Report on Procter & Gamble’s “One Supply Chain” Strategy and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Introduction: A Paradigm Shift in Supply Chain Management
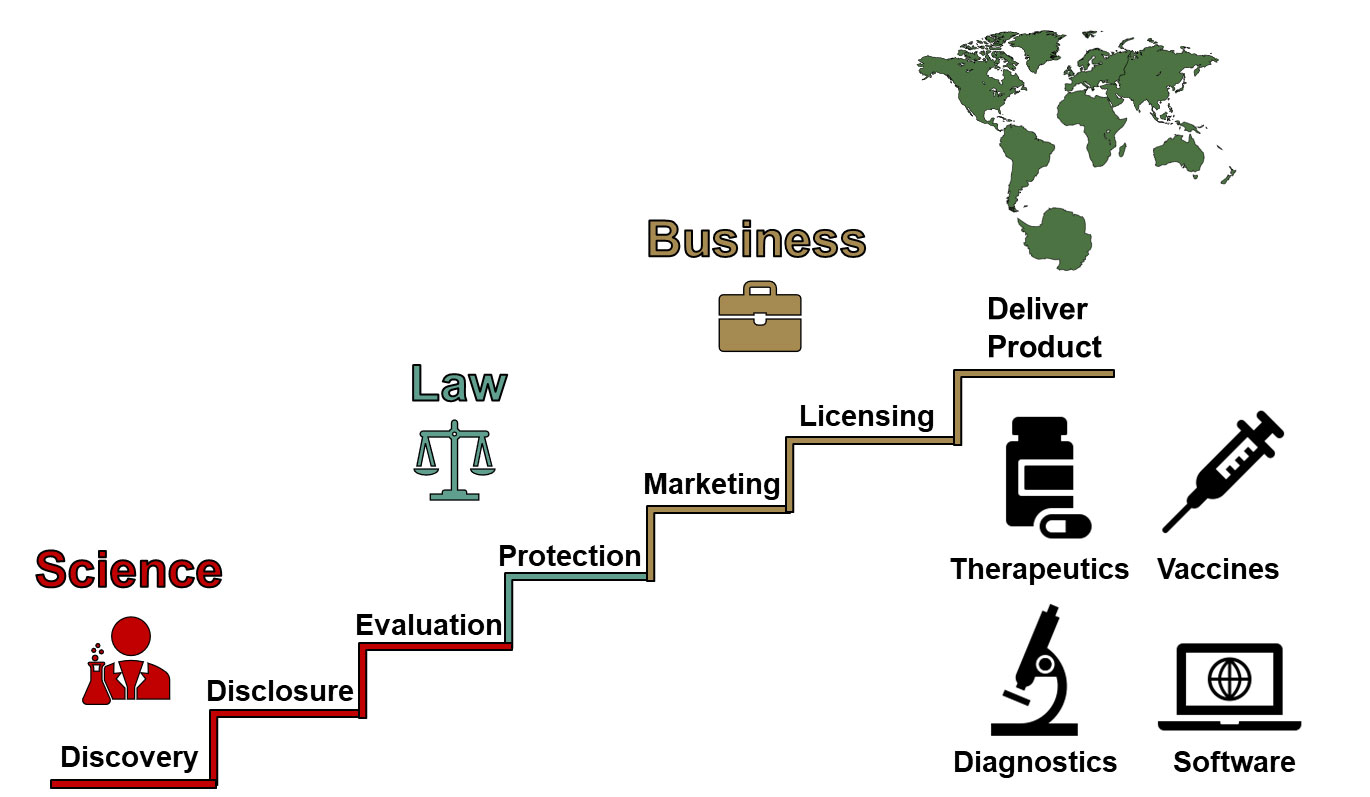
Historically viewed as a cost center, the supply chain has been transformed by pioneering companies into a strategic driver of growth and customer value. Procter & Gamble (P&G) exemplifies this evolution through its “One Supply Chain” strategy. This report analyzes how P&G’s integrated approach to supply chain management not only enhances business performance but also significantly contributes to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly in the areas of responsible production, innovation, decent work, and strategic partnerships.
Strategic Framework: Aligning Operations with Global Goals
The Evolution to Supply 3.0
P&G’s supply chain strategy has undergone a significant transformation, moving from a narrow focus on internal efficiency to a holistic, integrated system. This evolution can be summarized in three stages:
- Supply 1.0: Focused on manufacturing excellence and employee engagement.
- Supply 2.0: Integrated the end-to-end supply chain, from suppliers to distribution, to improve resilience.
- Supply 3.0: Extends integration to retailers and consumers, creating a transparent, agile, and cost-efficient system that actively supports sustainability objectives, aligning with SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production).
Core Pillars of a Sustainable Supply Chain
The current Supply 3.0 strategy is built upon four foundational pillars, each contributing to both business success and sustainable development:
- Supply in Full: Ensuring product availability to maintain market stability and consumer trust, which underpins sustainable economic activity.
