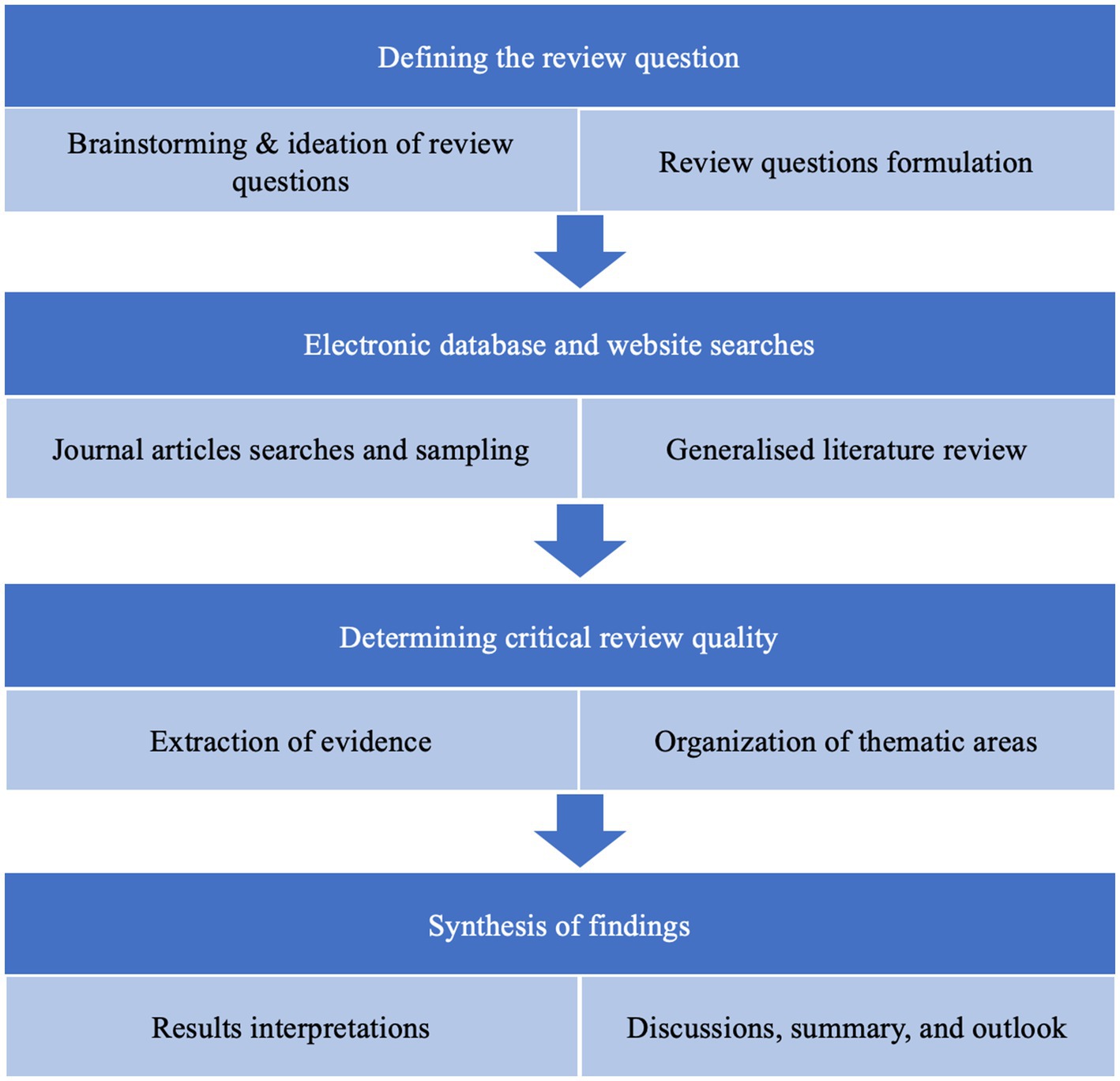
Report on Sustainable Development Initiatives in Lubbock’s District 6
Introduction
Tim Collins, elected over a year ago as the councilman for District 6 in Lubbock, Texas, has prioritized forward-looking development to meet the needs of his growing district. His efforts align with several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those focusing on sustainable cities and communities, clean water and sanitation, affordable and clean energy, and economic growth.
