Report on the Energy Management System Market and its Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals
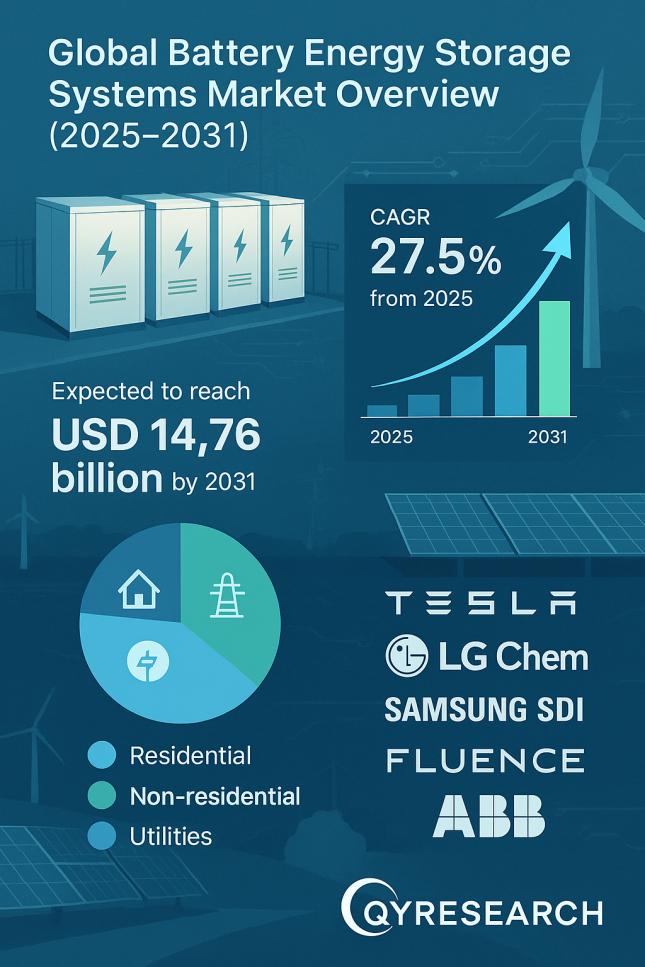
A recent analysis of the global Energy Management System (EMS) market indicates substantial growth, driven by a global imperative to enhance energy efficiency and advance sustainability. The market is projected to expand from an estimated value of USD 49.65 billion in 2025 to USD 139.48 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.9%. This expansion is intrinsically linked to the pursuit of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The growth of the EMS market is a direct enabler for achieving several key SDGs. These systems provide the technological foundation for monitoring, controlling, and conserving energy, which is critical for sustainable development.
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
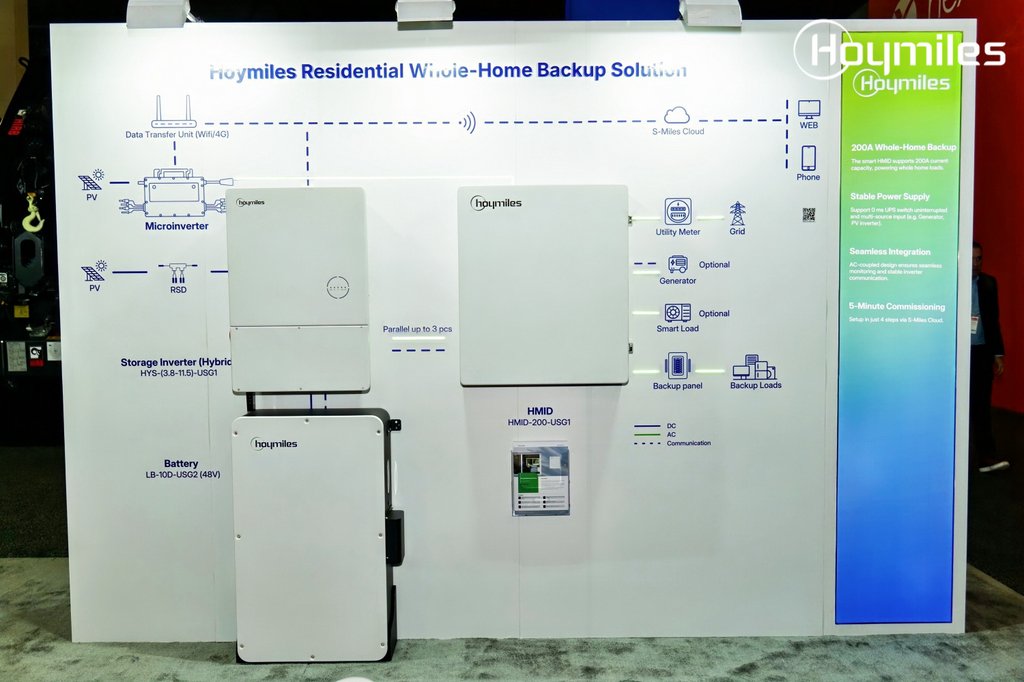
EMS technologies are fundamental to achieving SDG 7. By optimizing energy consumption in industrial, commercial, and residential sectors, these systems reduce overall energy costs, making energy more affordable. Furthermore, they facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid by managing fluctuations in supply and demand, thereby promoting the transition to cleaner energy.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The adoption of EMS represents a significant innovation in industrial processes and infrastructure. It supports the goal of building resilient infrastructure and fostering sustainable industrialization by enabling industries to drastically improve their energy efficiency, reduce their operational footprint, and modernize their facilities in line with sustainable practices.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
EMS are a cornerstone of smart city development. They are integral to building automation and smart grid infrastructure, which help manage energy use across urban areas. This leads to more efficient public services, reduced pollution, and the creation of more sustainable, resilient, and inclusive urban environments.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
This goal is directly addressed by the core function of an EMS, which is to ensure the efficient use of resources. By providing detailed data and control over energy usage, these systems empower organizations to minimize waste and adopt sustainable consumption and production patterns, decoupling economic growth from environmental degradation.
