World Bank Intensifies Focus on Economic Inequality to Advance Sustainable Development Goals
Addressing SDG 10: A Core Component of the World Bank’s Vision
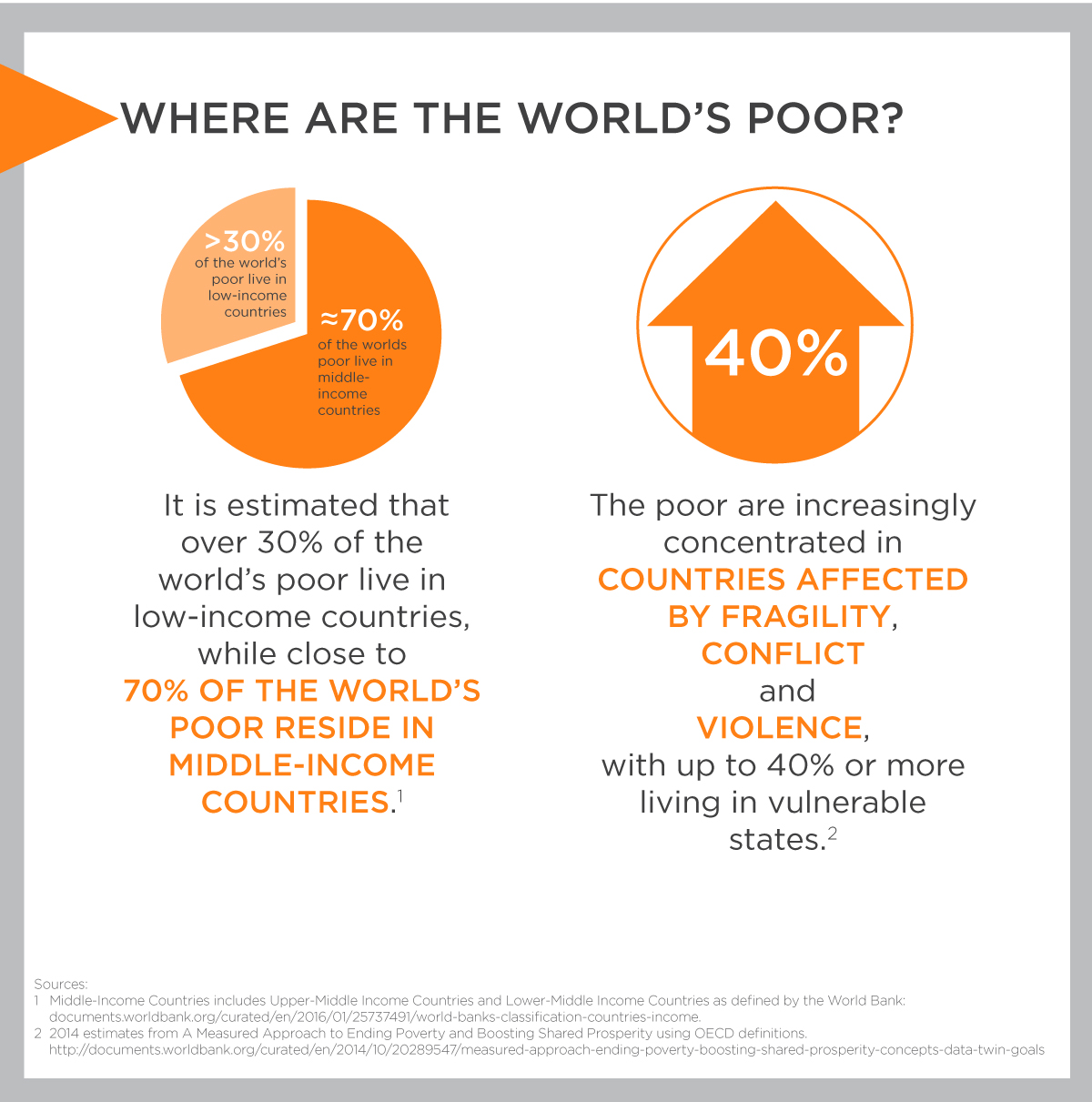
In alignment with its new vision for a world free of poverty on a livable planet, the World Bank has initiated an explicit policy to monitor global inequality. This strategic focus directly supports the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 10 (Reduced Inequalities), recognizing that high levels of inequality, affecting one in five people globally, represent a significant barrier to sustainable development. The initiative acknowledges that economic disparity can severely hinder socioeconomic mobility and impede progress toward SDG 1 (No Poverty) and the goal of shared prosperity.
