Report on the U.S. Solid Waste Management Market and its Alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Executive Summary
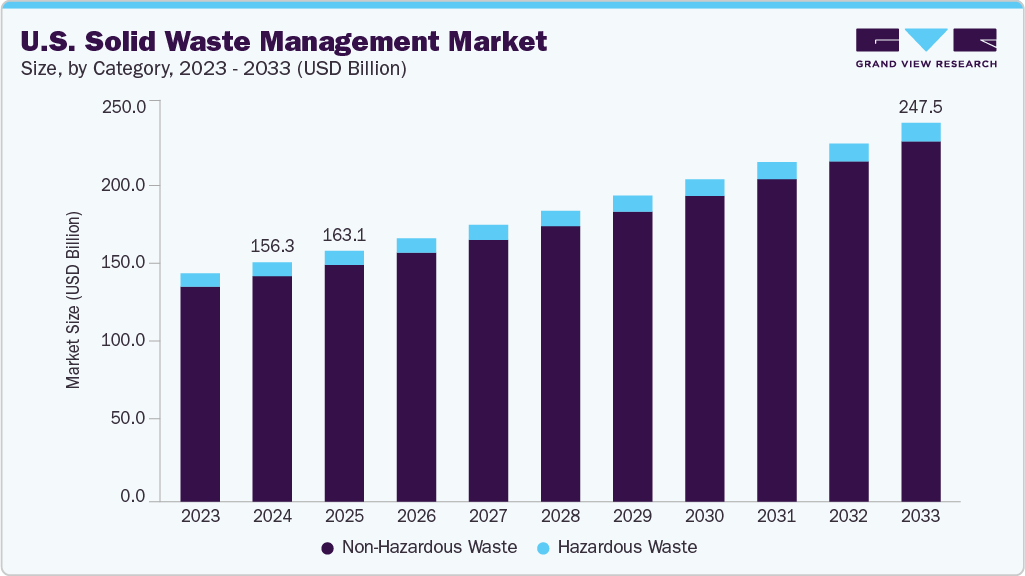
The United States solid waste management market was valued at USD 156.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to expand to USD 247.5 billion by 2033, reflecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization and industrial activity, which escalates waste generation. The sector’s evolution is critical for achieving national and global sustainability targets, particularly Sustainable Development Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production). The industry is increasingly adopting innovative technologies and sustainable practices to mitigate environmental impact and support a circular economy.
Market Dynamics and Contribution to Sustainable Development
Market Drivers
The primary driver for market growth is the rising volume of municipal and industrial waste. This trend presents a direct challenge to SDG 11.6, which aims to reduce the adverse environmental impact of cities through effective waste management. Concurrently, stringent environmental regulations from bodies like the EPA are compelling investment in sustainable infrastructure, aligning the industry with SDG 12.4 (environmentally sound management of wastes) and SDG 13 (Climate Action) by promoting landfill diversion and emissions reduction.
Opportunities for Advancing the 2030 Agenda
Significant opportunities exist in expanding infrastructure for recycling and composting, which are central to achieving SDG 12.5 (substantially reduce waste generation). The growing public and regulatory focus on the circular economy creates demand for advanced material recovery and organic waste processing. Furthermore, the expansion of waste-to-energy solutions directly supports SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) by converting non-recyclable waste into a power source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Market Restraints and Challenges
Key challenges include the high capital investment required for advanced waste management technologies, which can be a barrier for smaller municipalities and hinder progress toward SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). Inconsistent state-level regulations create a fragmented policy landscape, complicating unified efforts towards national sustainability goals. Public opposition to new facility construction and persistent labor shortages can also impede the development of necessary infrastructure.
Market Characteristics and Innovation
Industry Structure
The market is moderately fragmented, featuring a mix of large national corporations and smaller regional providers. Major players like Waste Management Inc. and Republic Services, Inc. lead in urban areas, while a competitive landscape of smaller firms serves specialized niches. Mergers and acquisitions are a key trend, enabling companies to expand their geographic footprint and scale the deployment of sustainable technologies, thereby accelerating the industry’s contribution to the SDGs.