- Seamless Data, Touchless Flow: Utilizing digital integration and automation to build resilient and efficient infrastructure, directly supporting SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure).
- Superior Employee Experience: Empowering the workforce through upskilling and a positive work environment, which is central to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- Sustainability: Embedding environmental responsibility into core operations to reduce ecological impact, a direct commitment to SDG 12.
Advancing Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12)
Sustainable Product and Packaging Innovation
P&G integrates sustainability directly into product design and delivery. For example, the Olay Cleansing Melts, a waterless facial cleansing product, are lighter to transport, reducing carbon emissions. Furthermore, by shipping products directly to customers in their original packaging where feasible, P&G minimizes additional handling and packaging waste, directly addressing targets under SDG 12 related to waste reduction.
Logistics and Transportation Efficiency
P&G’s network of seven North American “mixing centers” is a prime example of operationalizing sustainability. These centers allow for the consolidation of diverse product lines into single shipments. By mixing heavier products (e.g., fabric care) with lighter ones (e.g., baby care), P&G maximizes truck capacity. This strategy achieves several goals aligned with SDG 12:
- Reduces the number of trucks on the road.
- Lowers fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improves the overall resource efficiency of its distribution network.
Fostering Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure (SDG 9)
Technology as an Enabler of Sustainability
Technology is central to P&G’s ability to build a resilient and efficient supply chain. The company leverages artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation to achieve:
- Enhanced Visibility: Real-time data integration with retailers and suppliers provides a transparent view of the entire supply chain.
- Optimized Inventory: AI-driven forecasting minimizes overproduction and waste.
- Improved Quality Control: Automated inspection systems using vision and sensors ensure 100% of products are checked, reducing defects and resource loss.
The goal to automate 75% of manual processes in its personal care planning team demonstrates a commitment to building the modern, intelligent infrastructure required by SDG 9.
Cross-Divisional Innovation
P&G leverages its scale to foster innovation that can be applied across business units. The development of Tide Pods, for instance, utilized engineering expertise from the company’s diaper division, which specializes in containing liquids within fabric at high speeds. This collaborative approach prevents redundant work, accelerates technological adoption, and ensures that innovations contribute broadly to the company’s efficiency and sustainability goals.
Promoting Decent Work and Economic Growth (SDG 8)
Workforce Transformation and Empowerment
P&G recognizes that its people are fundamental to its success, making “superior employee experience” a core strategic pillar. With nearly two-thirds of its workforce in the Product Supply function, the company invests heavily in education and upskilling. This initiative transitions employees from repetitive manual tasks to higher-value roles in advanced analytics and supply chain optimization. This focus on workforce development directly supports SDG 8 by promoting productive employment and decent work.
Measurable Impact on Employee Well-being
The success of P&G’s commitment to its workforce is reflected in key metrics. An 85% employee retention rate and high satisfaction scores in third-party surveys indicate a safe, empowering, and secure working environment, aligning with the principles of SDG 8.
Building Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17)
Integrated Networks with Retailers and Suppliers
P&G’s strategy extends beyond its own operations to create deeply integrated partnerships with retailers and suppliers. Through “connected replenishment” and shared data systems, P&G and its partners develop joint business plans. This collaborative model allows them to collectively identify and eliminate inefficiencies in the shared supply chain. This approach exemplifies SDG 17, which calls for multi-stakeholder partnerships to achieve sustainable development.
The Economic Case for Collaboration
The effectiveness of these partnerships is demonstrated by tangible business results. In one instance, a retailer’s promotion triggered a real-time demand signal that flowed directly to P&G’s manufacturing systems. The seamless collaboration enabled P&G to meet the demand surge without disruption, resulting in millions of dollars in additional sales. This proves that partnerships built on transparency and shared goals are not only sustainable but also highly profitable.
Conclusion: A Replicable Model for Sustainable Growth
P&G’s “One Supply Chain” strategy offers a compelling blueprint for how companies can transform their operations into engines for both business growth and sustainable development. Key lessons include:
- Strategic Alignment: Position the supply chain as a driver of revenue and sustainable value, not merely a cost center.
- Purposeful Technology: Leverage AI and automation to enhance efficiency, transparency, and quality, directly supporting SDG targets.
- Integrated Sustainability: Embed environmental and social goals, such as those in SDG 12 and SDG 8, into core business strategy.
- Collaborative Ecosystems: Build strong partnerships with suppliers and customers, in line with SDG 17, to create shared value and resilience.
