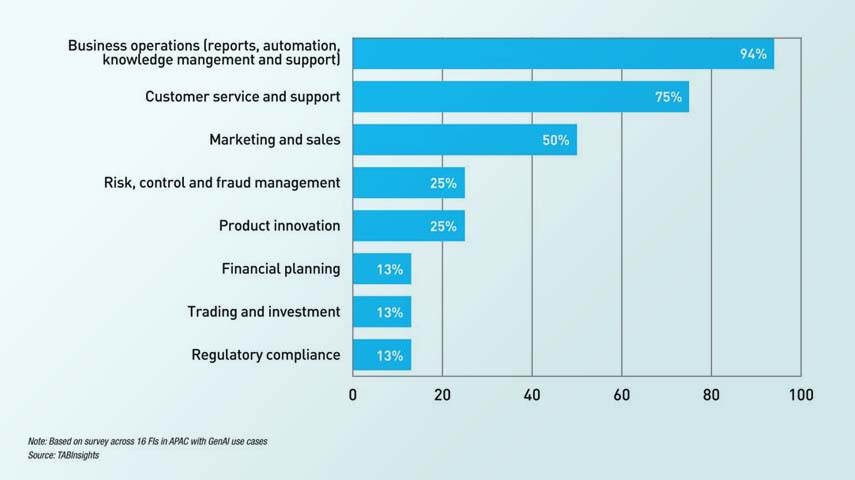
Corporate Governance and Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals
Executive Leadership and Strategic Direction
The day-to-day management of the corporation is directed by the Group President & CEO, Henrik Andersen. The executive leadership structure is designed to ensure comprehensive operational and organisational performance, which is fundamental to achieving key United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This centralized leadership is pivotal in steering the company’s strategy towards critical global objectives, primarily Sustainable Development Goal 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
The “one enterprise” philosophy promotes global alignment and the implementation of best practices, directly contributing to SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by optimizing resource use and operational efficiency across the organization.
Organisational and Regional Framework
The corporate operating model is structured around two primary dimensions: global functions and regional execution. This framework ensures both strategic coherence and localized effectiveness.
- Centralised Leadership: Direction is provided by the Group President & CEO and the Executive Management Team.
- Functional Areas: The structure is organized into six key functional areas, representing all core company disciplines and ensuring global best-practice implementation.
- Regional Divisions: A lean organisation is maintained across five strong regions, each headed by a Regional President, with offices in 30 countries to ensure focused strategy execution.
- The regional structure ensures a focused execution of corporate strategy tailored to local contexts. This approach fosters SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) by creating local employment opportunities and stimulating regional economies.
- Global functional alignment facilitates the sharing of best practices and drives innovation, which is fundamental to advancing SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) through the development of resilient and sustainable energy systems.
- This integrated operating model ensures that both global standards and regional specificities are addressed, maximising the company’s impact on the global transition to renewable energy.
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The article is from Vestas, a company that manufactures wind turbines, as shown in the image. Their core business is central to the production of clean, renewable energy, directly contributing to this goal.
-
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
The text mentions the company’s structure, including “employees,” “offices in 30 countries,” and “five strong regions.” This indicates the creation of jobs and economic activity on a global scale, which is a key aspect of SDG 8.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Vestas operates in the renewable energy industry and provides critical infrastructure (wind turbines) for a sustainable future. The article’s focus on “best practice” and achieving “‘one enterprise’ thinking across global functions” points towards innovation in operations to support this industry.
-
SDG 13: Climate Action
By producing technology that generates clean energy, Vestas directly enables climate action. The deployment of their wind turbines helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating climate change.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
The entire business model of Vestas, implied by the image and company name, is geared towards achieving this target by manufacturing and supplying wind turbines.
-
Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation.
The article’s emphasis on “operational and organisational performance” and sharing “best practice” to achieve “‘one enterprise’ thinking” aligns with the goal of improving productivity through innovative management and operational strategies.
-
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable…and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
Vestas’ products are a prime example of “clean and environmentally sound technologies” used to upgrade energy infrastructure globally.
-
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.
While not directly mentioned, Vestas provides the technological means for countries and corporations to implement their climate strategies, making the integration of such measures feasible.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article does not mention explicit quantitative indicators. However, several are implied by the nature of the company’s business and its organizational structure:
-
Implied Indicator for Target 7.2:
The existence of the company and its products (e.g., the V150 turbine in the image) implies a contribution to Indicator 7.2.1 (Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption). The number and capacity of turbines produced and installed would be a direct measure.
-
Implied Indicator for Target 8.2:
The focus on “operational and organisational performance” implies a goal of increasing productivity. This relates to Indicator 8.2.1 (Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person), to which the company’s efficiency contributes.
-
Implied Indicator for SDG 8 (General):
The mention of “employees” and “offices in 30 countries” implies the use of indicators related to job creation, such as the number of people employed by the company globally and regionally.
-
Implied Indicator for Target 9.4:
The company’s technology is designed to reduce CO2 emissions. Therefore, its impact can be measured by Indicator 9.4.1 (CO2 emission per unit of value added), specifically by calculating the emissions avoided through the use of its turbines.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from Article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | Contribution to renewable energy share (Indicator 7.2.1) through the manufacturing of wind turbines. |
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth | 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through innovation. | Focus on “operational and organisational performance” as a measure of productivity (related to Indicator 8.2.1). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and industries to be sustainable with clean technologies. | Deployment of wind turbines as a clean technology, contributing to lower CO2 emissions per unit of value added (Indicator 9.4.1). |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policies and strategies. | Providing the technology that enables the implementation of national climate strategies. |
Source: vestas.com