Demographic Analysis of the U.S. Latino Population and its Implications for Sustainable Development Goals
Population Growth and Contribution to Sustainable Economic Development (SDG 8)
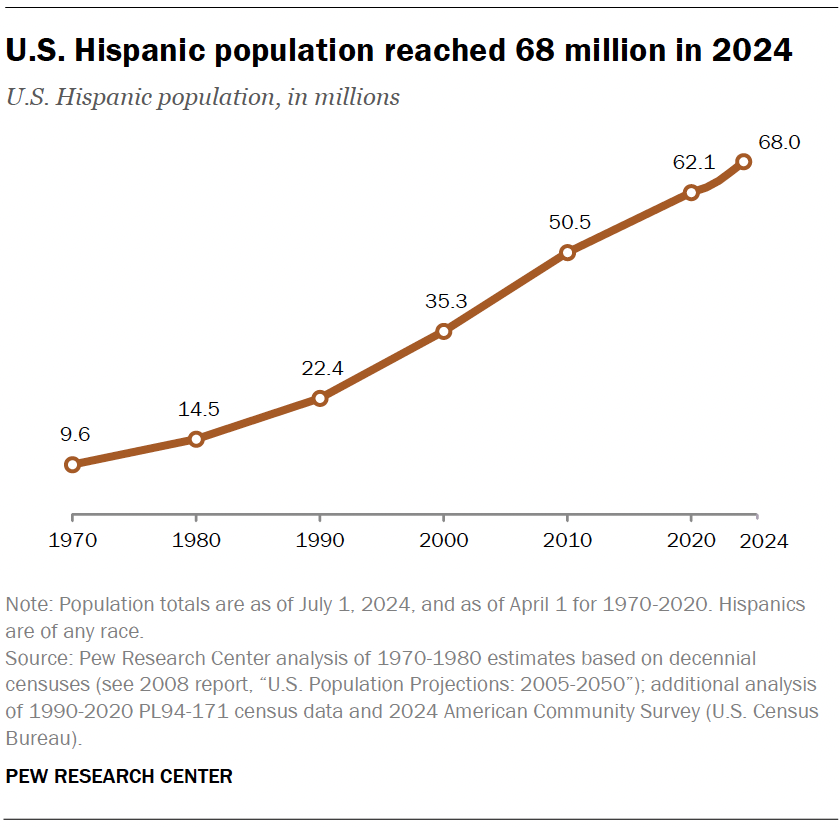
An analysis of the U.S. Latino population between 2000 and 2024 reveals significant demographic shifts that directly impact several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). The data indicates that this demographic is a primary engine of national growth.
- The Latino population nearly doubled, increasing from 35.3 million in 2000 to 68 million in 2024.
- As of 2024, Latinos constitute 20% of the total U.S. population, making them the second-largest ethnic group.
- This group accounted for 56% of all U.S. population growth between 2000 and 2024, representing a significant expansion of the nation’s human capital and labor force, which is a key component for achieving SDG 8.
Drivers of Growth: Immigration, Births, and Alignment with SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities)
The sources of population growth have varied, reflecting changing economic and policy landscapes. These dynamics are crucial for understanding and addressing SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities), as they influence the integration and status of different population segments.
- Pre-2000s Growth: Immigration was the principal driver of population increase during the 1980s and 1990s.
- Post-2000 Shift: From 2000 to 2021, natural births became the primary source of growth, particularly as immigration slowed after the 2008 recession and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Recent Immigration Surge: A sharp rise in both legal and illegal immigration from 2021 to 2024 once again made immigration a leading factor in population growth.
- Contribution to National Births: In 2024, 32% of all infants born in the U.S. had at least one Hispanic parent, a figure that significantly outpaces the group’s 20% share of the total population. This highlights the demographic’s foundational role in future generations.
Demographic Profile: Age, Citizenship, and Social Inclusion (SDG 3, SDG 10, SDG 16)
The demographic profile of the U.S. Latino population presents unique characteristics relevant to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being), SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities), and SDG 16 (Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions).
- Youthful Population: The median age for U.S. Latinos was 31.2 in 2024, substantially younger than the median ages for White (43.2), Asian (39.0), and Black (36.2) Americans. This youth demographic is a vital asset for economic vitality but also places specific demands on health and education systems, aligning with SDG 3.
- Citizenship Status: In 2024, 79% of Latinos were U.S. citizens, an increase from 71% in 2000. This includes 67% who are citizens by birth and 13% who are naturalized citizens.
- Immigrant Legal Status: Among Hispanic immigrants, an estimated 41% are unauthorized. This status creates significant barriers to accessing services, legal protections, and economic opportunities, presenting a direct challenge to the objectives of SDG 10 and SDG 16.
National Origins and Geographic Distribution: Implications for Sustainable Communities (SDG 11)
The diversity of origins and geographic settlement patterns of the Latino population are critical factors for planning and developing inclusive and resilient urban and rural areas, as outlined in SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities).
- Diverse Origins: While diverse, the population is led by individuals of Mexican origin (57%), followed by Puerto Rican, Salvadoran, Cuban, and Dominican groups. The fastest-growing groups since 2019 are of Venezuelan, Ecuadorian, and Chilean origin.