Technological Advancements and SDG 9
Innovation is a crucial enabler for sustainable waste management, directly aligning with SDG 9. The industry is adopting advanced solutions to improve efficiency and environmental outcomes:
- AI-Powered Sorting Systems: Enhance the accuracy and speed of material recovery, increasing recycling rates and supporting SDG 12.
- Smart Bins and Route Optimization: Improve collection efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, and lower the carbon footprint of waste transportation, contributing to SDG 11 and SDG 13.
- Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Provide a sustainable disposal alternative that generates clean energy, supporting SDG 7.
Market Segmentation Analysis
Category Insights
- Non-Hazardous Waste: This segment, representing 94.3% of the market in 2024, is dominated by municipal solid waste. Its management is fundamental to creating sustainable urban environments as outlined in SDG 11. The projected CAGR of 5.4% highlights the growing need for efficient collection and recycling systems to handle waste from households and commercial entities.
- Hazardous Waste: Expected to grow at a 3.7% CAGR, this segment’s management is critical for protecting ecosystems and public health. Proper handling and disposal are essential for achieving SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and SDG 12.4 by preventing the contamination of water sources and soil from industrial, healthcare, and chemical waste.
Service Type Insights
- Collection: Accounting for 59.8% of revenue in 2024, collection services are the foundation of an organized waste management system. Investments in smart technologies are making collection more efficient and sustainable.
- Disposal: This segment is projected to grow at a 5.7% CAGR, driven by a necessary shift away from traditional landfilling. To align with climate goals (SDG 13), the industry is increasingly focused on sustainable disposal methods such as waste-to-energy, composting, and other material recovery techniques that support a circular economy (SDG 12).
Waste Type Insights
- Industrial Waste: This segment held the largest market share (69.4%) in 2024. Managing industrial waste responsibly is a core component of SDG 12, as it requires specialized handling to minimize the environmental footprint of manufacturing, construction, and energy production.
- Municipal Waste: Projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 6.6%, this segment’s growth underscores the urgency for cities to implement comprehensive waste management strategies. Effective municipal waste systems, including robust recycling and composting programs, are vital for achieving the targets of SDG 11.
Competitive Landscape and Key Developments
Leading Companies
Key market players are actively integrating sustainability into their business models. Companies are investing in advanced recycling facilities, expanding hazardous waste treatment capabilities, and offering comprehensive environmental solutions that help clients meet their own sustainability objectives.
- Waste Management Inc.
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Waste Connection, Inc.
- GFL Environmental Inc.
- Veolia
- Reworld
- Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- CLEAN HARBORS, INC.
Recent Strategic Developments
- June 2025: Veolia expanded its global hazardous waste treatment capacity by 530,000 tonnes, enhancing its ability to provide environmentally sound management of hazardous materials in line with SDG 12.4.
- July 2025: Casella Waste Systems acquired Mountain State Waste, expanding its service area and strengthening its capacity to deliver integrated waste solutions that promote regional sustainability.
Analysis of SDGs in the U.S. Solid Waste Management Market Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
-
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
The article addresses the management of hazardous waste from sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and chemicals. Proper handling and treatment of these materials, as mentioned in the text, are crucial for preventing pollution and contamination of air, water, and soil, which directly impacts human health and well-being.
-
SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
This goal is central to the article, which highlights significant investment in modernizing waste management infrastructure. It emphasizes “technological advancements such as smart bins, AI-powered optical sorters, and automation” to improve efficiency and sustainability in the industry. This reflects the push to upgrade infrastructure and adopt cleaner, more efficient technologies.
-
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
The article directly connects waste management to urbanization, stating that “rising urban populations and consumer goods consumption are driving demand for efficient waste collection, recycling, and landfill services.” The focus on managing “municipal solid waste from households, commercial centers, and institutions” is a core component of creating sustainable cities with a reduced environmental footprint.
