Report on Emerson’s Appleton Group Facility Energy Efficiency Achievements
Executive Summary
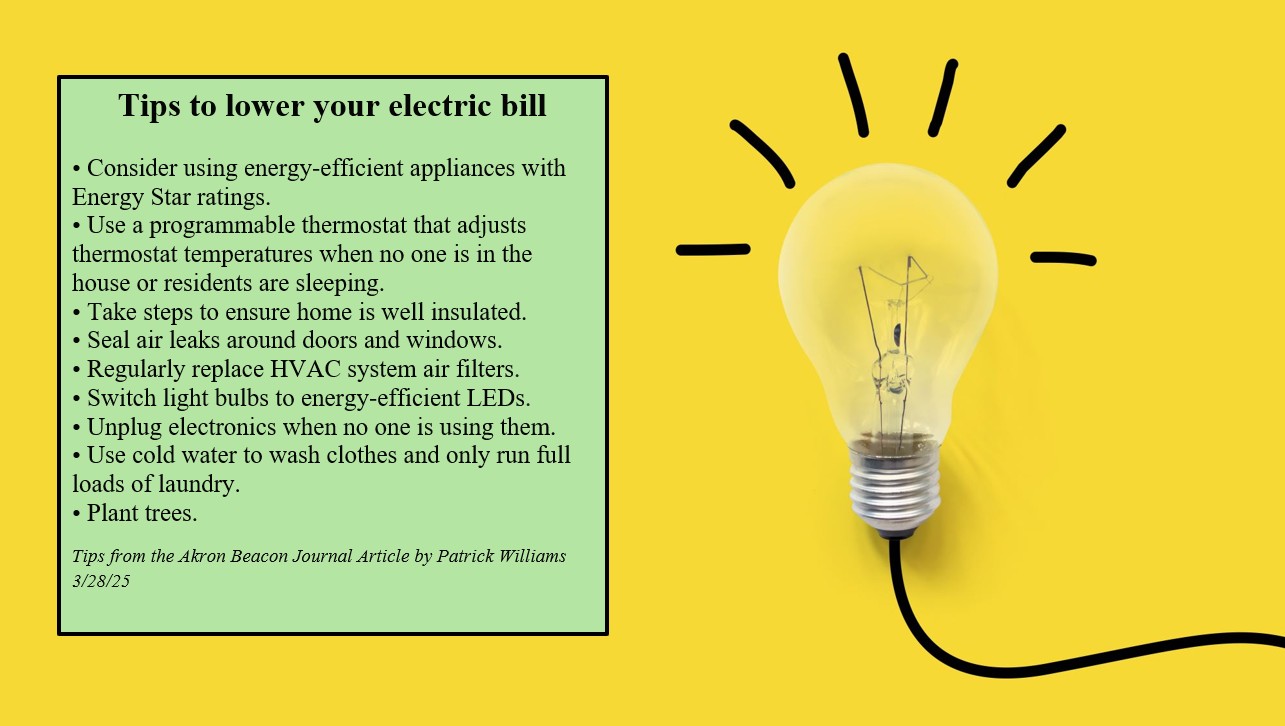
Emerson’s Appleton Group iron casting facility in South Milwaukee has been recognized with a 2025 Energy Excellence Award by Focus on Energy for its significant advancements in energy efficiency. Through a strategic partnership and targeted infrastructure upgrades, the facility has substantially reduced its energy consumption, operational costs, and environmental emissions. These achievements directly contribute to several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), establishing the facility as a model for sustainable industrial practices.
Partnership and Project Implementation in Support of SDG 17
Since 2017, Emerson has collaborated with Focus on Energy, Wisconsin’s statewide energy efficiency and renewable energy program. This partnership (SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals) has been instrumental in identifying, designing, and implementing high-impact energy-saving projects. The collaboration demonstrates a successful public-private model for advancing sustainable development.
Key Technological Upgrades and Contribution to SDG 9
The facility’s modernization efforts represent a significant investment in sustainable industrial infrastructure (SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). Key projects included:
- Installation of new controls on makeup air units to optimize energy use.
- Replacement of legacy channel furnaces with modern, efficient cordless induction melting furnaces.
- A comprehensive lighting overhaul, replacing over 800 fluorescent lights with energy-efficient Appleton industrial LED fixtures.
Quantifiable Outcomes and Impact on Sustainable Development Goals
The implemented projects have yielded substantial and measurable improvements, aligning with critical global sustainability targets.
Performance Metrics
The combined energy efficiency measures have resulted in significant annual savings and reductions:
- Energy Savings: Over 10,000 megawatt-hours (MWh) and 65,000 million British thermal units (MMBtu).
- Cost Savings: Over $1 million in annual energy costs.
- Emissions Reduction: A one-third reduction in the facility’s total energy consumption and associated emissions since 2017.
- Financial Incentives: Nearly $350,000 in energy-related incentives were secured through the partnership.