- Geographic Concentration: The population is concentrated but increasingly dispersed. The top five states by Latino population in 2024 were:
- California (16.1 million)
- Texas (12.6 million)
- Florida (6.7 million)
- New York (4.0 million)
- Illinois (2.5 million)
- Metropolitan Diversity: Major metropolitan areas exhibit different origin compositions. Mexican-origin populations are dominant in Los Angeles and Chicago, while New York features large Dominican and Puerto Rican communities, and Miami is characterized by its large Cuban population. This diversity necessitates tailored approaches to community development under SDG 11.
Socio-Economic Progress: Advances in Quality Education (SDG 4) and Social Integration
Significant progress in educational attainment and language proficiency indicates positive trends toward achieving SDG 4 (Quality Education) and fostering greater social inclusion, which supports SDG 10.
- Educational Attainment: The share of Latinos aged 25 and older with at least some college experience rose from 36% in 2010 to 46% in 2024. Those with a bachelor’s degree or higher increased from 13% to 21% in the same period. This upward trend in education is a cornerstone for reducing poverty (SDG 1) and promoting economic growth (SDG 8).
- Language Proficiency: English proficiency among Latinos aged 5 and older grew from 59% in 2000 to 71% in 2024. This linguistic integration facilitates greater participation in civic and economic life.
Analysis of Sustainable Development Goals in the Article
1. Which SDGs are addressed or connected to the issues highlighted in the article?
The article, which provides a detailed demographic analysis of the Latino population in the United States, connects to several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The primary SDGs addressed are:
- SDG 4: Quality Education: The article discusses the educational attainment of the Latino population, specifically the rising shares of those with college experience.
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities: This goal is central to the article, which focuses on a specific racial and ethnic group, their demographic trends, migration status, citizenship, and social integration within the U.S. population.
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals: The article’s methodology and data-driven approach highlight the importance of robust statistical capacity and the availability of disaggregated data, which is a key aspect of SDG 17.
2. What specific targets under those SDGs can be identified based on the article’s content?
Based on the article’s content, the following specific SDG targets can be identified:
- Target 4.3: “By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university.”
- Explanation: The article directly addresses this target in the section “The share of U.S. Hispanics with college experience is rising.” It provides statistics on the increasing percentage of Latinos aged 25 and older who have attended college and obtained degrees, including a breakdown by gender.
- Target 10.2: “By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status.”
- Explanation: The article’s entire focus is on the demographic and social profile of the Latino population, a specific ethnic group. It details their growing share of the total U.S. population, their contribution to population growth, and their citizenship status, all of which are measures of social presence and inclusion.
- Target 10.7: “Facilitate orderly, safe, regular and responsible migration and mobility of people, including through the implementation of planned and well-managed migration policies.”
- Explanation: The article extensively discusses migration as a key driver of Latino population growth. It quantifies the number of immigrants, distinguishes between legal and unauthorized status (“59% are lawful immigrants while 41% are unauthorized immigrants”), and analyzes how immigration trends have shifted over time, reflecting the outcomes of migration policies.
- Target 17.18: “By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries… to increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by income, gender, age, race, ethnicity, migratory status, disability, geographic location and other characteristics relevant in national contexts.”
- Explanation: While the U.S. is not a developing country, the principle of this target is fundamental to the article. The “How we did this” section explicitly states that the analysis relies on data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the American Community Survey. The entire article is an example of using high-quality data disaggregated by ethnicity (Latino), origin (Mexican, Puerto Rican, etc.), migratory status (immigrant vs. U.S. born), age, and geographic location to understand a population group.
3. Are there any indicators mentioned or implied in the article that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets?
Yes, the article provides several quantitative indicators that can be used to measure progress towards the identified targets:
- Indicators for Target 4.3 (Quality Education):
- The percentage of Latinos (ages 25+) with at least some college experience, which rose from 36% in 2010 to 46% in 2024.
- The percentage of Latinos with a bachelor’s degree or more, which increased from 13% in 2010 to 21% in 2024.
- Gender-disaggregated data on educational attainment: 24% of Hispanic women and 19% of Hispanic men had at least a bachelor’s degree in 2024.
- Indicators for Target 10.2 (Reduced Inequalities – Inclusion):
- The share of the total U.S. population that is Latino, which grew from 13% in 2000 to 20% in 2024.
- The proportion of U.S. population growth accounted for by Latinos (56% of the increase from 2000 to 2024).
- The citizenship rate among U.S. Latinos, which was 79% in 2024.
- Indicators for Target 10.7 (Reduced Inequalities – Migration):
- The total number of Hispanic immigrants (22.7 million in 2024).
- The share of the Hispanic population who are immigrants (33% in 2024).
- The legal status of Hispanic immigrants: The article provides an estimate that 41% are unauthorized immigrants.
- Indicators for Target 17.18 (Partnerships – Data):
- The use of disaggregated population counts by specific origin groups (e.g., Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban).
- The analysis of demographic data by nativity (U.S.-born vs. immigrant) and age (median age of 31.2 for Hispanics vs. other groups).
- The availability of population data at sub-national levels, such as for states (California, Texas) and metropolitan areas.
4. Summary Table of SDGs, Targets, and Indicators
| SDGs | Targets | Indicators Identified in the Article |
|---|---|---|
| SDG 4: Quality Education | 4.3: Ensure equal access for all to affordable and quality tertiary education. |
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | 10.2: Empower and promote the social inclusion of all, irrespective of ethnicity or origin. |
|
| SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities | 10.7: Facilitate orderly, safe, regular and responsible migration and mobility of people. |
|
| SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals | 17.18: Increase the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by ethnicity, migratory status, age, and location. |
|
Source: pewresearch.org