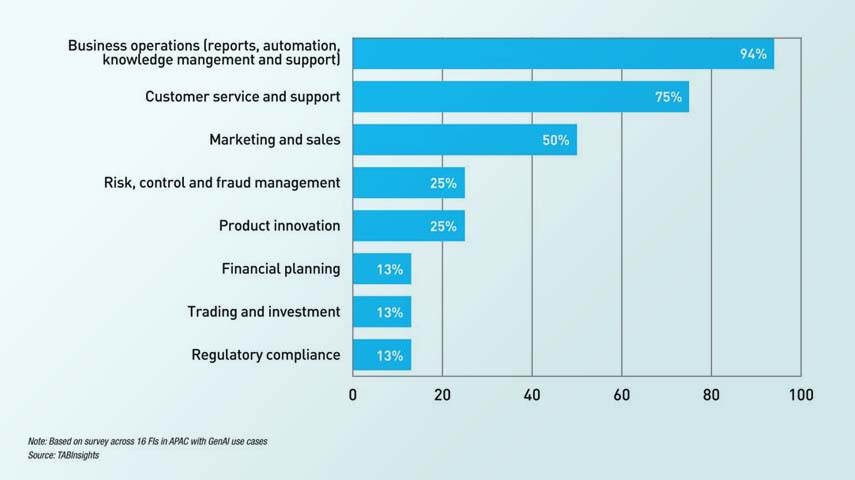
Emergency Energy Conservation Request Issued by AEP Ohio Amid Extreme Heat
Context and Background
AEP Ohio has issued an emergency request for energy conservation to prevent rolling outages during an ongoing heatwave. The extreme heat is placing a significant burden on the electric grid that supplies electricity to Ohio and 12 other states.
Details of the Energy Conservation Request
- Customers are urged to limit energy use during peak hours from 3 to 7 p.m.
- Recommended actions include:
- Turning off or unplugging unused devices and lights
- Raising thermostats to reduce cooling demand
- Avoiding the use of large appliances such as dishwashers, ovens, and washing machines
Grid Management and Outlook
Matt Bennett, AEP Ohio Director of Operations, stated on June 23 that PJM Interconnection—the organization managing the 13-state electricity grid—has not indicated any anticipated electrical outages in the coming weeks, though the possibility remains.
AEP Ohio’s media relations spokesperson confirmed that small adjustments by customers help reduce demand on the electrical system, thereby alleviating stress on the grid.
Coordination with PJM and Energy Supply Constraints
The spokesperson emphasized close coordination with PJM, noting that forecasted supply aligns with anticipated demand across the 13-state region. However, as Ohio is a deregulated state, AEP Ohio cannot influence energy supply but can assist in proactively reducing demand.
This demand reduction helps:
- Reduce stress on the electric grid during peak demand
- Help customers save on their energy bills
Heatwave Impact and Weather Advisory
- Temperatures are projected to remain in the high 90s for the next few days, with heat index values reaching up to 104 degrees.
- From June 25, temperatures are expected to slightly decrease but remain in the low 90s through at least June 29.
- A heat advisory is in effect for Columbus and much of Ohio until 8 p.m. on June 25, issued by the National Weather Service due to prolonged high heat and humidity.
Emphasis on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
The emergency conservation request aligns with SDG 7 by promoting energy efficiency and encouraging responsible energy consumption during peak demand periods. This helps optimize the use of existing energy resources and supports grid stability without increasing fossil fuel consumption.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
By managing energy demand and preventing rolling outages, AEP Ohio contributes to resilient infrastructure and sustainable urban living conditions, ensuring that communities maintain access to reliable electricity during extreme weather events.
SDG 13: Climate Action
Encouraging reduced energy consumption during heatwaves mitigates the environmental impact of increased electricity generation, often reliant on carbon-intensive sources. This proactive approach supports climate action by lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with peak energy demand.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
The call for customers to limit energy use and avoid unnecessary appliance operation promotes responsible consumption patterns, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Conclusion
AEP Ohio’s emergency energy conservation request during the heatwave highlights the critical role of consumer behavior in supporting sustainable energy systems. Through coordinated efforts with PJM and adherence to SDGs, these measures aim to maintain grid reliability, protect public health, and contribute to broader sustainability goals.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article discusses energy conservation efforts and managing electricity demand during extreme heat, which relates to ensuring access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- The extreme heatwave and its impact on the electric grid highlight the challenges posed by climate change and the need for climate adaptation and mitigation strategies.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- The heat advisory and high temperatures pose health risks, linking to the goal of ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all ages.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Managing energy demand and preventing power outages contribute to making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.3: By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency.
- Target 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services.
- SDG 13: Climate Action
- Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
- Target 13.3: Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction, and early warning.
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- Target 3.d: Strengthen the capacity of all countries for early warning, risk reduction, and management of national and global health risks.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.b: Increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion, resource efficiency, mitigation and adaptation to climate change.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- Energy Demand and Supply Metrics
- The article mentions coordination with PJM Interconnection to forecast supply and demand, implying the use of indicators such as peak electricity demand (MW) and supply capacity.
- Energy Conservation Actions
- Indicators related to energy efficiency improvements, such as reduction in electricity consumption during peak hours, are implied through the emergency request for energy conservation.
- Heatwave and Health Advisory Data
- Heat index values (e.g., reaching 104 degrees) and issuance of heat advisories by the National Weather Service serve as indicators for climate-related health risks and early warning systems.
- Power Outage Incidence
- Although no outages are currently expected, tracking the frequency and duration of rolling outages would be an indicator of grid resilience and reliability.
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy |
|
|
| SDG 13: Climate Action |
|
|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
Source: dispatch.com