Alignment with Global Goals
The facility’s success story provides a tangible example of corporate action towards the SDGs:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: The project drastically reduced energy consumption, making operations more efficient and less costly, thereby promoting the principles of affordable and clean energy within an industrial context.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: By fundamentally altering its production processes to consume less energy, the facility has implemented a model of responsible production, minimizing its resource footprint.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The one-third reduction in energy consumption and emissions is a direct and significant contribution to climate action, mitigating the facility’s impact on the environment.
Conclusion: A Replicable Model for Sustainable Industry
The achievements of Emerson’s South Milwaukee foundry, once one of the company’s largest energy consumers, prove that even energy-intensive operations can become leaders in sustainability. The facility’s commitment to reducing its environmental impact while enhancing economic efficiency serves as a powerful case study for the global manufacturing sector. This initiative highlights how targeted investments in energy efficiency can drive progress on multiple Sustainable Development Goals, fostering a healthier environment and a stronger local economy.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article highlights several initiatives undertaken by Emerson’s Appleton Group that directly or indirectly connect to a number of Sustainable Development Goals. The primary focus on energy efficiency and sustainable industrial practices links the content to the following SDGs:
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: The core theme of the article is the facility’s successful efforts to improve energy efficiency, which is a key component of this goal.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article describes the retrofitting of an industrial facility with modern, energy-efficient technologies, which aligns with the goal of building resilient infrastructure and promoting sustainable industrialization.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: By significantly reducing its energy consumption, the foundry is promoting more sustainable production patterns and the efficient use of natural resources.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The reduction in energy consumption directly leads to a reduction in emissions, contributing to efforts to combat climate change.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The success of the project is explicitly attributed to the partnership between Emerson, a private company, and Focus on Energy, a statewide program, demonstrating a public-private partnership for sustainable development.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the actions described in the article, the following specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 7.3: “By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.”
- Explanation: The article is centered on the Appleton foundry’s commitment to “optimizing energy efficiency.” The implementation of new controls, cordless induction furnaces, and LED lighting are all direct measures to improve energy efficiency, aligning perfectly with this target.
- Target 9.4: “By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes…”
- Explanation: The article details how the “century-old foundry” was upgraded. Specific examples include the “replacement of channel furnaces with cordless induction melting furnaces” and the “replacement of over 800 fluorescent lights with Appleton industrial LED fixtures.” These actions represent a clear retrofitting of an industry to make it more sustainable and efficient.
- Target 12.2: “By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.”
- Explanation: Energy is a critical natural resource. The article states that the improvements save the facility “over 10,000 megawatt-hours (MWh)” and “65,000 million British thermal units (MMBtu)” annually. This represents a more efficient use of natural resources in the production process.
- Target 13.2: “Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.”
- Explanation: While the article focuses on a single company, its actions contribute to broader climate goals. The article explicitly states that the team’s commitment has “cut the facility’s total energy consumption and emissions by about a third since 2017, drastically reducing its own emissions.” This reduction in emissions is a direct action to combat climate change.
- Target 17.17: “Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships…”
- Explanation: The article highlights that the foundry “has worked with the Focus on Energy initiative since 2017” and that “the partnership has made it possible for the foundry to identify, evaluate, design and implement many successful energy efficiency… projects.” This collaboration between a private company (Emerson) and a statewide program (Focus on Energy) is a textbook example of a public-private partnership for sustainability.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article provides several specific, quantifiable indicators that can be used to measure progress:
- Energy Savings: The article quantifies the annual energy savings as “over 10,000 megawatt-hours (MWh)” and “65,000 million British thermal units (MMBtu).” This is a direct indicator of improved energy efficiency (Target 7.3) and more efficient resource use (Target 12.2).
- Emission Reductions: The text states that the facility has “cut the facility’s total energy consumption and emissions by about a third since 2017.” This percentage reduction is a clear indicator for measuring progress on climate action (Target 13.2).
- Financial Savings and Incentives: The article mentions “$1 million in energy costs annually” saved and “nearly $350,000 in energy-related incentives” identified. These financial figures serve as indicators of the economic viability and success of the sustainable upgrades (Target 9.4) and the effectiveness of the partnership (Target 17.17).
- Technology Adoption: The specific mention of replacing “over 800 fluorescent lights with Appleton industrial LED fixtures” and replacing “channel furnaces with cordless induction melting furnaces” serves as a qualitative indicator of the adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies (Target 9.4).
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Summary
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.3: By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. | Annual energy savings of over 10,000 MWh and 65,000 MMBtu. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | Replacement of channel furnaces with cordless induction melting furnaces; replacement of 800+ fluorescent lights with industrial LED fixtures. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | Reduction in total energy consumption by about a third since 2017. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | Reduction in the facility’s emissions by about a third since 2017. |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.17: Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships. | Ongoing partnership between Emerson and Focus on Energy since 2017, resulting in nearly $350,000 in identified incentives. |
Source: fmindustry.com