Report on Massachusetts’ Top-Ranked School System and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Overview of State Ranking and Commitment to SDG 4 (Quality Education)
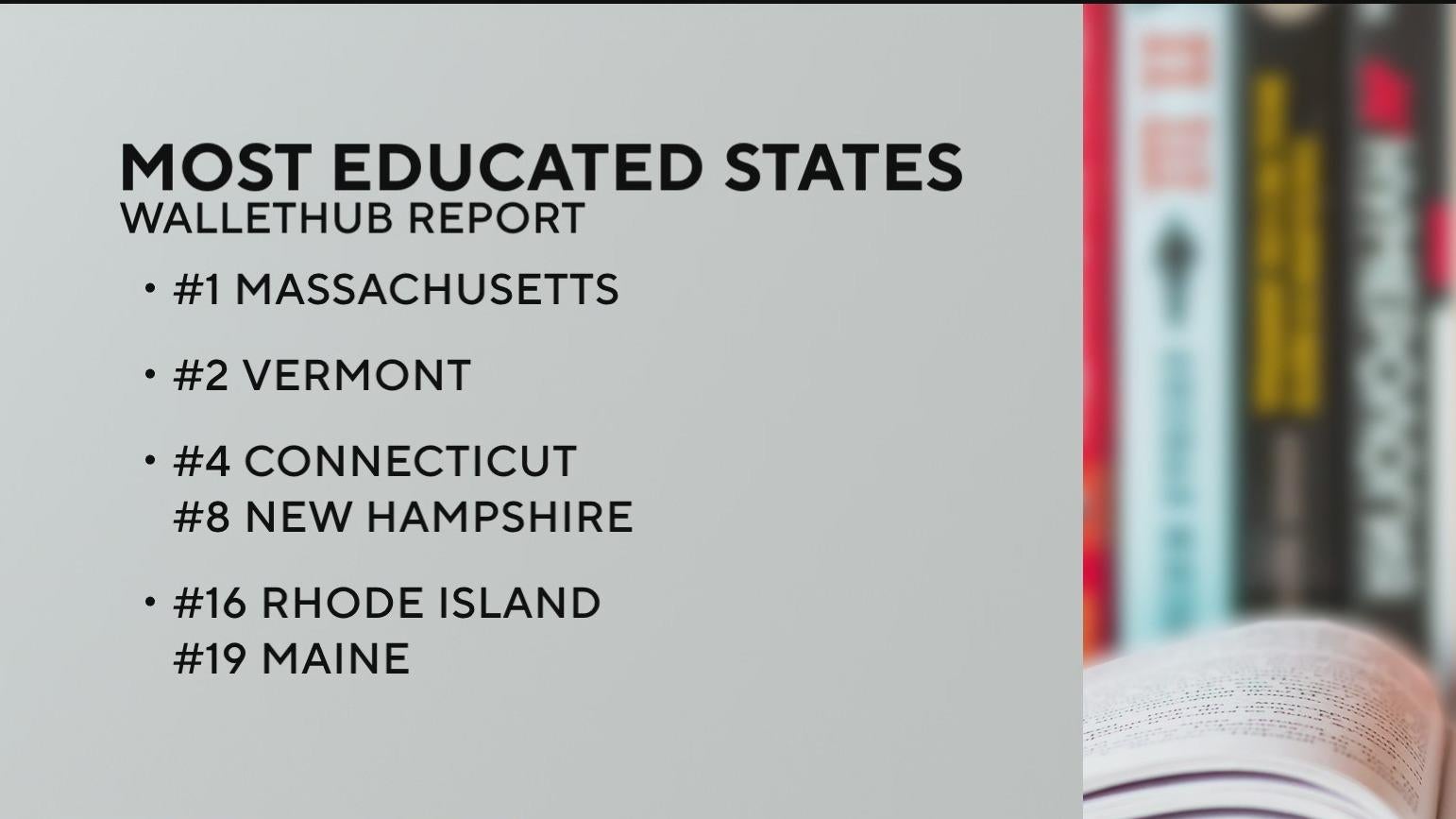
A recent national assessment by WalletHub has ranked the Massachusetts school system as the best in the United States. This achievement reflects the state’s significant progress toward fulfilling Sustainable Development Goal 4 (Quality Education), which aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
- The ranking was based on 32 metrics, highlighting the state’s commitment to comprehensive educational excellence.
- Dr. Patrick Tutwiler, Secretary of Education, affirmed the state’s dedication to providing high-quality education for every student, “regardless of circumstance and zip code,” a core principle of SDG 4.
- Elementary and Secondary Education Commissioner Pedro Martinez attributed the success to dedicated educators and a “steadfast commitment to investing in schools.”
Key Performance Indicators and SDG 4 Targets
Massachusetts’ top ranking is supported by several key performance indicators that align directly with specific targets of SDG 4.
- Excellence in Core Academics (Target 4.6): The state demonstrated nation-leading math and reading scores, directly contributing to the goal of achieving literacy and numeracy for all youth.
- Advanced Achievement and Skills for Employment (Target 4.4): A top share of students achieved high scores (three or higher) on Advanced Placement (AP) exams, indicating readiness for higher education and skilled employment.
- Safe and Inclusive Learning Environments (Target 4.a): The state received high marks for school safety, a crucial component for building and upgrading education facilities to be child, disability, and gender-sensitive.
Strategic Investments in Education and Broader SDG Impact
The state has implemented strategic financial commitments and programs that not only bolster SDG 4 but also contribute to other interconnected goals.
