SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals. Such collaborations are essential for mobilizing the resources needed to build the technological foundation for future sustainable development.
- Projected Infrastructure Demand: Global demand for data center capacity is projected to increase by approximately 20% annually over the next five years. Meeting this demand requires constructing, in a fraction of the time, double the capacity built since the year 2000. This rapid expansion is critical for achieving the targets of SDG 9 but also presents significant challenges.
2.0 The Enterprise Preparedness Gap: A Risk to Sustainable Economic Growth
While large-scale investment proceeds, a concerning gap is emerging at the enterprise level. Many organizations are not upgrading their foundational infrastructure at a pace that matches their AI software investments, posing a risk to long-term economic and sustainable progress.
2.1 Inefficient Resource Allocation and Legacy System Constraints
Enterprises report that AI spending is their largest single technology budget item. However, without concurrent infrastructure modernization, these investments are at risk of being underutilized. This inefficiency hinders progress towards SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth, as potential productivity gains from AI are not fully realized.
- Legacy database and compute systems were not designed for the data volume and velocity required by modern AI, creating bottlenecks that limit innovation.
- Failure to modernize these underlying systems puts a strain on business operations and impedes the ability to retrofit industries for sustainability, a core target of SDG 9.4.
2.2 The Energy Imperative: Connecting Infrastructure to SDG 7 and SDG 12
The exponential growth in data centers required for AI places immense pressure on energy resources. This directly implicates SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
- The massive power consumption of data centers necessitates a strategic shift towards renewable energy sources (SDG 7.2) and significant improvements in energy efficiency (SDG 7.3).
- Sustainable infrastructure design must account for the entire lifecycle of hardware, promoting responsible production and consumption patterns to manage electronic waste and resource use (SDG 12).
3.0 Strategic Recommendations for Sustainable and Resilient Enterprise Infrastructure
To bridge the preparedness gap and ensure AI development contributes positively to the SDGs, enterprises must adopt a forward-looking and holistic approach to their infrastructure strategy.
3.1 Proactive Planning and Stress-Testing for Future Workloads
Organizations must shift from planning for current workloads to anticipating future demands. This involves rigorous testing and simulation to ensure infrastructure can handle exponential growth in data and model complexity.
- Conduct extensive performance tests that simulate future AI-driven data volumes, not just current operational loads.
- Develop a strategic roadmap for scaling infrastructure in alignment with business and sustainability objectives.
- Adopt multi-cloud strategies to enhance agility, reduce vendor lock-in, and build the resilient infrastructure required by SDG 9 and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
3.2 Architecting for Scalability, Resilience, and Sustainability
Infrastructure architecture must be re-engineered with core principles that support both business objectives and global sustainability targets.
- Scalability: Implement databases and compute platforms that can scale elastically to accommodate data growth without performance degradation, fostering the innovation central to SDG 9.
- Resilience: Build resilience into the core architecture to prevent outages and ensure the reliability of critical services, a foundational element of SDG 9.1.
- Sustainability: Prioritize energy efficiency in all architectural decisions and actively pursue renewable energy sources for data center operations to meet the goals of SDG 7.
By prioritizing the modernization of their foundational infrastructure, enterprises can unlock the full potential of their AI investments, drive strategic differentiation, and make a tangible contribution to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The text is centered on the critical need for investment in and development of “scalable and resilient infrastructure” to support the advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It discusses the formation of a massive “AI Infrastructure Fund,” the construction of new “data centers,” and the evolution of “cross-cloud platforms.” The entire narrative revolves around building the foundational infrastructure (Target 9.1), fostering innovation (AI), and upgrading industry capabilities to handle future technological demands.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article connects infrastructure investment directly to economic activity and business competitiveness. It highlights that “44% of companies report AI spending as their single largest budgetary line item,” indicating a major economic shift. The discussion about enterprises needing to adapt to avoid “missed opportunities to capitalize on AI-driven insights” and “differentiate strategically” points directly to achieving higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation (Target 8.2).
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
While not the main focus, this goal is implicitly relevant. The article states that global demand for data center capacity is surging and mentions a partnership to invest “over $25 billion in projects to power data centers.” The exponential growth in compute power and data centers, as described by McKinsey and Nvidia’s CEO, implies a colossal increase in energy consumption. This directly links the article’s subject to the challenge of providing sufficient and sustainable energy infrastructure (Target 7.a) to power this technological expansion.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure
The article is a direct call to action for this target. It repeatedly emphasizes the need for “scalable and resilient infrastructure” and warns that “databases that can’t scale linearly or elastically will become serious liabilities.” The formation of the $100 billion AI Infrastructure Fund and other multi-billion dollar investments are presented as essential steps to develop the reliable infrastructure required to support the AI economy.
-
Target 9.c: Significantly increase access to information and communications technology
The core topic is the expansion of the world’s Information and Communications Technology (ICT) backbone. The article discusses building more data centers, increasing computing power, and developing multi-cloud strategies. These actions are fundamental to increasing the capacity and accessibility of advanced ICT services like AI for enterprises and, eventually, the wider economy.
-
Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation
The article argues that enterprises must invest in modern infrastructure to fully leverage AI. It states that businesses that get their infrastructure right “will be the ones that use AI not just to improve processes, but to differentiate strategically through data, talent, and agility.” This is a clear articulation of using technological upgrading (modern infrastructure) and innovation (AI) to boost economic productivity and competitiveness.
-
Target 7.a: Enhance international cooperation and promote investment in energy infrastructure
The article provides a concrete example of this target in action. It mentions a partnership between ADQ and Energy Capital Partners to “invest over $25 billion in projects to power data centers.” This highlights significant investment flowing into the energy infrastructure needed to support the growing technology sector.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article contains several specific quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress.
-
Investment in Infrastructure: The article provides concrete financial figures that serve as direct indicators of investment.
- “$100 billion” target for the AI Infrastructure Fund.
- “Over $25 billion” investment in projects to power data centers.
- “Over $16 billion” in loans sought by SoftBank for AI growth.
-
Enterprise Technology Spending: A key statistic indicates the level of private sector investment in technological upgrading.
- “44% of companies report AI spending as their single largest budgetary line item in tech spending.”
-
Growth in Infrastructure Demand and Capacity: The article cites a McKinsey study with specific metrics for the required growth in data center infrastructure.
- “Global demand for data center capacity could rise at an annual rate of roughly 20% over the next five years.”
- The need to “at least double the capacity that has been built since 2000… in a quarter of the time.”
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure |
9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
9.c: Significantly increase access to information and communications technology. |
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. |
|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.a: Promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. |
|
Source: solutionsreview.com