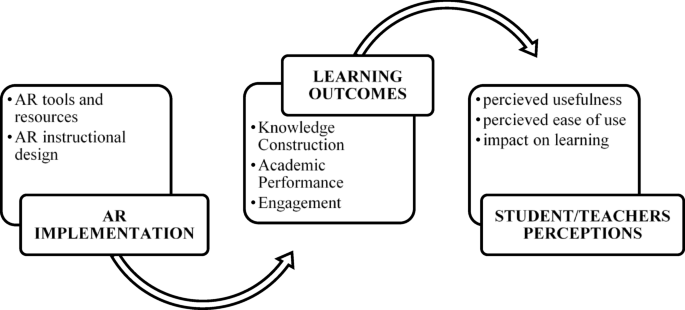
Executive Summary: Augmented Reality’s Role in Advancing Sustainable Development Goal 4
This report details an investigation into the perceptions of students and teachers regarding the use of Augmented Reality (AR) in educational settings. It evaluates the technology’s impact on student cognition and academic performance, aligning the findings with the objectives of Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), which aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education. Utilizing a mixed-methodology with 88 participants, the study gathered data on the efficacy of AR as a pedagogical tool. The findings indicate that AR significantly enhances the learning experience and contributes to positive academic outcomes, positioning it as a key technology for building effective learning environments as outlined in SDG Target 4.a. While both students and teachers identified certain implementation challenges, the overall conclusion supports the strategic integration of AR to advance global educational standards and promote lifelong learning opportunities.
Introduction: Aligning Educational Technology with Sustainable Development Goals
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) into educational frameworks represents a significant step towards achieving SDG 4. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, AR has the potential to revolutionize traditional teaching methods and create inclusive, effective learning environments. This technological advancement directly supports the global commitment to enhancing educational quality and accessibility. As institutions increasingly adopt innovative technologies, it is crucial to assess their alignment with sustainable development principles, particularly their capacity to improve learning outcomes for all. This report examines the perspectives of educators and learners on AR’s utility and effectiveness, addressing a critical gap in research concerning its practical impact on academic achievement and its role in fostering the skills necessary for sustainable development.
Literature Review: AR’s Role in Achieving SDG 4 – Quality Education
An expanding body of research investigates AR’s potential to improve educational outcomes, directly contributing to the targets of SDG 4. The literature suggests that AR offers substantial benefits by creating dynamic and engaging learning environments.
Enhancing Learning Environments (SDG Target 4.a)
Studies consistently show that AR enhances student engagement and motivation, which are foundational to quality education. By transforming abstract concepts into tangible, interactive experiences, AR facilitates deeper comprehension and knowledge retention, particularly in STEM fields. This aligns with SDG Target 4.a, which calls for building and upgrading education facilities that are child, disability, and gender-sensitive and provide safe, non-violent, inclusive, and effective learning environments for all.
Stakeholder Perceptions and Inclusivity (SDG 4 & SDG 10)
The successful integration of AR is contingent on the perceptions of its primary users: teachers and students.
- Teacher Perspectives: While many educators recognize AR’s potential, adoption is often hindered by a lack of technical training and resources. To achieve SDG 4, it is imperative to provide teachers with professional development opportunities that empower them to effectively utilize innovative technologies.
- Student Perspectives: Students generally respond positively to AR, reporting increased engagement and satisfaction. However, careful design is required to manage cognitive load and prevent distraction, ensuring the technology is an effective and equitable learning tool for diverse student populations, thereby supporting SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities).
Identifying Gaps in Sustainable Implementation
Current research has several limitations regarding the sustainable and equitable implementation of AR. There is a notable lack of longitudinal studies assessing the long-term impact on learning. Furthermore, more investigation is needed into the specific challenges teachers face and how AR affects diverse student demographics. Addressing these gaps is essential for developing strategies that ensure AR technology contributes effectively and equitably to achieving quality education for all.
Methodology for Assessing AR’s Contribution to Sustainable Education
A mixed-methods research design was employed to provide a comprehensive evaluation of AR’s impact on educational outcomes, in line with the evidence-based approach required to monitor progress towards SDG 4.
Research Design
The study combined quantitative and qualitative methods to triangulate data, enhancing the validity of the findings.
- Quantitative Component: Pre-test and post-test evaluations were conducted to measure changes in academic performance, providing empirical data on AR’s effectiveness.
- Qualitative Component: Semi-structured interviews and focus groups were used to gather in-depth insights into the subjective experiences of teachers and students, exploring perceptions of AR’s role in the learning process.
Participant Profile
The study involved 88 participants, comprising 84 undergraduate students and 4 teachers from two universities with prior experience using AR in educational programs. A stratified purposive sampling strategy was used to ensure a diverse range of experiences was captured, reflecting the need for inclusive educational solutions as championed by the SDGs.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data was collected through standardized exams and semi-structured interviews. Quantitative data were analyzed using paired sample t-tests in SPSS to identify statistically significant differences in learning outcomes. Qualitative data from interviews and focus groups underwent thematic analysis to identify recurring themes related to user experience, perceived usefulness, and implementation challenges.