SDG 13: Climate Action
By significantly reducing energy consumption and waste, EMS plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change. Lower energy demand translates directly to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel-based power generation. The widespread implementation of EMS is a critical strategy for nations and corporations to meet their climate action targets.
Market Segmentation Analysis
The market is segmented based on deployment models and the industry verticals they serve, with each segment contributing to sustainability objectives.
By Deployment Model
- Cloud-Based: Offers scalability and accessibility, allowing a broader range of organizations to adopt energy management practices without significant upfront infrastructure investment.
- On-premise: Provides robust, secure control for large-scale industrial and critical infrastructure applications, ensuring high levels of efficiency and reliability.
By Industry Vertical
The application of EMS across various sectors highlights its versatile role in promoting sustainability:
- Power and Energy: Optimizing grid stability and efficiency, supporting the integration of renewables (SDG 7, SDG 13).
- Building Automation: Creating smart, energy-efficient buildings for sustainable cities (SDG 11).
- Manufacturing: Reducing the carbon footprint and resource intensity of industrial production (SDG 9, SDG 12).
- Oil & Gas: Improving operational efficiency and minimizing the environmental impact of extraction and processing.
- Automotive: Enhancing energy efficiency in production facilities and supporting the infrastructure for electric vehicles.
- Pharmaceutical: Ensuring energy-efficient and stable environments for sensitive manufacturing processes.
- Others (Food & Beverages, Government): Driving energy efficiency across diverse public and private sector operations.
Competitive Landscape
The market is characterized by the presence of major technology and industrial corporations that are pivotal in developing and deploying the solutions necessary to meet global energy and climate goals. Key players include:
- Schneider Electric SE
- Asea Brown Boveri (ABB) Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation PLC
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- CA Technologies
- General Electric Company
- Emerson Process Management
- Honeywell International, Inc.
- Siemens AG
- International Business Machine Corporation
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The article focuses on the Energy Management System (EMS) market. The primary purpose of an EMS is to optimize energy consumption and improve energy efficiency, which is a cornerstone of SDG 7.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
The report discusses “technological advancements” and the adoption of EMS across various industrial verticals like “Manufacturing,” “Oil & Gas,” and “Building Automation.” This directly relates to upgrading infrastructure and industries with innovative and sustainable technologies.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The inclusion of “Building Automation” as a key market vertical for EMS connects to making cities more sustainable by improving the energy efficiency of buildings, which are major energy consumers in urban areas.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Energy is a critical resource. By enabling more efficient use of energy in industrial and commercial sectors, EMS contributes directly to more sustainable patterns of consumption and production.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
Improved energy efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption, which in turn lowers greenhouse gas emissions from power generation. The growth of the EMS market is an implicit measure of climate action being taken by various industries.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 7, Target 7.3
“By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.”
- The entire article is about the market for Energy Management Systems, which are technologies designed specifically to improve energy efficiency. The projected strong market growth indicates an accelerated adoption of these systems, directly contributing to this target.
-
SDG 9, Target 9.4
“By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes…”
- The article’s market segmentation highlights the adoption of EMS in “Automotive,” “Building Automation,” “Oil & Gas,” and “Manufacturing.” This shows that industries are retrofitting their operations with these advanced technologies to increase energy (resource) efficiency.
-
SDG 11, Target 11.6
“By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities…”
- The “Building Automation” vertical mentioned in the market segmentation directly addresses the energy consumption of buildings within cities. Implementing EMS in urban infrastructure helps reduce the overall energy footprint and environmental impact of cities.
-
SDG 12, Target 12.2
“By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.”
- Energy is a fundamental natural resource. The article describes a growing market for systems whose sole purpose is the efficient management of energy, which aligns perfectly with this target.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Market Size and Growth Rate
“Energy Management System Market is estimated to be valued at USD 49.65 Bn in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 139.48 Bn in 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.9%.”
- This financial data serves as a powerful proxy indicator for the rate of adoption of energy efficiency technologies. A high CAGR suggests accelerated investment and implementation across industries, which can be used to measure progress towards Target 7.3 and 9.4.
-
Market Segmentation by Vertical
“Global Energy Management System (EMS) Market, By Vertical: Automotive, Building Automation, Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Pharmaceutical, Power and Energy, Others…”
- The breakdown of the market by industry serves as an indicator of the breadth of adoption of sustainable technologies. Tracking the growth within these specific segments can measure how different parts of the economy are contributing to upgrading infrastructure as per Target 9.4.
-
Investment in Research and Development
“This Report includes…investment in research and development, new market initiatives…”
- The article implies that investment in R&D by key players like Schneider Electric and Siemens is a crucial factor. This investment can be seen as an indicator of ongoing innovation in clean and environmentally sound technologies, relevant to Target 9.4.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | Target 7.3: Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. | The market’s compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.9% for Energy Management Systems. |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable and increase resource-use efficiency. | Market segmentation data showing adoption in verticals like Manufacturing, Oil & Gas, and Building Automation. |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. | Growth in the “Building Automation” market segment as an indicator of improved energy efficiency in urban buildings. |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | Target 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | The total market value (projected to reach USD 139.48 Bn) as a measure of investment in efficient energy management. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policies, strategies and planning. | Widespread adoption of EMS by major corporations reflects the integration of climate-friendly practices into business strategies. |
Source: openpr.com