Project Report: Cross Trails Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
Executive Summary
A global developer of grid-scale energy storage, Energy Vault, has secured project financing and a long-term offtake agreement for its Cross Trails Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) in Scurry County, Texas. This project represents a significant advancement in energy infrastructure, directly contributing to several United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by enhancing grid stability, integrating renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainable economic models.
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: By storing and dispatching energy, the BESS facilitates greater use of intermittent renewable sources, ensuring a reliable and cleaner energy supply.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: The project deploys innovative energy storage technology to build resilient and sustainable infrastructure critical for economic development.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: It enhances the reliability of the energy grid for Texas communities, a foundational element for sustainable urban living.
- SDG 13: Climate Action: The facility is a key tool in mitigating climate change by enabling a transition away from fossil-fuel-based power generation.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The project’s success is built on a strategic partnership between technology providers, power marketers, and financial institutions.
Financial Framework and Sustainable Economic Growth
Project Financing and Investment
The financial architecture of the Cross Trails project underscores a commitment to sustainable investment and economic growth, aligning with SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
- Project Financing: Energy Vault has closed $18 million in project financing.
- Federal Incentives: The project is anticipated to receive over $12 million in federal Investment Tax Credits (ITCs), promoting investment in clean energy infrastructure.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The project is projected to deliver a levered IRR of approximately 15%, demonstrating the economic viability of sustainable energy assets.
This financing builds upon Energy Vault’s “Own & Operate” asset management strategy, which focuses on generating predictable, high-margin, and recurring revenue streams through the ownership of critical energy infrastructure.
Technical Specifications and Contribution to SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy)
System Details and Grid Services
The Cross Trails BESS is a 57-MW/114-MWh installation serving the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) market. Having achieved full commercial operation in June, ahead of schedule, the facility directly supports SDG 7 by:
- Supporting Renewable Energy: Providing essential energy and ancillary services that enable the grid to accommodate a higher penetration of variable renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
- Improving Grid Resiliency: Enhancing the stability and reliability of the power supply within ERCOT’s territory, ensuring affordable and clean energy access for residents.
Innovation and Resilient Infrastructure (SDG 9 and SDG 11)
Advanced Technology Deployment
The project serves as a showcase for technological innovation in the energy sector, a core component of SDG 9. It is the first deployment of Energy Vault’s second-generation B-VAULT AC product, a fully integrated solution designed for rapid, cost-effective delivery and high system availability. The system’s operations are managed by the VaultOS Energy Management System, which optimizes performance and control. By strengthening the Texas power grid, this project contributes to building the resilient infrastructure necessary for sustainable communities (SDG 11) and industries (SDG 9).
Strategic Partnerships for Climate Action (SDG 17 and SDG 13)
Offtake Agreement and Collaborative Impact
A key element of the project is a 10-year offtake agreement with power marketer Gridmatic. This partnership is a model for achieving the SDGs through collaboration (SDG 17). According to Energy Vault, this is the first physically settled revenue floor contract for a BESS in the ERCOT market, creating a new model for risk management and revenue assurance in energy storage.
This collaboration between Energy Vault and Gridmatic is pivotal for climate action (SDG 13). By ensuring the financial stability of the BESS, the partnership guarantees its role in providing grid reliability, which in turn accelerates the integration of renewable energy and contributes to a more sustainable, low-carbon energy future for Texas.
Global Strategy and Future Outlook
Expanding a Portfolio of Sustainable Assets
The Cross Trails project is part of Energy Vault’s expanding global portfolio of “Own & Operate” assets. This strategy includes other key projects such as the Calistoga Resiliency Center in California and the planned acquisition of the 125-MW/1,000-MWh Stoney Creek BESS in Australia. The company’s long-term vision is to develop a robust pipeline of projects that generate predictable, high-margin tolling revenues, delivering sustainable, long-term value to shareholders while advancing global clean energy and climate goals.
SDGs Addressed in the Article
SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
- The article focuses on a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) project, which is a critical technology for clean energy. The project’s stated purpose is to “support renewable energy production,” directly contributing to the transition to cleaner energy sources. It also aims to deliver “increased grid reliability and affordability for Texas residents,” aligning with the goal of providing affordable and reliable energy.
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- The development of the Cross Trails BESS represents an investment in new, resilient energy infrastructure. The article highlights that the project will “improve grid resiliency in ERCOT’s territory.” Furthermore, it showcases technological innovation through the deployment of “Energy Vault’s fully integrated solution stack of hardware, software, and service offerings,” including its “second-generation B-VAULT AC product” and “VaultOS Energy Management System.”
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
- By working to “improve grid resiliency” and “deliver increased grid reliability,” the project contributes to making community infrastructure safer and more dependable. A stable power grid is fundamental for the functioning of sustainable cities and communities, especially in the face of increasing energy demands and climate-related stress.
SDG 13: Climate Action
- The project supports climate action by enabling greater use of renewable energy. BESS technology helps solve the intermittency problem of sources like wind and solar, thus facilitating their integration into the grid and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Strengthening grid resilience also enhances the adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards, such as extreme weather events that can disrupt power supplies.
Specific Targets Identified
-
Target 7.2: By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix.
