Commercial Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Market Report: 2025-2034
Executive Summary
The global commercial solar PV market is projected for significant growth from 2025 to 2034, driven by corporate commitments to sustainability and operational cost reduction. The adoption of solar PV systems provides a reliable, long-term energy solution, directly contributing to the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 13 (Climate Action). Technological advancements and a global shift towards sustainable energy for commercial and industrial use are primary catalysts for market expansion. This report analyzes market dynamics, key trends, and regional growth, with a focus on the market’s role in achieving global sustainability targets.
Market Analysis and Sustainable Development Goals
The expansion of the commercial solar PV market is intrinsically linked to the advancement of several SDGs. By providing clean energy, the market is a key enabler of SDG 7, while its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions directly supports SDG 13. Furthermore, innovations within the sector contribute to SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), and the deployment of solar technologies in urban environments aids in the development of SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
Market Dynamics
- Drivers: Stringent environmental regulations and government incentives are compelling businesses to adopt renewable energy sources. Policies such as tax exemptions and renewable purchase obligations align with national commitments to SDG 13. Solar power offers businesses energy self-sufficiency, enhancing resilience against grid disruptions and contributing to the reliable infrastructure goals of SDG 9.
- Restraints: Challenges include high initial investment costs, grid connection complexities, and the intermittent nature of solar power. These hurdles impede the universal achievement of SDG 7, highlighting the need for innovation in energy storage solutions and grid infrastructure to ensure a consistent supply of clean energy.
- Opportunities: The market presents a significant opportunity for businesses to achieve substantial cost savings and energy independence. On-site electricity generation reduces reliance on fluctuating grid prices and enhances corporate reputation by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability. This aligns with creating sustainable economic models and supports SDG 11 by making commercial infrastructure more resilient and environmentally friendly.
Key Market Trends and Technological Innovation
Technological advancements are crucial for enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of solar energy, directly supporting SDG 9.
- Advanced Panel Technology: The adoption of high-efficiency panels, such as bifacial and n-type silicon cells (TOPCon and heterojunction), is a notable trend. These technologies maximize energy output from a given area, a critical factor for urban installations and advancing the goals of SDG 11.
- System Intelligence and Energy Storage: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and battery storage systems is transforming the market. AI optimizes panel placement and predictive maintenance, while energy storage ensures a continuous power supply. These innovations are vital for building reliable and resilient clean energy systems as envisioned in SDG 7 and SDG 9.
Market Segmentation Analysis
System Type Insights
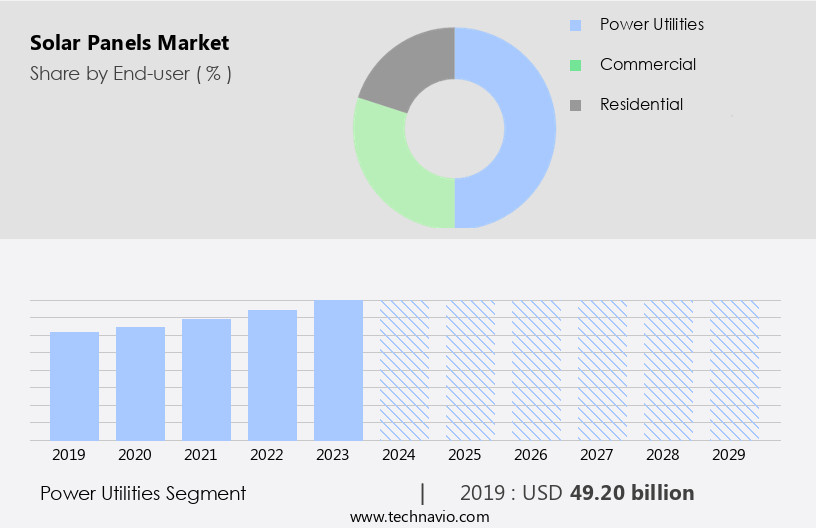
- Grid-Tied PV Systems: This segment dominated the market in 2024 due to its cost-effectiveness and reliability. By allowing businesses to feed surplus energy back into the grid, these systems promote an integrated and efficient energy infrastructure, supporting SDG 9.