Findings: Empirical Evidence of AR’s Impact on Educational Goals
The analysis yielded significant findings regarding AR’s impact on learning outcomes and stakeholder perceptions, providing strong evidence of its potential to support the achievement of SDG 4.
Quantitative Impact on Learning Outcomes (SDG 4)
The quantitative results demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in academic performance for the experimental group using AR compared to the control group.
- The t-test for post-test results showed a significant difference between the groups (t(84) = 5.14, p < 0.001).
- The analysis of improvement scores further confirmed that the AR intervention led to substantially greater learning gains (t(84) = 4.73, p < 0.001).
These findings indicate that AR is an effective tool for enhancing educational achievement, a core objective of SDG 4.
Student Perceptions: Engagement and Collaborative Learning (SDG 4)
Thematic analysis of student feedback revealed three primary themes:
- Engagement and Enjoyment: Students found AR-based lessons to be highly engaging and enjoyable, which fostered active participation and motivation.
- Cognitive Load: An initial challenge for some students was the cognitive load associated with a new technology, though this diminished with familiarity. This highlights the need for structured implementation to ensure technology is an aid, not a barrier, to learning.
- Collaborative Learning: AR was found to enhance teamwork and group discussions, promoting the development of collaborative problem-solving skills essential for 21st-century learners.
Teacher Perceptions: Usefulness and Instructional Impact (SDG 4)
Analysis of teacher interviews identified three key themes:
- Perceived Usefulness: Teachers perceived AR as highly useful for visualizing abstract concepts and improving student comprehension and information retention.
- Ease of Use: After an initial learning period, teachers found the AR tools to be user-friendly, though they emphasized the need for initial technical support and training.
- Instructional Impact: Educators reported a clear positive impact on instructional delivery and student performance, reinforcing the quantitative findings.
Discussion: AR as a Catalyst for Quality Education (SDG 4) and Innovation (SDG 9)
The study’s findings confirm that AR can serve as a powerful catalyst for achieving SDG 4 by enhancing academic performance and student engagement. This aligns with SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), which encourages the development and adoption of innovative technologies to support sustainable development.
Enhanced Engagement and Deeper Learning
The high levels of engagement and enjoyment reported by students correlate directly with improved learning outcomes. This supports the constructivist learning theory, where active, immersive experiences lead to deeper understanding. By making learning more interactive, AR helps create the effective learning environments envisioned in SDG Target 4.a.
Addressing Cognitive Load and Ensuring Accessibility (SDG 10)
The initial cognitive load experienced by students underscores the importance of thoughtful pedagogical design. To ensure AR promotes equitable education and reduces inequalities (SDG 10), implementation must include proper scaffolding and support. This ensures that all learners, regardless of their technical proficiency, can benefit from the technology.
Fostering Collaborative and Inclusive Learning Environments
The theme of collaborative learning demonstrates AR’s potential to foster social interaction and peer-to-peer support, key components of an inclusive educational model. By facilitating shared experiences, AR can help build a cooperative classroom culture that aligns with the principles of inclusive education central to SDG 4.
Conclusion and Policy Implications for Sustainable Educational Development
Summary of Findings
This report provides compelling evidence that Augmented Reality, when implemented effectively, significantly improves student learning outcomes and engagement. The findings from both quantitative and qualitative data confirm that AR can transform traditional classrooms into dynamic, interactive, and effective learning spaces, thereby making a direct contribution to the ambitions of SDG 4.
Policy Recommendations for Integrating Technology in Education (SDG 4 & SDG 9)
To leverage AR for sustainable educational development, the following actions are recommended:
- Curriculum Integration: Educational institutions should strategically integrate AR into curriculum design to enrich learning, particularly for complex subjects.
- Teacher Training: Policymakers must invest in comprehensive professional development programs to equip educators with the skills to use AR effectively. This is crucial for the sustainable adoption of educational technologies.
- Infrastructure Investment: Governments and educational bodies should allocate resources to build the necessary technological infrastructure, ensuring equitable access to AR tools for all students and supporting SDG 9.
Future Research Directions
To ensure the long-term, equitable impact of AR in education, future research should focus on:
- Longitudinal Studies: Investigating the sustained impact of AR on knowledge retention and student engagement over time.
- Cross-Disciplinary Customization: Examining how AR can be tailored to meet the unique needs of different academic disciplines.
- Equity and Accessibility: Conducting further studies on AR’s impact across diverse student demographics to develop inclusive implementation strategies that leave no one behind.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article primarily addresses issues related to two Sustainable Development Goals:
- SDG 4: Quality Education: The entire study is centered on improving the quality of education. It investigates how a new technology, Augmented Reality (AR), can “revolutionize traditional teaching methods and improve students’ academic achievements.” The research focuses on enhancing learning experiences, student engagement, academic performance, and creating more dynamic and effective learning environments, all of which are core components of SDG 4.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The article explores the application of a specific technological innovation (AR) within the educational sector. It discusses the practical challenges of implementing this technology, such as “technology accessibility,” the need for “teacher training,” and the infrastructure required to support AR in classrooms. This aligns with SDG 9’s focus on fostering innovation and developing reliable and sustainable infrastructure, including information and communications technology (ICT).