By systematically integrating its supply chain with its corporate strategy, P&G demonstrates that operational excellence and a commitment to global sustainability goals are mutually reinforcing pathways to long-term success.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth – The article discusses P&G’s revenue growth, focus on employee experience, upskilling, and creating a positive work environment, all of which are central to promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth and decent work.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – The core of the article is about building a resilient and innovative supply chain (infrastructure) through technology, automation, AI, and data integration to drive efficiency and growth in the consumer goods industry.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production – The article explicitly highlights sustainability as a core pillar of P&G’s strategy, detailing efforts to reduce environmental impact through sustainable product design, reduced packaging waste, and efficient transportation.
Specific SDG Targets Identified
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.
Explanation: The article details P&G’s strategy to drive growth by transforming its supply chain into a “growth orchestrator.” This is achieved through technological innovation, including the use of AI, machine learning, and automation to optimize inventory, reduce defects, and automate manual processes. The article states, “In North America, P&G’s personal care planning team has automated more than 30% of manual supply chain processes, with a goal to reach 75% automation.” This directly relates to increasing economic productivity through technology. - Target 8.5: By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all.
Explanation: P&G’s focus on a “superior employee experience” is a foundational pillar of its strategy. The article mentions empowering employees, upskilling them from “repetitive data sorting work into more advanced analytics and supply chain optimization work,” and creating a positive culture. This commitment to employee development and a quality work environment aligns with the goal of providing decent work. - Target 8.8: Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers.
Explanation: The article highlights P&G’s efforts to create a positive work environment, citing a “Great Place to Work” survey where 71% of employees felt it was a great place to work and an employee retention rate of 85%. This demonstrates a commitment to a secure and positive working environment for its workforce.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and processes.
Explanation: P&G’s Supply 3.0 strategy is focused on making its supply chain (infrastructure) faster, more flexible, and cost-efficient. The sustainability pillar specifically aims to “reduce its environmental impact.” This is achieved through resource-efficient logistics, such as using mixing centers to ensure full truck utilization, and adopting processes that reduce waste, like shipping products in their original packaging. - Target 9.5: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors… encouraging innovation.
Explanation: The article is a case study in technological upgrading and innovation. P&G leverages “real-time data with retailers and suppliers,” “Artificial intelligence and machine learning,” and cross-division collaboration to innovate. The example of using diaper production expertise to perfect Tide Pods manufacturing showcases how the company enhances its technological capabilities across different sectors.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Target 12.2: By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
Explanation: The article describes how P&G optimizes its transportation network to improve resource efficiency. By using strategically located “mixing centers,” the company combines heavy and light products to “enable the full utilization of the truck.” This practice leads to more efficient use of fuel and reduces the overall environmental footprint of its logistics. - Target 12.5: By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse.
Explanation: P&G addresses waste reduction in two ways. First, by shipping items “in their original packaging when appropriate, eliminating additional touches and package handling,” which reduces packaging waste. Second, through product innovation like the “Olay Cleansing Melts,” which are in a waterless fiber form, making them “more sustainable and lighter to transport.” - Target 12.6: Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
Explanation: As a large transnational company, P&G has made “sustainability a core pillar of Supply 3.0.” The article notes that the company tracks “Sustainability metrics” such as “Packaging and logistics efficiency,” demonstrating the integration of sustainable practices and metrics into its operational strategy.
Indicators for Measuring Progress
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Revenue Growth: The article states that P&G’s revenue grew from $71 billion in 2020 to over $84 billion in 2024, indicating successful economic growth.
- Employee Retention Rate: An 85% employee retention rate is mentioned as a key metric, indicating a stable and decent work environment.
- Employee Survey Scores: A 2021 survey found that 71% of employees felt P&G was a great place to work, serving as a direct measure of employee satisfaction and work quality.
- Reduction in Manual Processes: The goal to automate 75% of manual supply chain processes is a clear indicator of technological upgrading and productivity improvement.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Automation Rate: The article specifies that over 30% of manual supply chain processes have been automated, with a target of 75%, which measures the adoption of new technology.
- Use of AI and Data Integration: The implementation of AI-driven quality control and real-time data integration with retailers are indicators of technological capability upgrades.
- Vehicle Fill Rate: This logistics metric, mentioned under “Transportation & logistics optimization,” measures the efficiency of the transportation infrastructure.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
- Packaging Waste Reduction: The practice of shipping products in original packaging to eliminate extra handling and materials is a direct indicator of waste prevention.
- Logistics Efficiency: The vehicle fill rate, achieved by mixing products, is an indicator of efficient natural resource (fuel) use.
- Sustainable Product Development: The creation of products like Olay Melts, which are lighter to transport and have less packaging, serves as an indicator of sustainable production patterns.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through technological upgrading and innovation. |
|
| 8.5 / 8.8: Achieve full and productive employment and decent, safe work for all. |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable and resource-efficient. |
|
| 9.5: Enhance research and upgrade technological capabilities of industrial sectors. |
|
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. |
|
| 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation. |
|
|
| 12.6: Encourage companies to adopt sustainable practices and reporting. |
|
Source: scmr.com