- Contribution to SDG 2 (Zero Hunger): A key initiative has been making universal school meals permanent, directly addressing Target 2.1 by ensuring all students have access to sufficient and nutritious food, which is fundamental for effective learning.
- Fostering Skills for Decent Work (SDG 4, Target 4.4): An investment of $100 million is being directed to expand Career Technical Education (CTE) programs. This includes the creation of 34 new early college partnerships, designed to place students on an accelerated path to career success.
- Ensuring Inclusive and Equitable Access (SDG 4, Target 4.5 & SDG 10): The FY 2026 budget demonstrates a strong commitment to reducing inequalities through targeted funding:
- $7.36 billion for local education aid.
- $675 million for special education, ensuring support for students with disabilities.
- $140.6 million for school transportation, addressing access barriers.
- Strengthening Institutions (SDG 16): These substantial and transparent budgetary allocations reflect the development of effective, accountable, and strong public institutions dedicated to education.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
The article on Massachusetts’ top-ranking school system addresses several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through its focus on educational quality, equity, student well-being, and preparation for future employment.
-
SDG 4: Quality Education
This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The entire text revolves around the state’s achievements in providing high-quality education, as evidenced by its number one national ranking. The article mentions specific achievements like “nation-leading math and reading scores,” investments in “record K-12 education funding,” and strategies for “early literacy,” all of which are central to SDG 4.
-
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
The article connects to this goal through the mention of a specific policy initiative. The statement that the state is working on making “universal school meals permanent” directly addresses food security for students, ensuring they have the nutrition needed to learn effectively.
-
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
The commitment to equity in education is a recurring theme. The Secretary of Education’s quote, “every student deserves a high-quality education – regardless of circumstance and zip code,” explicitly targets the reduction of inequalities. Furthermore, the specific budget allocation for “special education” shows a concrete effort to support vulnerable student populations.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The article touches upon this goal by highlighting programs designed to prepare students for the workforce. The investment of “$100 million to expand Career Technical Education programs” and the creation of “34 new early college partnerships to put students on a fast track to success” are direct efforts to equip youth with relevant skills for future employment and economic productivity.
Specific Targets Identified
Based on the article’s content, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
-
Target 4.1: Ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education.
The article’s focus on the state’s K-12 public school system, its “record K-12 education funding,” and its top ranking based on “math and reading scores” all point to efforts to achieve high-quality primary and secondary education for all students.
-
Target 4.4: Substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment.
This target is directly addressed by the state’s “$100 million” investment to “expand Career Technical Education programs” and the establishment of “early college partnerships,” which are designed to provide students with practical, job-relevant skills.
-
Target 4.5: Eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access to all levels of education and vocational training for the vulnerable.
The principle of this target is reflected in the Secretary of Education’s statement about providing education “regardless of circumstance and zip code” and the specific allocation of “$675 million for special education,” which aims to ensure equal access for students with disabilities.
-
Target 4.a: Build and upgrade education facilities… and provide safe, non-violent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all.
The article explicitly mentions that “High marks in school safety were also noted” as part of the 32 metrics used for the ranking, showing a clear focus on creating safe learning environments.
-
Target 2.1: End hunger and ensure access by all people… to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round.
The initiative to make “universal school meals permanent” is a direct action toward this target, aiming to ensure that all students have access to sufficient food through the school system.
Indicators Mentioned or Implied
The article provides several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
-
Indicator for Target 4.1 (Quality of Primary and Secondary Education):
The article explicitly mentions “nation-leading math and reading scores” and the “top share of students receiving a score of three or higher on an AP exam.” These are direct performance indicators of learning outcomes.
-
Indicator for Target 4.4 (Skills for Employment):
A financial input indicator is the “$100 million” invested to expand CTE. A process indicator is the creation of “34 new early college partnerships.”
-
Indicator for Target 4.5 (Equal Access):
A key financial indicator is the budget allocation of “$675 million for special education.” The policy commitment to serve students “regardless of circumstance and zip code” is a qualitative policy indicator.
-
Indicator for Target 4.a (Safe Learning Environments):
The article provides a qualitative performance indicator by stating the state received “High marks in school safety.”
-
Indicator for Target 2.1 (End Hunger):
The implementation of “permanent universal school meals” serves as a policy indicator of the state’s commitment to ensuring students are fed.
-
General Financial Indicators:
The article provides several financial input indicators, including “$7.36 billion for local education aid” and “$140.6 million for school transportation,” which demonstrate the overall investment in the education system.
SDGs, Targets, and Indicators Analysis
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education | 4.1: Ensure quality primary and secondary education. | – Nation-leading math and reading scores. – Top share of students with a score of 3+ on an AP exam. – $7.36 billion in local education aid. |
| 4.2: Ensure access to quality early childhood development and pre-primary education. | – Implementation of a “nation-leading early literacy strategy.” | |
| 4.4: Increase the number of youth with relevant skills for employment. | – $100 million investment to expand Career Technical Education programs. – Creation of 34 new early college partnerships. |
|
| 4.5: Ensure equal access for the vulnerable. | – Policy of providing education “regardless of circumstance and zip code.” – $675 million allocated for special education. |
|
| 4.a: Build and upgrade education facilities to be safe and inclusive. | – “High marks in school safety” in national ranking. | |
| SDG 2: Zero Hunger | 2.1: End hunger and ensure access to food. | – Policy to make “universal school meals permanent.” |
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | 10.2 / 10.3: Promote social inclusion and ensure equal opportunity. | – Commitment to education “regardless of circumstance and zip code.” – Financial allocation for special education ($675 million). |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.6: Reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education or training. | – Investment in Career Technical Education and early college partnerships to prepare students for the workforce. |
Source: capecod.com