Impact of Inequality on Sustainable Development
High inequality presents multifaceted challenges to the global development agenda. Key impacts include:
- Hindrance to SDG 1 (No Poverty): Systemic inequality slows the pace of poverty reduction, trapping populations in cycles of deprivation.
- Impediment to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): It curtails socioeconomic mobility, preventing equitable participation in economic growth and undermining shared prosperity.
- Threat to a Livable Planet: Disparities can exacerbate vulnerabilities to climate change and environmental degradation, working against goals for a sustainable and livable planet.
Strategic Initiatives and Policy Exploration
To address these challenges, the World Bank and its partners convened a summit in July 2025, bringing together leading experts and practitioners. The event was structured to advance the understanding and mitigation of economic inequality.
- To explore the critical nexus between economic inequality and overall development outcomes, with a direct focus on achieving the SDGs.
- To analyze the latest data and research findings to better understand the drivers and consequences of inequality.
- To identify and evaluate potential policy solutions that can effectively reduce inequality and foster inclusive growth, thereby accelerating progress on SDG 10 and related goals.
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 1: No Poverty
The article directly addresses this goal by stating the World Bank’s new vision is to “create a world free of poverty” and that high inequality can “slow progress on… poverty reduction.”
-
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
This is the central theme of the article. It opens by stating that “one in five people live in highly unequal societies” and highlights that the World Bank is now “explicitly monitoring inequality” because it can “hinder people’s socioeconomic mobility.”
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
The article mentions that “the World Bank and partners brought together leading experts and practitioners to explore how economic inequality affects development.” This collaboration to share knowledge and find policy solutions is a core component of SDG 17.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
SDG 1: No Poverty
- Target 1.2: By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions according to national definitions. The article’s focus on “poverty reduction” and creating a “world free of poverty” directly aligns with this target.
-
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- Target 10.1: By 2030, progressively achieve and sustain income growth of the bottom 40 per cent of the population at a rate higher than the national average. The article’s mention of “shared prosperity” is a direct reference to the principle behind this target.
- Target 10.2: By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all. The article’s concern that inequality can “hinder people’s socioeconomic mobility” directly relates to this target of ensuring inclusion and opportunity for everyone.
-
SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals
- Target 17.16: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge and expertise. The event where the “World Bank and partners brought together leading experts and practitioners” is a clear example of this target in action.
- Target 17.18: By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries… to increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data. The World Bank’s new initiative for “explicitly monitoring inequality” and using the “latest data and research” supports this target.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
For SDG 1 (No Poverty):
- The article implies the use of indicators that measure the proportion of the population living in poverty. The goal to “create a world free of poverty” and track “poverty reduction” necessitates such a measurement.
-
For SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities):
- The statement “one in five people live in highly unequal societies” implies an indicator that measures the level of inequality within a country, such as the Gini coefficient or income/wealth quintile ratios.
- The initiative for “explicitly monitoring inequality” and concern for “socioeconomic mobility” implies the use of indicators that track income distribution and intergenerational mobility.
- The concept of “shared prosperity” directly implies tracking Indicator 10.1.1: Growth rates of household expenditure or income per capita among the bottom 40 per cent of the population and the total population.
-
For SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals):
- The article implies an indicator related to the number and effectiveness of multi-stakeholder partnerships and knowledge-sharing platforms, as evidenced by the event held by the “World Bank and partners.”
- The mention of using the “latest data” implies an indicator measuring the availability and use of timely and reliable data for development policy.
4. Create a table with three columns titled ‘SDGs, Targets and Indicators” to present the findings from analyzing the article. In this table, list the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), their corresponding targets, and the specific indicators identified in the article.
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators (Implied from the article) |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 1: No Poverty | Target 1.2: Reduce poverty in all its dimensions. | Proportion of the population living below the national poverty line. |
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | Target 10.1: Sustain income growth of the bottom 40%. | Growth rates of income per capita among the bottom 40% of the population (related to “shared prosperity”). |
| Target 10.2: Promote social and economic inclusion. | Measures of socioeconomic mobility and levels of societal inequality (e.g., Gini coefficient). | |
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | Target 17.16: Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development. | Existence of multi-stakeholder partnerships and knowledge-sharing events. |
| Target 17.18: Enhance capacity-building for data. | Availability and use of timely and reliable data for monitoring inequality. |
Source: worldbank.org