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s discussion, several specific targets under SDG 4 and SDG 9 can be identified:
-
Under SDG 4: Quality Education
-
Target 4.1: By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and effective learning outcomes.
Explanation: Although the study is at the university level, its primary research question is, “How does using Augmented Reality (AR) in the classroom impact students’ learning outcomes compared to traditional instructional methods?” The study directly measures and confirms that AR leads to “a significant improvement in learning outcomes,” which is the central theme of this target. -
Target 4.4: By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship.
Explanation: The article discusses the need for both students and teachers to adapt to new technologies. It highlights challenges like “insufficient technical training” for teachers, implying the necessity of developing technical skills to effectively use tools like AR. Successfully integrating AR into education equips students with experience in using advanced digital tools, which is a relevant skill for the modern workforce. -
Target 4.a: Build and upgrade education facilities that are child, disability and gender sensitive and provide safe, non-violent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all.
Explanation: The research explores how AR can create more “effective learning environments.” The qualitative findings show that AR leads to “highly dynamic and enjoyable” sessions, fosters “collaborative learning,” and enhances “student engagement.” These elements contribute directly to creating a more effective and inclusive learning environment. -
Target 4.c: By 2030, substantially increase the supply of qualified teachers, including through international cooperation for teacher training in developing countries, especially least developed countries and small island developing States.
Explanation: The article identifies a major barrier to AR adoption as the “inadequate availability of professional development opportunities for instructors.” It suggests that to overcome implementation challenges, it is crucial to build “focused professional development programs that specifically target these obstacles.” This directly addresses the need to increase the supply of qualified teachers who are proficient in modern educational technologies.
-
Target 4.1: By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and effective learning outcomes.
-
Under SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all.
Explanation: The article points to “technology accessibility” as a critical factor in implementing AR. The successful use of AR in the study was possible because the participating universities had the necessary technological infrastructure. The implications section calls for policymakers to prioritize “the allocation of financing and resources to embrace and utilize augmented reality (AR) technologies in educational institutions,” which relates to building this infrastructure. -
Target 9.c: Significantly increase access to information and communications technology and strive to provide universal and affordable access to the Internet in least developed countries.
Explanation: The study’s focus on integrating AR, an advanced form of Information and Communications Technology (ICT), into education directly relates to this target. By demonstrating the benefits of AR, the article makes a case for increasing access to such technologies in educational settings to improve learning outcomes.
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article mentions or implies several quantitative and qualitative indicators that can measure progress:
- Student Academic Performance: The study uses quantitative data from pre- and post-tests to measure the impact on learning outcomes. As stated in the findings, “The post-test findings demonstrate a statistically significant disparity between the experimental and control groups (t (84) = 5.14, p < 0.001)." These test scores serve as a direct indicator for Target 4.1.
- Student Engagement and Perceptions: The qualitative analysis of student feedback provides indicators for an effective learning environment (Target 4.a). Themes like “Engagement and Enjoyment” and “Collaborative Learning,” derived from student interviews, measure the quality of the educational experience. For example, one student commented, “Normally, I will not talk during lessons, but this gadget made me interact more during lessons. D42.”
- Teacher Proficiency and Training: The article implies the need for indicators related to teacher skills (Target 4.4 and 4.c). The challenges mentioned, such as “insufficient technical training” and the initial difficulty teachers faced (“It was not easy to use before…”), suggest that the number of teachers receiving professional development in AR and their perceived “ease of use” are crucial progress indicators.
- Technology Accessibility and Infrastructure: The article highlights “technology accessibility” as a key factor for implementing AR (Targets 9.1 and 9.c). An implied indicator is the availability of AR devices and supporting infrastructure within educational institutions. The study’s selection criteria, which required participants to be from universities that “used augmented reality (AR) in their educational programs for three years,” points to the presence of this infrastructure as a prerequisite.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education | 4.1 Ensure all learners have effective learning outcomes. | Quantitative pre-test and post-test scores to measure improvements in academic performance (e.g., t-test results showing significant improvement in the experimental group). |
| 4.4 Increase the number of youth and adults with relevant technical skills. | Teachers’ perceived ease of use of AR technology; Mention of the need to overcome “insufficient technical training.” | |
| 4.a Build and upgrade education facilities to provide effective learning environments. | Qualitative feedback from students on “Engagement and Enjoyment” and “Collaborative Learning” as a result of using AR. | |
| 4.c Increase the supply of qualified teachers through training. | Identification of the “inadequate availability of professional development opportunities for instructors” as a key challenge. | |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1 Develop quality, reliable, and resilient infrastructure with equitable access. | Mention of “technology accessibility” as a crucial factor for AR implementation in educational institutions. |
| 9.c Significantly increase access to information and communications technology (ICT). | The study’s focus on implementing AR, an advanced ICT, and the call for policymakers to allocate resources for such technologies in schools. |
Source: nature.com