- Hybrid PV Systems: This segment is projected to be the fastest-growing. By combining solar PV with battery storage, hybrid systems provide energy security during grid outages, a critical component for reliable access to clean energy under SDG 7.
Component Insights
- Solar Modules: Holding the largest market share in 2024, the affordability and increasing efficiency of solar modules are key growth drivers. Continuous innovation in module technology makes clean energy more accessible to a wider range of commercial enterprises.
- Energy Storage Solutions: This segment is expected to witness the fastest growth. Advancements in battery technology are making energy storage more economically viable, which is essential for overcoming the intermittency of solar power and ensuring the reliability required by SDG 7.
Technology Insights
- Crystalline Silicon PV: This technology held the largest market share in 2024, owing to its proven reliability, durability, and the abundance of silicon. Its non-toxic nature aligns with broader environmental protection goals central to the SDG framework.
- Perovskite Solar PV: As the fastest-growing segment, perovskite technology offers lightweight, flexible solar cells suitable for diverse applications, including building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). Its lower carbon footprint contributes directly to sustainability goals and SDG 13.
Deployment Type Insights
- Rooftop Solar PV: The leading segment in 2024, rooftop installations utilize existing infrastructure to generate clean energy, making them a highly efficient solution for commercial facilities. This practice is fundamental to building sustainable cities and communities (SDG 11).
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Expected to be the fastest-growing segment, BIPV integrates solar technology directly into building materials. This approach supports sustainable architectural design and reduces the carbon footprint of buildings, aligning with SDG 11 and SDG 13.
Application Insights
- Office Buildings & Corporate Campuses: This segment was the largest market contributor in 2024. Adopting solar PV allows corporations to reduce operational costs, achieve predictable energy expenses, and meet their corporate social responsibility targets related to SDG 7 and SDG 13.
- Manufacturing Facilities & Industrial Units: Projected to be the fastest-growing segment, solar energy provides an affordable and reliable power source for energy-intensive industrial operations, helping the manufacturing sector reduce its carbon footprint and align with climate action goals (SDG 13).
Regional Market Outlook
Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region dominated the global market in 2024, driven by strong government policies aimed at achieving climate goals (SDG 13) and ensuring energy security (SDG 7). Countries like China, India, and Japan are leading the adoption of solar energy through substantial investments in manufacturing, research, and deployment incentives, positioning the region as a critical player in the global transition to renewable energy.
Middle East & Africa
This region is forecast to experience the fastest growth. Abundant solar resources, combined with government support for renewable energy targets and growing demand for sustainable power, are driving market expansion. The adoption of solar PV is crucial for the region’s economic diversification and supports rapid urbanization and industrial growth in a sustainable manner, contributing to SDG 7 and SDG 9.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Commercial Solar PV Market
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article on the commercial solar PV market directly and indirectly addresses several Sustainable Development Goals by focusing on the global shift towards renewable energy, technological innovation, and sustainable industrial practices.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: This is the most prominent SDG in the article. The entire text revolves around the growth of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, which are a key source of clean and increasingly affordable energy for commercial and industrial users. The article highlights how solar energy provides “reliable, clean, and long-term energy solutions.”
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article discusses significant innovation and technological advancements within the solar industry. It mentions “increasing research and development on solar energy,” the use of AI and machine learning for optimization, and the development of new technologies like “perovskite solar PV” and “bifacial panels.” This aligns with building resilient infrastructure and fostering sustainable industrialization.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: The article’s focus on applications like “rooftop solar PV,” “building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV),” and installations on “office buildings,” “shopping malls,” and “corporate campuses” directly relates to making cities more sustainable. These technologies help reduce the environmental footprint of urban infrastructure.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: By promoting a shift from traditional grid electricity (often generated from fossil fuels) to on-site solar power generation, the article supports sustainable consumption and production patterns. It notes that solar PV helps businesses “minimize dependency on fossil fuels” and achieve energy independence.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The article explicitly links the growth of the solar PV market to climate action. It states that the market is driven by “corporate sustainability goals” and government policies designed to “fulfill climate goals.” It also mentions how countries like China, Japan, and India are focusing on the “reduction of greenhouse gas emissions” through the adoption of solar energy.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the issues discussed, several specific SDG targets can be identified:
-
Target 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
The article’s central theme is the growing market for commercial solar PV, a renewable energy source. It details the expansion across various regions, stating, “Asia Pacific dominated the global commercial solar PV market in 2024,” and highlights the increasing adoption by commercial and industrial sectors to replace or supplement traditional energy sources. -
Target 7.a: Enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in clean energy technology.