- The article states that the BESS project is designed to “support renewable energy production.” By storing excess energy from renewables and dispatching it when needed, the system enables a higher proportion of clean energy to be reliably integrated into the grid.
-
Target 7.a: By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology… and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
- The article details significant investment in clean energy infrastructure, including “$18-million project financing” and over “$12 million in federal investment tax credit-related funds.” It also describes a global company, Energy Vault, deploying its advanced BESS technology in the U.S., demonstrating the promotion and application of clean energy technology.
-
Target 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure… to support economic development and human well-being.
- The Cross Trails project is a direct development of resilient infrastructure. The article explicitly mentions its role in providing “ancillary services to support renewable energy production and improve grid resiliency in ERCOT’s territory.”
-
Target 9.4: By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies.
- The BESS is a clean technology being integrated into the existing energy infrastructure to make it more sustainable. The article notes the deployment of Energy Vault’s “second-generation B-VAULT AC product,” which represents an upgrade and adoption of advanced, cost-effective technology.
-
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
- The project’s goal to “improve grid resiliency” directly contributes to this target. A more resilient grid is better equipped to withstand and recover from climate-related hazards like extreme heatwaves or storms, which can cause power outages.
Indicators for Measuring Progress
-
Investment in clean energy infrastructure
- The article provides specific financial figures that serve as indicators of investment, such as the “$18-million project financing” for the Cross Trails project and the “$28-million project financing” for the Calistoga Resiliency Center.
-
Installed capacity of energy storage
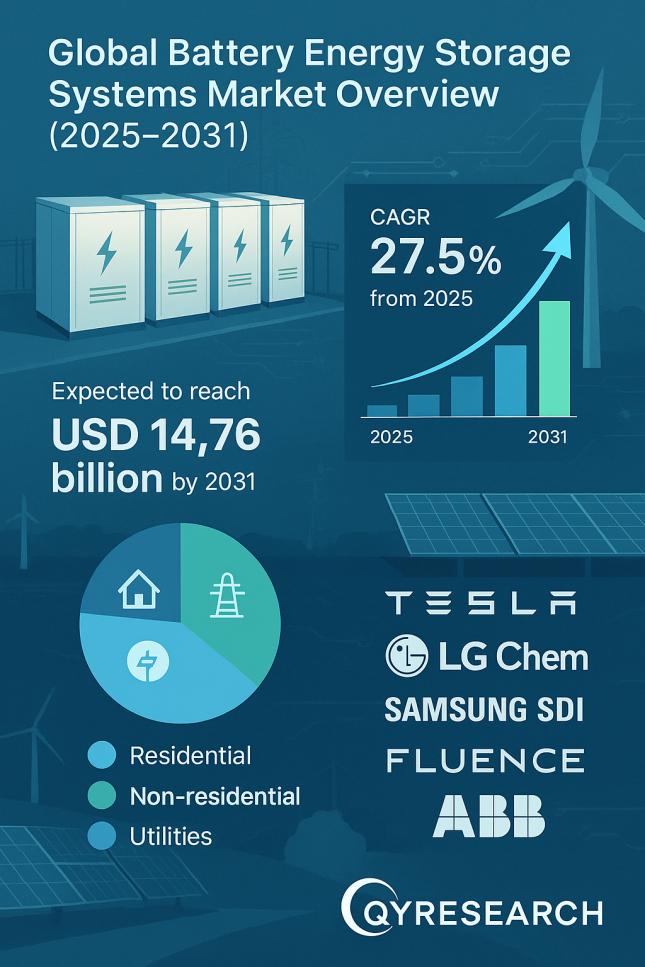
- A direct indicator mentioned is the project’s capacity: “Cross Trails is a 57-MW/114-MWh BESS.” This metric quantifies the scale of the new infrastructure. The article also mentions other projects, such as the “125-MW/1-GWh Stoney Creek BESS in Australia.”
-
Deployment of advanced energy management technology
- The article implies progress through the implementation of specific, named technologies. The deployment of the “VaultOS Energy Management System” to “control, manage, and optimize the BESS operations” is an indicator of technological upgrading.
-
Improvement in grid reliability and resiliency
- While the article does not provide quantitative data (e.g., reduction in outage frequency), it repeatedly states that the project’s purpose is to “improve grid resiliency” and “deliver increased grid reliability.” The successful commercial operation of the BESS is an implied indicator of progress toward this goal.
Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy | 7.2: Increase substantially the share of renewable energy.
7.a: Promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology. |
– Installed BESS capacity (57-MW/114-MWh). – Project’s function to “support renewable energy production.” – Financial investment figures ($18 million in financing, $12 million in tax credits). |
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.1: Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
9.4: Upgrade infrastructure… with greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies. |
– Project’s stated goal to “improve grid resiliency.” – Deployment of “second-generation B-VAULT AC product.” – Use of “VaultOS Energy Management System.” |
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.b: Implement integrated policies and plans towards… resilience to disasters. | – Project’s contribution to “increased grid reliability” for residents. – Enhancement of grid resilience, making community infrastructure more robust. |
| SDG 13: Climate Action | 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters. | – Improvement of “grid resiliency,” which strengthens adaptive capacity to climate-related events. – Support for renewable energy, which is a key climate mitigation strategy. |
Source: powermag.com