-
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
This is a primary theme of the article. It discusses the entire lifecycle of waste, from generation due to “increased consumerism” to its management through “recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy solutions.” The mention of “circular economy initiatives” and the goal to “reduce landfill use” directly align with promoting sustainable production patterns and substantially reducing waste generation.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
-
Target 3.9: Substantially reduce deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and pollution
The article identifies this target through its discussion of the hazardous waste segment. It notes that growth in this area is driven by “stricter environmental regulations” and the need for “specialized handling, treatment, and disposal” of waste from industrial and healthcare sectors. Veolia’s expansion of its “hazardous waste treatment capacity” is a direct action towards achieving this target.
-
Target 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries for sustainability
This target is evident in the article’s focus on innovation. It states that “technological advancements” and “data-driven, and more efficient waste management solutions” are being adopted to “improve operational efficiency and accuracy in waste segregation and material recovery.” This represents a clear effort to upgrade the waste management industry’s infrastructure with clean and environmentally sound technologies.
-
Target 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, particularly in waste management
The article points to this target by highlighting the challenges and solutions for municipal waste. It mentions that the municipal segment is growing due to “rising urban populations” and that local governments are “expanding curbside collection, recycling programs, and public awareness campaigns” to manage this waste more sustainably and divert it from landfills.
-
Target 12.4: Achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes
The entire article is centered on this target. It describes a market dedicated to the “collection, processing, and disposal” of both hazardous and non-hazardous waste. The influence of “strict environmental laws regarding landfill diversion, recycling mandates, and emissions reduction” shows a systemic approach to achieving environmentally sound waste management.
-
Target 12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse
This target is reflected in the article’s discussion of opportunities within the market, specifically the “expansion of recycling and composting infrastructure.” The text also mentions that innovations aim to “improve recycling rates, reduce landfill use,” which are key activities for reducing the final volume of waste requiring disposal.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
-
Economic and Growth Indicators
The article provides several quantitative indicators that can measure investment and activity in sustainable waste management:
- Overall Market Size and Growth: The market size (USD 156.3 billion in 2024) and projected CAGR (5.3%) indicate the economic scale of waste management efforts.
- Segment-Specific Growth Rates: The CAGR for the municipal segment (6.6%), disposal segment (5.7%), and hazardous waste segment (3.7%) can be used as indicators of focused growth in these specific areas of waste management.
- Revenue Share: The revenue share of different waste types (e.g., non-hazardous at 94.3%) provides insight into the current structure of the market.
-
Technological Adoption Indicators
Progress can be measured by the adoption of advanced technologies mentioned in the article:
- Investment in and implementation of “AI-powered sorting systems, smart bins, automation, and waste-to-energy technologies.”
- Use of “digital tracking technologies” for route optimization and efficiency.
-
Infrastructural and Capacity Indicators
The article implies progress can be tracked through physical infrastructure development:
- Expansion of “recycling and composting infrastructure.”
- Increased hazardous waste treatment capacity, such as Veolia adding “530,000 tonnes annually.”
- Investment in upgrading disposal facilities to move away from traditional landfills.
-
Policy and Regulatory Indicators
The article suggests that regulatory frameworks are a key driver and indicator of progress:
- Enforcement of “strict environmental laws” and “recycling mandates” by federal, state, and local governments.
- Level of compliance with regulations concerning “landfill diversion” and “emissions reduction.”
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being | 3.9: Substantially reduce deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and pollution. |
|
| SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure | 9.4: Upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries for sustainability and adoption of clean technologies. |
|
| SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities | 11.6: Reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, especially in waste management. |
|
| SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production | 12.4: Achieve environmentally sound management of all wastes.
12.5: Substantially reduce waste generation through recycling. |
|
Source: grandviewresearch.com