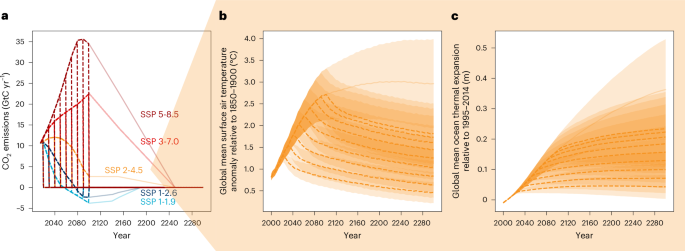
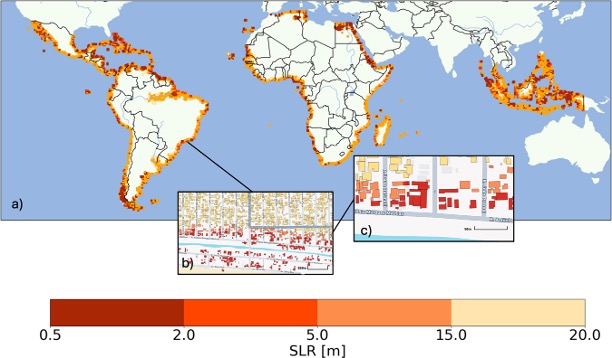
Strategic Analysis of Minnesota’s Energy Plan in the Context of UN Sustainable Development Goals
I. Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis of Minnesota’s proposed energy transition plan, focusing on its alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The plan outlines a strategic shift towards carbon-free energy sources, which directly supports and advances several key global development objectives, positioning the state as a leader in sustainable policy implementation.
II. Alignment with SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The cornerstone of the energy plan is its commitment to achieving 100% carbon-free electricity, a direct implementation of the targets within SDG 7. The primary objectives are designed to ensure a transition that is both sustainable and equitable.
- Target 7.1: Ensuring universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services for all residents.
- Target 7.2: Substantially increasing the share of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, in the state’s overall energy mix.
- Target 7.A: Promoting investment in and access to clean energy research, technology, and infrastructure to facilitate the transition.
III. Contribution to SDG 13: Climate Action
By establishing a clear, legally-binding timeline for phasing out fossil fuels in the electricity sector, the plan represents a significant and urgent measure for climate change mitigation, directly addressing the core tenets of SDG 13.
- Emission Reduction Targets: The plan sets ambitious targets for reducing statewide greenhouse gas emissions, integrating climate action directly into state policy.
- Building Climate Resilience: Investment in a modernized, decentralized energy grid enhances resilience to climate-related extreme weather events and ensures energy security.
- Policy and Planning Integration: The initiative integrates climate action into statewide economic strategy, demonstrating a comprehensive approach to combating climate change and its impacts.
IV. Broader Impacts on Interconnected Sustainable Development Goals
The energy plan’s influence extends beyond energy and climate, creating positive co-benefits across a spectrum of interconnected SDGs that are crucial for holistic community development.
- SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being): Reducing reliance on fossil fuels will lead to significantly improved air quality, decreasing the incidence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases linked to pollution.
- SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth): The transition is projected to stimulate sustainable economic growth by creating thousands of new, high-quality jobs in the renewable energy sector, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure): The plan necessitates significant investment in building resilient infrastructure and fostering innovation in energy storage, smart grid management, and next-generation renewable technologies.
- SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities): The provision of clean, reliable energy is fundamental to developing inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable communities with reduced environmental footprints and enhanced quality of life.
Analysis of SDGs in the Provided Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article’s content, which is a privacy policy statement, is primarily connected to the following Sustainable Development Goal:
-
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
This goal aims to promote peaceful and inclusive societies, provide access to justice for all, and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels. The article’s text directly relates to the principles of accountability and transparency of an institution (the media entity) in handling user data. By clearly stating how personally identifying information will be used and protected, the organization demonstrates a commitment to building trust and operating as an accountable institution. Furthermore, protecting personal data is linked to protecting fundamental freedoms.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the connection to SDG 16, the following specific target can be identified:
-
Target 16.10: Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements.
The article’s text is a direct implementation of this target.- Public access to information: The statement is a form of public communication that gives users access to information about how their data is managed. The inclusion of a link to a full “Privacy Policy” further supports this.
- Protect fundamental freedoms: The right to privacy is a fundamental freedom. The article explicitly states measures to protect this right: “The personally identifying information you provide will not be sold, shared, or used for purposes other than to communicate with you…”. It also empowers users with the freedom to “opt-out at any time,” reinforcing individual control over personal information.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
While the article does not explicitly mention a formal SDG indicator, its content implies a connection to an indicator used to measure progress for Target 16.10:
-
Implied Indicator 16.10.2: Number of countries that adopt and implement constitutional, statutory and/or policy guarantees for public access to information.
The privacy statement in the article is a practical example of an organization’s adherence to such statutory or policy guarantees (like GDPR, CCPA, etc.). The existence and enforcement of such a policy by an entity is a micro-level reflection of the macro-level implementation measured by this indicator. The specific commitments mentioned—such as not selling or sharing data and providing an opt-out mechanism—are tangible actions that demonstrate the implementation of data protection laws designed to guarantee public access to information and protect freedoms.
4. Summary Table of Findings
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 16: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions | Target 16.10: Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements. | Indicator 16.10.2 (Implied): The article’s privacy policy serves as evidence of an organization implementing statutory guarantees for public access to information and data protection, which is what this indicator measures at a national level. |
Source: mprnews.org