The article points to global R&D efforts, such as the development of “perovskite solar cells” by a Chinese manufacturer and the introduction of new “N-type panel design” modules in the U.S. This, along with “substantial investment into R&D for renewable energy sources” in countries like China, reflects progress toward this target. -
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
The article describes how “manufacturing facilities and industrial units” are adopting solar PV to reduce energy costs and align with “carbon reduction aims.” The use of technologies like building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) and rooftop solar on commercial buildings represents the upgrading of infrastructure for sustainability. -
Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities.
The deployment of “rooftop solar PV” and “building-integrated photovoltaics” on urban structures like “office buildings,” “shopping malls,” and “hospitals” directly contributes to this target by generating clean energy at the point of consumption, thereby reducing the city’s overall reliance on centralized, often polluting, power plants. -
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning.
The article provides clear examples of this target in action. It mentions “strong government policies, incentives to fulfill climate goals,” and specific examples like “India’s National Solar Mission” and Japan’s investment in solar to support its “greenhouse gas reduction initiatives.” These are direct instances of national strategies promoting climate action.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
The article contains several quantitative and qualitative points that can serve as indicators for measuring progress towards the identified SDG targets.
- Indicator for Target 7.2 (Renewable energy share): The “Commercial Solar PV Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034” is a direct indicator of the growing share of solar energy. The article also provides regional market data, noting that “Asia Pacific held the largest market share in 2024” and “The Middle East & Africa is expected to witness the fastest CAGR,” which can be used to track the renewable energy share by region.
- Indicator for Target 7.3 (Energy efficiency): The article mentions specific improvements in solar panel efficiency. For example, it refers to a new module with “22.8% efficiency” and discusses how innovations in “n-type silicon cells such as TOPCon and heterojunction” provide better longevity and efficiency compared to older technology. The use of AI for “predictive maintenance to increase efficiency” is another implied measure of progress.
- Indicator for Target 9.4 (Adoption of clean technologies in industry): The growth rate of specific application segments serves as a clear indicator. The article states that the “manufacturing facilities & industrial units segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR,” which directly measures the rate of adoption of clean solar technology by industries.
- Indicator for Target 11.6 (Reducing environmental impact of cities): The market share of different deployment types is an implied indicator. The article notes that the “rooftop solar PV segment led the market in 2024,” and the “building-integrated photovoltaics segment is expected to witness the fastest CAGR.” Tracking these segments’ growth indicates how much urban infrastructure is being adapted for clean energy generation.
- Indicator for Target 13.2 (Integration of climate policies): The article provides concrete examples of national policies that serve as an indicator. The mention of “India’s National Solar Mission,” “financial subsidies,” “tax credits,” and “renewable purchase obligation” regulations are qualitative indicators that climate change measures are being integrated into national planning.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. | Market size and forecast for commercial solar PV (2025-2034); Regional market share and CAGR (e.g., Asia Pacific dominance, MEA fastest growth). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. | CAGR of the manufacturing facilities and industrial units segment; Adoption of new technologies like perovskite solar PV and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities. | Market share and growth of the rooftop solar PV segment and the building-integrated photovoltaics segment in urban applications (office buildings, malls, hospitals). |
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.2: Achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources. | The shift of commercial entities from grid electricity to on-site solar generation, minimizing dependence on fossil fuels. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning. | Mention of specific government policies and initiatives such as “India’s National Solar Mission,” “tax credits,” “subsidies,” and national “greenhouse gas reduction initiatives” in Japan and China. |
Source: precedenceresearch.com