District 6 Growth and Development
District 6, located on the west side of Lubbock, is experiencing significant growth. To support this expansion, the city has initiated a Tax Increment Finance District (TIF) aimed at creating a new park. This initiative promotes SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities by enhancing green spaces and recreational areas for residents.
- Tax Increment Finance District (TIF): Utilizes future tax revenue increases to fund development projects that boost property values and community amenities.
- Park Development: Provides additional green space, contributing to environmental sustainability and improved quality of life.
Infrastructure Improvements and Water Security
Infrastructure development is a critical focus area, with ongoing road improvements funded by Lubbock road bond packages and enhancements to water infrastructure. The creation of the west water pressure plane will supply water to growth areas west of town, supporting SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation.
- West Water Pressure Plane: Expands water supply to new growth zones, ensuring sustainable water access.
- Lake 7 System: An innovative wastewater management system allowing safe return of treated wastewater, enhancing water security.
These efforts contribute to sustainable urban growth and water resource management, addressing critical challenges related to water scarcity and infrastructure resilience.
Energy Infrastructure and Economic Development
Collins emphasizes the importance of upgrading Lubbock’s power supply and generation capacity to attract emerging industries, such as AI data centers, which require substantial energy resources. This focus supports SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy and SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth.
- Power Supply Upgrades: Necessary to meet increasing energy demands and support industrial growth.
- Collaboration with ERCOT: Coordination with the Electric Reliability Council of Texas to ensure reliable electricity provision.
- Economic Development: Generating revenue through industrial growth to maintain low taxes for residents.
Future Outlook and Community Engagement
Looking ahead, Collins plans to continue advocating for economic development and infrastructure improvements that enhance the quality of life for current and future generations, aligning with SDG 11 and SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
Community members can contact Councilman Tim Collins via phone at (806) 775-2031 or email at TCollins@mylubbock.us. Correspondence can also be sent to City of Lubbock, P.O. Box 2000, Lubbock, Texas 79457.
Conclusion
District 6’s development under Councilman Collins demonstrates a commitment to sustainable urban growth, water security, clean energy, and economic prosperity. These initiatives contribute significantly to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, ensuring a resilient and thriving community for future generations.
1. Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Addressed or Connected
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- The article discusses water infrastructure investments, water supply improvements, and wastewater management in Lubbock, Texas.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Focus on upgrading power supply and electrical infrastructure to attract emerging industries such as AI data centers.
- Development of economic infrastructure through Tax Increment Finance District (TIF) for parks and road improvements.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Creation of green spaces (parks), road improvements, and planning for future city growth and infrastructure needs.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Concerns about power supply and generation, and the need to upgrade electricity infrastructure to support growth and industries.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Economic development efforts to generate revenue and attract industries to maintain low taxes and improve quality of life.
2. Specific Targets Under the Identified SDGs
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- Target 6.1: Achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water.
- Target 6.3: Improve water quality by reducing pollution and increasing recycling and safe reuse.
- Target 6.a: Expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water and sanitation-related activities.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure to support economic development and human well-being.
- Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Target 11.3: Enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated planning and management.
- Target 11.7: Provide universal access to safe, inclusive, and accessible green and public spaces.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- Target 7.1: Ensure universal access to affordable, reliable, and modern energy services.
- Target 7.a: Enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology.
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Target 8.2: Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading, and innovation.
- Target 8.3: Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and decent job creation.
3. Indicators Mentioned or Implied to Measure Progress
- SDG 6 Indicators
- Proportion of population using safely managed drinking water services (implied by water supply improvements).
- Proportion of wastewater safely treated (implied by the Lake 7 system for wastewater return).
- SDG 9 Indicators
- Proportion of the rural population who live within 2 km of an all-season road (implied by road improvements).
- Research and development expenditure as a proportion of GDP (implied by efforts to attract AI data centers and innovation).
- SDG 11 Indicators
- Proportion of urban population living in slums, informal settlements, or inadequate housing (implied by urban planning and infrastructure development).
- Proportion of urban green space per capita (implied by creation of parks and green spaces).
- SDG 7 Indicators
- Proportion of population with access to electricity (implied by power supply upgrades).
- Renewable energy share in the total final energy consumption (implied by concerns about sustainable power generation).
- SDG 8 Indicators
- Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person (implied by economic development efforts).
- Unemployment rate, by sex, age, and persons with disabilities (implied by job creation efforts).
4. Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation |
|
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure |
|
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities |
|
|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy |
|
|
| SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth |
|
|
Source: lubbockonline.com